- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is the Agile Development Method?20
- Advantages of Agile Project Management
- Flexibility and Adaptability:
- Improved Customer Satisfaction:
- Enhanced Collaboration:
- Faster Time to Market:
- Continuous Improvement:
- Disadvantages of Agile Project Management
- Less Predictability:
- Requires Experienced Team Members:
- Potential for Scope Creep:
- Documentation Challenges:
- Cultural Shift:
- What is the Waterfall Development Method?
- Pros and Cons of Waterfall Project Management
- Advantages of Waterfall Project Management
- Disadvantages of Waterfall Project Management
- Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management: Comparison
- Approach:
- Flexibility:
- Customer Involvement:
- Documentation:
- Risk Management:
- Time to Market:
- What to Consider When Choosing Between Agile and Waterfall Project Management
- 1- Project Complexity and Size:
- 2- Customer Involvement:
- 3- Timeline and Budget Constraints:
- 4- Team Experience and Skillset:
- 5- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements:
- 6- Nature of the Product:
- 7- Risk Tolerance:
- What is the Hybrid Approach and Is It for You?
- When to Consider a Hybrid Approach
- How to Implement a Hybrid Approach
- 1- Assess Project Requirements:
- 2- Define Clear Objectives:
- 3- Create a Flexible Framework:
- 4- Establish Roles and Responsibilities:
- 5- Implement Agile Practices:
- 6- Maintain Comprehensive Documentation:
- 7- Foster Communication and Collaboration:
- 8- Monitor and Adapt:
- 9- Train and Support the Team:
- 10- Evaluate Outcomes and Iterate:
- Conclusion
Introduction
Project management has evolved significantly over the years, leading to the development of various methodologies that cater to different project needs. Among these, Agile and Waterfall stand out as two of the most widely used approaches. This blog post delves into the intricacies of Agile and Waterfall project management, exploring their definitions, advantages, disadvantages, and how they compare against each other. Additionally, we will discuss what to consider when choosing between these methodologies, introduce the hybrid approach, and provide guidance on its implementation. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of which method may best suit your project requirements.
What is the Agile Development Method?20
Agile project management is an iterative and incremental approach that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction. Unlike traditional methodologies, Agile promotes adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, and continuous improvement. The Agile Manifesto, created in 2001 by a group of software developers, outlines the core principles of Agile development:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools: Agile prioritizes teamwork and communication among team members.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation: The focus is on delivering functional software rather than extensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation: Agile encourages ongoing collaboration with stakeholders to ensure the final product meets their needs.
- Responding to change over following a plan: Agile teams are flexible and can adapt to changes in requirements or market conditions.
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum – which remains the most popular Agile framework, with 87% of organizations favoring its use – Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP), provide frameworks for implementing these principles. Each of these methodologies has its unique practices and terminologies, but they all share the common goal of delivering high-quality products that align with customer expectations.
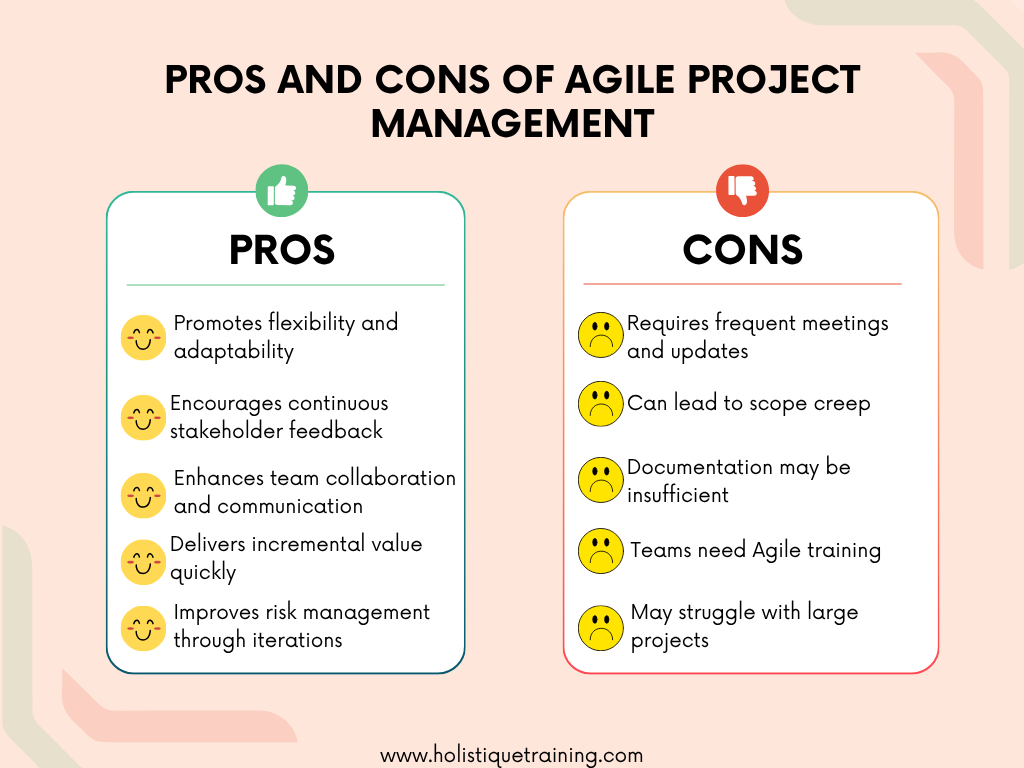
Advantages of Agile Project Management
As of 2026, Agile methodologies are widely adopted, with 61% of users reporting over five years of experience. This demonstrates Agile's lasting success compared to declining approaches like Waterfall. It also offers several advantages that make it an attractive choice for many organizations:
Flexibility and Adaptability:
