- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Procurement Fraud?
- The Three Requirements for Fraud
- 1. Deception
- 2. Concealment
- 3. Financial Gain
- How to Spot Procurement Fraud
- 1. Discrepancies in Invoices and Documentation
- 2. Suspicious Vendor Relationships and Transactions
- 3. Unusual Patterns in Purchasing Behaviour
- 4. Employee Behaviour and Lifestyle Discrepancies
- 5. Unusual Supplier Locations and Background Checks
- 6. Inconsistent Data in Procurement Records
- 6 Common Procurement Fraud Schemes
- 1. Phantom Vendors and Fictitious Invoices
- 2. Bid Rigging and Collusion
- 3. Kickbacks and Bribery
- 4. Overbilling and Inflated Pricing
- 5. Change Order Fraud
- 6. Vendor Master File Manipulation
- Investigating Procurement Fraud
- 1. Forensic Accounting
- 2. Data Mining and Analysis
- 3. Whistleblower Tips and Interviews
- 4. Digital Forensics
- 5. Collaboration with Law Enforcement and Legal Experts
- Applying Network Analytics and Visualisation to the Investigation
- 1. Network Analytics
- 2. Visualisation Tools
- 3. Graph Databases
- 4. Predictive Analytics
- 5. Machine Learning Algorithms
- The Benefits of Utilising Technology to Prevent Procurement Fraud Early-On
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
- Data Analytics for Pattern Recognition
- Fraud Predictive Modelling
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Enhanced Due Diligence
- Blockchain Technology for Transparency
- 8 Strategies to Mitigate Procurement Fraud
- 1. Implement Robust Internal Controls
- 2. Conduct Regular Audits and Forensic Reviews
- 3. Foster a Culture of Ethics and Integrity
- 4. Promote Transparency and Vendor Due Diligence
- 5. Leverage Advanced Data Analytics and AI
- 6. Strengthen Collaboration Between Departments
- 7. Implement Blockchain Technology for Transparency
- 8. Engage in Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
- Federal Programmes and Procurement Fraud
- 1. The False Claims Act (FCA)
- 2. The Whistleblower Protection Act
- 3. The Procurement Integrity Act (PIA)
- 4. Inspector General Oversight
- 5. Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR)
- 6. Government Accountability Office (GAO) Oversight
- In Conclusion
Introduction
Procurement, the lifeblood of any organisation, can sometimes become the breeding ground for deception and dishonesty. Procurement fraud, a term that sends shivers down the spines of business owners and procurement professionals alike, is a multifaceted threat that can seep into the very core of an organisation, leaving behind a trail of financial loss and reputational damage. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricate web of procurement fraud, from its definition to strategies that can safeguard businesses from its clutches.
What Is Procurement Fraud?
At its essence, procurement fraud refers to any unlawful activity conducted during the procurement process with the intent to derive financial benefits dishonestly. This fraudulent behaviour undermines the integrity of procurement systems, jeopardises fair competition, and ultimately results in substantial losses for organisations. According to SAS, it's estimated that companies experience a 5% annual loss due to procurement fraud, waste, and abuse, resulting in losses ranging from $10,000 to $150,000 per year.
The Three Requirements for Fraud
Fraud, regardless of its context, follows a predictable pattern rooted in three fundamental elements: deception, concealment, and financial gain. Understanding these requirements is pivotal in recognising and combating fraud, including the intricate realm of procurement fraud.
1. Deception
At the heart of any fraudulent activity lies deception, a crafty art where individuals deliberately misrepresent facts, events, or information to deceive others. In the case of procurement fraud, deception may take various forms. For instance, a vendor might falsify product quality certificates, making substandard goods appear superior. Deceptive practices can also involve misrepresenting prices, quantities, or delivery timelines to secure contracts illicitly.
The perpetrators of procurement fraud often employ sophisticated tactics to create a facade of legitimacy. They might forge documents, manipulate digital records, or impersonate legitimate vendors or employees. Deception serves as the initial gateway, allowing fraudsters to infiltrate procurement processes, concealing their malicious intent beneath a veneer of authenticity.