Agile allows teams to respond quickly to changes in project requirements, market conditions, or customer feedback. This adaptability is crucial in fast-paced industries where requirements can evolve rapidly. Agile teams can pivot their focus based on real-time insights, ensuring that the product remains relevant and aligned with user needs. This continuous feedback loop not only enhances the end product but also fosters a culture of innovation, as teams are encouraged to explore new ideas throughout the development process.
Improved Customer Satisfaction:
By involving customers throughout the development process and delivering incremental updates, Agile ensures that the final product aligns closely with their needs and expectations. Regular demonstrations and reviews allow stakeholders to see progress and provide input, leading to a sense of ownership and investment in the project. This ongoing collaboration helps build trust and strengthens relationships, ultimately resulting in higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enhanced Collaboration:
Agile fosters a collaborative environment where team members communicate openly and work together towards common goals. Daily stand-up meetings and regular retrospectives encourage transparency and accountability. This collaborative spirit not only improves team dynamics but also leverages diverse perspectives and expertise, leading to more innovative solutions. Team members are empowered to share ideas and address challenges collectively, which enhances overall productivity and morale.
Faster Time to Market:
Agile's iterative approach enables teams to release functional increments of the product more frequently. This allows organizations to deliver value to customers sooner and gain a competitive edge. By prioritizing features based on customer feedback and market demands, Agile teams can ensure that the most critical functionalities are developed first. This incremental delivery not only accelerates time to market but also allows for quicker adjustments based on user reactions, further refining the product.
Continuous Improvement:
Agile promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Teams regularly reflect on their processes and outcomes, identifying areas for enhancement and implementing changes accordingly. This focus on introspection encourages a growth mindset, where mistakes are viewed as opportunities for learning rather than failures. By fostering an environment that values experimentation and innovation, organizations can adapt to changing circumstances and continuously enhance their workflows and products. This commitment to improvement ultimately leads to higher quality outcomes and more efficient processes.
Disadvantages of Agile Project Management
Despite its many benefits, Agile project management also has its drawbacks:
Less Predictability:
The iterative nature of Agile can lead to challenges in predicting project timelines and budgets. Stakeholders may find it difficult to estimate costs or completion dates accurately, as the scope can evolve throughout the development process. This unpredictability can create anxiety among project sponsors and clients who prefer clear, fixed timelines. Additionally, without a well-defined end date, teams may struggle with prioritization, potentially leading to extended development cycles if not managed carefully.
Requires Experienced Team Members:
Agile methodologies often demand a high level of expertise and experience from team members. Inexperienced teams may struggle to implement Agile practices effectively, leading to inconsistencies and inefficiencies. Moreover, the success of Agile relies heavily on team dynamics and individual contributions; if team members lack the necessary skills or understanding of Agile principles, the entire project can suffer. Organizations may need to invest in training and development to equip their teams with the required knowledge and skills, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Potential for Scope Creep:
The flexibility of Agile can sometimes lead to scope creep, where additional features or changes are continuously added, causing projects to extend beyond their original scope. This phenomenon can result from the constant influx of new ideas and feedback, which, while beneficial, may overwhelm the development team. Without strong prioritization and management, teams might find themselves chasing after new requests instead of focusing on delivering the core product. This can lead to frustration among team members and stakeholders, as deadlines slip and resources become stretched.
Documentation Challenges:
While Agile emphasizes working software over documentation, a lack of comprehensive documentation can create challenges for future maintenance or onboarding of new team members. In fast-pacedAgile environments, essential details may be overlooked or inadequately recorded, leading to knowledge gaps. New team members may struggle to understand the project’s history and decisions made, which can hinder their ability to contribute effectively. Furthermore, insufficient documentation can complicate compliance with regulatory requirements, particularly in industries where detailed records are necessary.
Cultural Shift:
Transitioning to Agile from a traditional project management approach may require significant cultural changes within the organization, which can be met with resistance from team members accustomed to established processes. This shift necessitates a re-evaluation of roles, responsibilities, and workflows, which can create discomfort and uncertainty. Organizations must invest in change management strategies to facilitate this transition, including training sessions, workshops, and ongoing support. If not handled properly, the resistance to change can undermine the potential benefits of Agile, leading to a fragmented implementation that fails to deliver the desired outcomes.
What is the Waterfall Development Method?
The Waterfall development method is a linear and sequential approach to project management. It is characterized by distinct phases, where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. The typical phases of the Waterfall model include:
- Requirements Gathering: Stakeholders define the project requirements and expectations.
- Design: The project team creates a detailed design based on the requirements.
- Implementation: Developers build the software according to the design specifications.
- Testing: The product undergoes thorough testing to identify and fix any defects.
- Deployment: The final product is delivered to the customer.
- Maintenance: Ongoing support and updates are provided as needed.
Waterfall is often favored for projects with well-defined requirements and low likelihood of changes. It is commonly used in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and software development.
Pros and Cons of Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall project management has its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of Waterfall Project Management
Clear Structure:
The linear nature of Waterfall provides a clear roadmap for project execution, making it easy to understand and manage. Each phase has defined objectives and deliverables, allowing project managers to track progress systematically. This structured approach also helps in assigning responsibilities and ensuring that all team members are aligned with the project's goals. As a result, stakeholders can easily follow the project's trajectory, which enhances accountability and communication.
Well-Defined Milestones:
Each phase has specific deliverables and milestones, allowing for straightforward tracking of progress. This clarity helps teams maintain focus and ensures that they meet deadlines at each stage. Well-defined milestones facilitate better planning and resource allocation, as project managers can identify potential bottlenecks early on. Additionally, having clear checkpoints allows for regular evaluations of the project's status, enabling timely interventions if issues arise.
Comprehensive Documentation:
Waterfall emphasizes thorough documentation at each stage, which can be beneficial for future maintenance and knowledge transfer. Detailed documentation ensures that all project requirements, designs, and changes are recorded, providing a valuable reference for future projects or iterations. This comprehensive record-keeping is particularly advantageous in industries with strict regulatory requirements, where documentation is essential for compliance. Furthermore, it aids in onboarding new team members, as they can quickly familiarize themselves with the project’s history and decisions.
Easier Budgeting and Scheduling:
The predictability of Waterfall allows for more accurate budgeting and scheduling since the entire project timeline is established upfront. This upfront planning helps organizations allocate resources effectively and set realistic expectations for stakeholders. By defining costs and timelines in advance, project managers can minimize the risk of budget overruns and ensure that the project remains financially viable. This level of predictability is especially appealing to stakeholders who prefer clear financial commitments.
Ideal for Simple Projects:
Waterfall works well for projects with straightforward requirements and minimal changes expected throughout the development process. In such cases, the linear approach allows teams to efficiently execute tasks without the need for constant adjustments. Simple projects, such as small software applications or straightforward construction tasks, benefit from Waterfall’s structured methodology, as it enables teams to deliver results efficiently and effectively.
Disadvantages of Waterfall Project Management
Inflexibility:
Once a phase is completed, it is challenging to go back and make changes. This rigidity can lead to problems if requirements evolve during the project. If a client or stakeholder identifies a change after the design phase, for instance, it can result in significant delays and additional costs to revisit previous phases. This inflexibility can stifle creativity and innovation, as teams may feel constrained by the initial requirements and unable to explore new ideas or solutions.
Late Testing:
Testing occurs only after the implementation phase, which can result in discovering significant issues late in the process, leading to costly fixes. This late-stage testing often means that major flaws or misalignments with user expectations are identified only after substantial resources have been invested in development. Consequently, the project may require extensive rework, increasing the overall timeline and budget. This approach can also create frustration among stakeholders who expect a polished final product upon delivery.