2. Concealment
Concealment is the second pillar upon which fraud stands. Once deception has paved the way, fraudsters work diligently to cloak their activities, ensuring they remain undetected by internal checks and audits. In procurement fraud, concealment can involve a myriad of tactics.
One common method is the creation of fictitious vendors or shell companies. These entities, while appearing legitimate on paper, exist solely to facilitate fraudulent transactions. Fraudsters manipulate financial records, invoices, and payment documents, making it challenging for even the most vigilant auditors to discern the illicit activities amidst the sea of legitimate transactions.
Additionally, concealment often extends to collusion among employees or vendors. By working together, individuals involved in procurement fraud create a network of complicity, further obfuscating their actions from prying eyes within the organisation.
3. Financial Gain
Financial gain serves as the ultimate objective of any fraudulent endeavour. Whether it's syphoning off funds, securing contracts through unfair means, or inflating prices, the primary motivation behind procurement fraud is monetary profit. Fraudsters seek to enrich themselves or their accomplices at the expense of the organisation they defraud.
This financial gain is not merely a byproduct but a driving force that fuels the entire fraudulent process. It motivates fraudsters to refine their tactics, explore new schemes, and exploit vulnerabilities within procurement systems. The allure of substantial profits often blinds individuals to the ethical and legal ramifications of their actions, leading them down a dangerous path of deceit and betrayal.
Understanding these three requirements for fraud is essential for organisations aiming to bolster their defences. By recognising the signs of deception, unveiling concealed activities, and deciphering the motives behind fraudulent actions, businesses can proactively implement measures to prevent, detect, and combat procurement fraud. Vigilance, education, and technological advancements are the keys to dismantling the intricate web of deception that fraudsters weave, ensuring the integrity of procurement processes and safeguarding the financial health of organisations.
How to Spot Procurement Fraud
Procurement fraud, with its elusive nature, often hides in plain sight, requiring a discerning eye and a vigilant mindset to uncover its deceitful schemes. The ability to spot procurement fraud is not merely a skill; it's an art grounded in a deep understanding of the procurement process and human behaviour. Here's a look at the subtle nuances and telltale signs that can help organisations spot procurement fraud before it inflicts irreparable damage:
1. Discrepancies in Invoices and Documentation
One of the primary indicators of procurement fraud lies in the examination of invoices and related documentation. Discrepancies between quoted prices and invoiced amounts, especially when these variations cannot be justified by market fluctuations or contractual changes, raise a red flag. Inconsistencies in product or service descriptions, quantities, or delivery dates might indicate fraudulent activities, prompting a closer investigation.
2. Suspicious Vendor Relationships and Transactions
Anomalies in vendor relationships and transactions can provide valuable insights into potential fraud. Unusually close ties between employees and vendors, especially if accompanied by a rapid increase in business transactions, could suggest collusion. Similarly, a vendor suddenly winning multiple contracts without a competitive bidding process might indicate favouritism or bid rigging, both common procurement fraud tactics.
3. Unusual Patterns in Purchasing Behaviour
Monitoring purchasing patterns is essential in spotting irregularities. Sudden spikes in procurement activities without corresponding increases in operational demands or production needs can be a sign of fraudulent activities. Fraudsters might inflate procurement volumes to generate more significant payouts from their schemes. Analysing historical purchasing data can reveal deviations from established norms, providing valuable clues for further investigation.
4. Employee Behaviour and Lifestyle Discrepancies
Changes in employee behaviour, especially concerning financial matters, can be indicative of involvement in procurement fraud. Sudden lifestyle upgrades, unexplained wealth accumulation, or extravagant spending by employees might be red flags. It's essential for organisations to encourage an open culture where employees can report suspicions discreetly, ensuring that these behavioural changes do not go unnoticed.
5. Unusual Supplier Locations and Background Checks
The geographical location of suppliers can also be a source of suspicion. P.O. Box addresses, temporary office spaces, or locations in high-risk jurisdictions might indicate fictitious or shell companies. Conducting thorough background checks on suppliers, including site visits and verifying their legitimacy, is crucial in ensuring the authenticity of vendors and mitigating the risk of fraud.
6. Inconsistent Data in Procurement Records
Consistency in data is key in detecting procurement fraud. Discrepancies between procurement records, inventory levels, and actual stock on hand can point to fraudulent activities like inventory theft or false reporting. Implementing regular reconciliations and cross-verification of data sets can help identify inconsistencies and discrepancies that might otherwise go unnoticed.
By cultivating a culture of awareness, providing adequate training to employees, and leveraging advanced data analytics tools, organisations can enhance their ability to spot procurement fraud. Recognising these subtle indicators and acting swiftly not only protects the financial health and reputation of the organisation but also acts as a deterrent, sending a clear message that fraudulent activities will not be tolerated. In the intricate dance between fraudsters and organisations, astute observation and proactive measures can tilt the balance in favour of integrity, transparency, and ethical conduct.
6 Common Procurement Fraud Schemes
In recent times, procurement fraud has become an alarming global challenge, infiltrating organisations worldwide. According to research by Accuracy, a reputable international advisory firm cited in the International Accounting Bulletin, instances of procurement fraud have surged by 13% in the UK, illustrating the pervasive nature of this threat. Navigating the complex terrain of procurement amidst this rise demands a keen awareness of prevalent fraud schemes. Recognising these deceptive tactics is akin to illuminating the obscured corners, empowering organisations to identify warning signs and bolster their defenses against these insidious practices:
1. Phantom Vendors and Fictitious Invoices
One of the oldest tricks in the fraudulent playbook involves the creation of phantom vendors and fictitious invoices. Fraudsters fabricate suppliers, complete with forged documentation and contact information. They then submit invoices for goods or services that were never delivered. These phantom transactions can easily slip through the cracks if not meticulously scrutinised, resulting in organisations paying for goods or services they never received.
2. Bid Rigging and Collusion
Bid rigging occurs when competing vendors collaborate to manipulate the bidding process, ensuring that a particular vendor wins the contract. This collusion stifles fair competition, driving up prices and undermining the procurement process's integrity. Colluding vendors might agree to submit artificially high bids or take turns winning contracts, all at the expense of the organisation seeking the services or goods.
3. Kickbacks and Bribery
Kickbacks and bribery involve offering or accepting undue incentives to influence procurement decisions. Vendors might offer kickbacks to employees in exchange for preferential treatment, such as awarding contracts or inflating purchase quantities. Bribery, on the other hand, involves offering bribes to decision-makers to secure contracts. These unethical practices not only inflate costs but erode the trust and integrity of the entire procurement process.
4. Overbilling and Inflated Pricing
Overbilling schemes involve vendors submitting invoices that exceed the agreed-upon contract prices or charging for goods and services not provided. Fraudsters may exploit small discrepancies, assuming they'll go unnoticed in the vast sea of transactions. Similarly, inflated pricing occurs when vendors charge significantly higher prices for goods or services compared to market rates. Such schemes can lead to substantial financial losses for organisations if not detected promptly.
5. Change Order Fraud
Change order fraud involves manipulating the terms of existing contracts after they have been awarded. Fraudsters exploit change orders—legitimate modifications made to contracts—to sneak in unauthorised alterations, such as inflated pricing or additional, unnecessary services. By disguising fraudulent activities as legitimate changes, perpetrators can embezzle funds and evade scrutiny.
6. Vendor Master File Manipulation
In this scheme, fraudsters gain access to an organisation's vendor master file and alter the bank account details of legitimate vendors. When payments are processed, the funds are diverted to the fraudster's accounts. This subtle manipulation often goes unnoticed until vendors start reporting missing payments, by which time significant financial losses might have already occurred.
By understanding these common procurement fraud schemes, organisations can implement targeted preventive measures and enhance their detection capabilities. Vigilance, stringent vendor due diligence, regular audits, and employee training are vital components of a robust anti-fraud strategy. By shining a light on these deceptive practices, businesses can thwart the efforts of fraudsters and safeguard their financial resources and reputation from the clutches of procurement fraud.