Risk of Miscommunication:
If requirements are not clearly defined at the outset, misunderstandings can arise, leading to misaligned expectations and project failures. Waterfall relies heavily on upfront documentation to communicate requirements, but if those documents are ambiguous or incomplete, teams may build a product that does not meet stakeholder needs. This risk is particularly pronounced in large projects involving multiple stakeholders, where differing interpretations of requirements can lead to significant discrepancies in the final deliverable.
Limited Customer Involvement:
Waterfall typically involves customers primarily during the requirements gathering and final delivery phases, reducing opportunities for feedback throughout the development process. This limited engagement can result in a product that does not fully align with customer expectations or market demands. Stakeholders may feel disconnected from the project, leading to dissatisfaction if the final product does not meet their needs. The lack of ongoing feedback can also hinder the team's ability to adapt to changing circumstances or new insights.
Not Suited for Complex Projects:
For projects with uncertain or changing requirements, Waterfall may not be the best approach, as it lacks the flexibility needed to adapt to new information. Complex projects often require iterative development and frequent reassessment of goals, which Waterfall does not accommodate. As a result, teams may find themselves struggling to keep up with evolving requirements, leading to delays and increased costs. This rigidity can ultimately compromise the project's success, making it essential to carefully evaluate the suitability of Waterfall for complex initiatives.
Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management: Comparison
When comparing Agile and Waterfall project management methodologies, several key differences emerge:
Approach:
- Agile: Agile employs an iterative and incremental approach, breaking projects into smaller, manageable units called iterations or sprints. Each sprint culminates in a potentially shippable product increment, allowing teams to refine and adapt based on feedback.
- Waterfall: Waterfall follows a linear and sequential approach, where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. This structure is straightforward but can be limiting when changes are necessary.
Flexibility:
- Agile: Agile is characterized by its high flexibility, enabling teams to respond quickly to changes in project requirements or market conditions. This adaptability allows for adjustments throughout the development process, fostering innovation and responsiveness.
- Waterfall: Waterfall is rigid, making it challenging to accommodate changes once a phase is completed. This inflexibility can lead to issues if new requirements emerge after initial planning, as reverting to previous phases can be time-consuming and costly.
Customer Involvement:
- Agile: Agile promotes continuous customer involvement throughout the project. Stakeholders are engaged during every sprint, providing feedback and insights that guide development. This ongoing collaboration ensures that the final product aligns closely with customer expectations.
- Waterfall: In Waterfall, customer involvement is typically limited to the initial requirements gathering and the final delivery phases. This lack of ongoing engagement can result in a disconnect between customer expectations and the final product.
Documentation:
- Agile: Agile emphasizes minimal documentation, focusing on essential information that directly supports development. This approach allows teams to prioritize working software over extensive documentation, streamlining the development process.
- Waterfall: Waterfall requires comprehensive documentation at each phase, which can be beneficial for future maintenance and knowledge transfer. However, this extensive documentation can also slow down the process and create bureaucratic hurdles.
Risk Management:
- Agile: Agile incorporates ongoing risk assessment and adaptation into its framework. Teams regularly evaluate risks throughout the project, allowing them to address potential issues proactively and adjust their strategies as needed.
- Waterfall: In Waterfall, risk is primarily assessed at the beginning of the project. This upfront evaluation can lead to unforeseen challenges later in the process, as new risks may emerge that were not accounted for in the initial planning.
Time to Market:
- Agile: Agile’s iterative approach enables teams to deliver functional increments of the product more frequently. This faster time to market allows organizations to respond to customer needs quickly and gain a competitive edge.
- Waterfall: Waterfall often results in longer delivery times, as the entire project is typically completed before any product is delivered to stakeholders. This extended timeline can delay the realization of value for customers and the organization.
By understanding these differences, organizations can make informed decisions about which project management methodology to adopt based on their specific project requirements, team dynamics, and stakeholder expectations.
Aspect | Agile | Waterfall |
Approach | Iterative and incremental | Linear and sequential |
Flexibility | Highly flexible and adaptable | Rigid with little room for changes |
Customer Involvement | Continuous throughout the project | Limited to initial and final phases |
Documentation | Minimal, focused on essential information | Comprehensive at each phase |
Risk Management | Ongoing risk assessment and adaptation | Risk assessed primarily at the beginning |
Time to Market | Faster delivery of functional increments | Longer delivery time, often until project completion |
What to Consider When Choosing Between Agile and Waterfall Project Management
Selecting the right project management methodology is crucial for the success of any project. Both Agile and Waterfall have distinct advantages and are suited for different types of projects. Here are several key factors to consider when deciding between Agile and Waterfall:
1- Project Complexity and Size:
- Agile: Agile is ideal for complex projects with evolving requirements, where flexibility and adaptability are essential. If a project involves many unknowns or is likely to change significantly during development, Agile's iterative approach allows teams to respond effectively to new information and feedback.