Table 1: Common procurement fraud schemes
Fraud Scheme | Description | Impact |
Phantom Vendors | Creation of fictitious vendors | Payment for non-existent goods/services |
Bid Rigging | Collusion to manipulate bidding process | Artificial price inflation |
Kickbacks and Bribery | Offering or accepting undue incentives | Biassed contract awards, inflated costs |
Overbilling and Pricing | Charging excess or inflating product cost | Financial losses, inaccurate budgets |
Change Order Fraud | Unauthorised alterations in contract terms | Hidden costs, distorted project scope |
Investigating Procurement Fraud
When the shadow of procurement fraud looms over an organisation, swift and meticulous action is essential. Investigating procurement fraud demands a blend of expertise, persistence, and advanced analytical tools. Unravelling the tangled threads of deceit requires a strategic approach, incorporating various techniques to uncover the truth behind the façade. Here’s a detailed exploration of the investigative process and the tools employed to expose the intricacies of procurement fraud schemes:
1. Forensic Accounting
Forensic accountants play a pivotal role in procurement fraud investigations. Armed with a deep understanding of financial records, they meticulously examine invoices, receipts, purchase orders, and payment transactions. By identifying irregularities, discrepancies, and suspicious patterns, forensic accountants trace the flow of funds, revealing hidden connections and potential fraudulent activities. Through financial analysis, they provide a comprehensive overview of the fraud, aiding investigators in understanding the scope and impact of the deception.
2. Data Mining and Analysis
In the digital age, vast amounts of data are generated and stored by organisations. Data mining and analysis tools serve as powerful allies in the fight against procurement fraud. By processing large datasets, these tools unveil patterns, trends, and anomalies that human investigators might overlook. By scrutinising procurement data, these tools can identify suspicious vendor relationships, unusual purchasing patterns, and discrepancies between quoted prices and actual payments. Data-driven insights enable investigators to focus their efforts efficiently, maximising the chances of uncovering fraudulent activities.
3. Whistleblower Tips and Interviews
Whistleblower tips and employee interviews are invaluable sources of insider knowledge. Employees within the organisation often possess crucial information about suspicious activities or unethical behaviour. Whistleblower programmes, which protect the identity of informants, encourage employees to come forward with their concerns. Skilled interviewers, trained in techniques to elicit information effectively, extract details that can lead investigators to the heart of procurement fraud schemes. These firsthand accounts shed light on hidden agendas, enabling investigators to corroborate findings and build a compelling case.
4. Digital Forensics
In an era dominated by technology, digital forensics has become indispensable in fraud investigations. Digital forensic experts delve into electronic devices, emails, and communication channels, tracing digital footprints left by fraudsters. Digital evidence, such as incriminating emails, instant messages, or financial transactions, can provide a clear trail of fraudulent activities. By analysing metadata, IP addresses, and server logs, digital forensic experts reconstruct the sequence of events, strengthening the evidentiary foundation of the investigation.
5. Collaboration with Law Enforcement and Legal Experts
Collaboration with law enforcement agencies and legal experts enhances the investigative process. Law enforcement agencies bring their expertise in criminal investigations, ensuring that the investigation adheres to legal standards and regulations. Legal experts provide insights into relevant laws, regulations, and precedents, guiding the investigation and ensuring its compliance with the legal framework. Working in tandem with these professionals strengthens the investigative team, ensuring a comprehensive and legally sound approach to uncovering procurement fraud.
Investigating procurement fraud is a meticulous and multifaceted process. By leveraging the expertise of forensic accountants, data analysts, whistleblower programmes, digital forensic experts, and legal professionals, organisations can meticulously dissect the intricacies of fraud schemes. Through these collaborative efforts, the truth emerges from the tangled threads of deceit, enabling organisations to take decisive action against fraudsters, safeguard their assets, and restore the integrity of their procurement processes.