- Waterfall: Waterfall is better suited for smaller, simpler projects with well-defined requirements. If the project scope is clear and unlikely to change, Waterfall’s structured approach can facilitate straightforward execution and delivery.
2- Customer Involvement:
- Agile: If customer involvement is a priority, Agile is the preferred choice.Agile methodologies encourage continuous collaboration and feedback from stakeholders throughout the project. This engagement ensures that the final product aligns closely with customer expectations and needs.
- Waterfall: In cases where customer involvement is limited or where stakeholders prefer to review the product only at specific milestones, Waterfall may be more appropriate. This approach allows for comprehensive planning and documentation upfront, which can be beneficial in certain organizational contexts.
3- Timeline and Budget Constraints:
- Agile: Agile can be advantageous when there is a need for rapid delivery and when budget flexibility exists. The iterative nature of Agile allows for quicker releases of functional increments, enabling organizations to start realizing value sooner.
- Waterfall: If the project has strict timelines and budgets, Waterfall may provide a clearer path to manage these constraints. With its defined phases and milestones, Waterfall enables more accurate budgeting and scheduling, making it easier to forecast costs and completion dates.
4- Team Experience and Skillset:
- Agile: Agile methodologies often require experienced teams that are familiar with its principles and practices. If the team has a strong background in Agile practices, they are more likely to successfully implement Agile methodologies and leverage their benefits.
- Waterfall: Waterfall can be easier to adopt for teams that are accustomed to traditional project management approaches. If the team lacks experience with Agile or if there is resistance to change, Waterfall may provide a more comfortable framework for project execution.
5- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements:
- Agile: In industries with stringent regulatory requirements, Agile can present challenges due to its emphasis on flexibility and minimal documentation. However, Agile can still be adapted to meet compliance needs by incorporating necessary documentation practices within its framework.
- Waterfall: Waterfall is often preferred in highly regulated environments where comprehensive documentation and adherence to predefined processes are critical. Its structured approach ensures that all necessary documentation is created and maintained throughout the project lifecycle.
6- Nature of the Product:
- Agile: Agile is particularly effective for software development projects or products that require frequent updates and iterations. If the product is expected to evolve based on user feedback or market trends, Agile’s iterative cycles can facilitate continuous improvement.
- Waterfall: Waterfall may be more suitable for projects with fixed requirements, such as construction or manufacturing, where changes during development can be costly and complicated. In such cases, a linear approach can ensure that all specifications are met before moving on to the next phase.
7- Risk Tolerance:
- Agile: If the organization has a high tolerance for risk and is open to experimentation, Agile can provide the flexibility needed to explore innovative solutions and adapt to unforeseen challenges. Agile encourages teams to embrace change and learn from failures, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Waterfall: For organizations with a low tolerance for risk, Waterfall’s structured approach can provide a sense of security. By thoroughly planning and documenting each phase, teams can minimize uncertainties and ensure that all aspects of the project are carefully considered.
By carefully evaluating these factors, organizations can make informed decisions about whether Agile or Waterfall is the most suitable project management methodology for their specific needs. Understanding the unique characteristics of each approach will help ensure that the chosen methodology aligns with project goals, stakeholder expectations, and team capabilities.
What is the Hybrid Approach and Is It for You?
The hybrid approach combines elements of both Agile and Waterfall methodologies, allowing teams to tailor their project management strategy to best fit their specific needs. This approach recognizes that not all projects are purely Agile or Waterfall and that a combination of both can often yield better results.
When to Consider a Hybrid Approach
- Diverse Project Requirements: If a project has both stable and dynamic components, a hybrid approach can accommodate both by applying Waterfall to the stable parts and Agile to the more fluid aspects.
- Mixed Stakeholder Involvement: In cases where some stakeholders prefer detailed documentation and others favor iterative feedback, a hybrid approach can balance these preferences.
- Team Skill Set: If your team has experience with both methodologies, a hybrid approach allows them to leverage their strengths in different areas of the project.
- Complex Environments: In complex environments where regulatory compliance is necessary, a hybrid approach can provide the structure needed for documentation while allowing for flexibility in development.
How to Implement a Hybrid Approach
A hybrid approach to project management combines elements from both Agile and Waterfall methodologies, allowing teams to leverage the strengths of each while mitigating their weaknesses. Implementing a hybrid approach can enhance flexibility, improve stakeholder engagement, and optimize resource allocation. Here are key steps to successfully implement a hybrid project management approach:
1- Assess Project Requirements:
Begin by thoroughly analyzing the project’s scope, complexity, and requirements. Identify which aspects are well-defined and stable, and which are likely to evolve. This assessment will help determine which parts of the project can benefit from a Waterfall approach (e.g., initial planning and documentation) and which can adopt Agile practices (e.g., development and testing).
2- Define Clear Objectives:
Establish clear project objectives and goals that align with both Agile and Waterfall methodologies. Define what success looks like for the project and ensure that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of these objectives. This clarity will guide decision-making throughout the project and help maintain focus.
3- Create a Flexible Framework:
Develop a project framework that integrates Agile and Waterfall elements. For instance, you might use Waterfall for the initial planning and requirements gathering phases, followed by Agile sprints for development and testing. This hybrid framework should allow for flexibility in responding to changes while maintaining structure in areas where it is needed.
4- Establish Roles and Responsibilities:
Clearly define roles and responsibilities for team members within the hybrid framework. Ensure that everyone understands their contributions to both Agile and Waterfall components of the project. This clarity will help facilitate collaboration and communication across different teams and disciplines.
5- Implement Agile Practices:
Incorporate Agile practices such as daily stand-ups, iterative development, and sprint reviews into the project. These practices promote continuous feedback and collaboration, enabling teams to adapt to changes and improve the product incrementally. Ensure that Agile ceremonies are scheduled alongside Waterfall milestones to maintain alignment.
6- Maintain Comprehensive Documentation:
While Agile emphasizes minimal documentation, it is essential to maintain comprehensive records for the Waterfall components of the project. Strike a balance by documenting key decisions, requirements, and changes without overwhelming the team with excessive paperwork. This approach ensures that necessary information is available for compliance and future reference.
7- Foster Communication and Collaboration:
Encourage open communication and collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and customers. Use collaborative tools and platforms to facilitate information sharing and transparency. Regular check-ins and updates can help ensure that everyone is aligned and aware of project progress and changes.
8- Monitor and Adapt:
Continuously monitor the project’s progress and performance, evaluating the effectiveness of the hybrid approach. Gather feedback from team members and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. Be prepared to adapt the framework as needed, adjusting the balance of Agile and Waterfall elements based on project dynamics and stakeholder input.
9- Train and Support the Team:
Provide training and support to team members to help them understand and effectively implement the hybrid approach. This may involve workshops on Agile methodologies, Waterfall processes, or specific tools used in the hybrid framework. Ensuring that the team is well-equipped to navigate the hybrid model will enhance overall project success.
10- Evaluate Outcomes and Iterate:
After project completion, evaluate the outcomes and effectiveness of the hybrid approach. Analyze what worked well and what could be improved for future projects. Use these insights to refine the hybrid framework and inform best practices for subsequent initiatives.
Table: Metrics to measure the effectiveness of a hybrid approach in project management
Metric | Description |
Customer Satisfaction | Measures stakeholder feedback and satisfaction levels with the final product and project process |
Time to Market | Evaluates the speed at which the project delivers functional increments to stakeholders |
Team Collaboration | Assesses the effectiveness of communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders |
Budget Adherence | Tracks whether the project stays within budget and identifies any variances from initial estimates |
Quality of Deliverables | Measures the quality of the final product through defect rates, rework, and adherence to requirements |
By thoughtfully implementing a hybrid approach, organizations can harness the benefits of both Agile and Waterfall methodologies, leading to improved project outcomes, enhanced stakeholder satisfaction, and greater adaptability in an ever-changing environment.
Conclusion
Choosing between Agile and Waterfall project management methodologies is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Each approach has its strengths and weaknesses, making it essential to evaluate the specific needs of your project, team, and organization. The Agile methodology thrives in environments that require flexibility and adaptability, while Waterfall provides a structured and predictable framework for projects with well-defined requirements.
For many organizations, a hybrid approach may offer the best of both worlds, allowing for tailored solutions that meet diverse project demands. By understanding the nuances of each methodology and considering the factors outlined in this blog post, you can make informed decisions that enhance project success and drive organizational growth. Embrace the opportunity to experiment with different methodologies, and find the approach that resonates most with your team and stakeholders.