Applying Network Analytics and Visualisation to the Investigation
In the intricate landscape of procurement fraud, where deception weaves a complex web of clandestine activities, traditional investigative methods may fall short. The advent of advanced technologies has ushered in a new era of detection and analysis, with network analytics and visualisation standing as formidable tools in the investigator's arsenal. By applying these cutting-edge techniques, investigators can unmask the web of deceit, revealing hidden patterns and connections that lie beneath the surface of procurement fraud schemes.
1. Network Analytics
Network analytics involves the analysis of relationships and interactions between various entities, such as vendors, employees, and transactions. By constructing a network model based on these connections, investigators can gain profound insights into the dynamics of fraudulent activities. Suspicious patterns, such as frequent collaborations between specific vendors and employees, can be identified, highlighting potential collusion or kickback schemes. Network analytics also facilitate the identification of influential nodes—individuals or entities that play a central role in fraudulent activities—enabling investigators to focus their efforts effectively.
2. Visualisation Tools
Visualisation tools serve as the lens through which investigators can gain a holistic view of complex datasets. By transforming raw data into visually intuitive graphs, charts, and diagrams, these tools enable investigators to discern patterns, trends, and anomalies that might be imperceptible in raw numerical data. Visual representations of procurement networks provide a clear and concise overview of relationships, allowing investigators to identify clusters of interconnected entities. Anomalies, outliers, and suspicious transactions are highlighted, making it easier to pinpoint areas that require in-depth investigation.
3. Graph Databases
Graph databases are tailored to handle interconnected data, making them ideal for analysing the intricate relationships within procurement fraud schemes. Unlike traditional databases, graph databases store data in nodes and edges, representing entities and their relationships. This unique structure allows investigators to traverse the data efficiently, exploring the connections between vendors, employees, contracts, and transactions. By querying the graph database, investigators can uncover hidden relationships and unveil the layers of complexity inherent in procurement fraud.
4. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics harness the power of historical data and statistical algorithms to forecast future events, including potential fraudulent activities. By analysing past procurement fraud cases and identifying common patterns, predictive models can predict the likelihood of similar schemes occurring in the future. Early detection of these patterns empowers organisations to implement preventive measures proactively, mitigating the risk of fraud before it escalates.
5. Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms excel at processing vast volumes of data to identify intricate patterns and trends. In the context of procurement fraud, these algorithms can analyse diverse datasets, ranging from financial records to email communications. By identifying subtle correlations and deviations, machine learning algorithms uncover indicators of fraudulent activities that might go unnoticed through traditional methods. Continuous learning and adaptation enable these algorithms to evolve alongside the ever-changing landscape of fraud schemes.
By harnessing the power of network analytics, visualisation tools, graph databases, predictive analytics, and machine learning algorithms, investigators can navigate the labyrinthine world of procurement fraud with unprecedented precision. These technologies provide not only a magnifying glass for scrutinising existing data but also a crystal ball for anticipating and preventing future fraudulent activities. In the face of evolving fraud tactics, the synergy between human expertise and cutting-edge technology emerges as the ultimate weapon, allowing organisations to stay one step ahead of fraudsters and preserve the integrity of their procurement processes.
The Benefits of Utilising Technology to Prevent Procurement Fraud Early-On
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Technology allows for the implementation of real-time monitoring systems that continuously analyse procurement data. By scrutinising transactions, vendor activities, and employee interactions in real-time, these systems can flag suspicious patterns and anomalies as soon as they occur. Automated alerts ensure that potential fraud incidents are identified promptly, allowing organisations to take immediate action and prevent further fraudulent activities.
Data Analytics for Pattern Recognition
Advanced data analytics tools have the capacity to process vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds. By analysing historical procurement data, these tools identify patterns and trends associated with fraud schemes. Machine learning algorithms can recognise subtle deviations and irregularities in purchasing behaviour, vendor relationships, and transactional patterns, signalling the presence of fraudulent activities. Early recognition of these patterns enables organisations to intervene before the fraud escalates.
Fraud Predictive Modelling
Predictive modelling, a powerful application of data analytics, uses historical data to forecast future events. In the context of procurement fraud, predictive models analyse past fraud incidents to identify common features and markers. By recognising these indicators, organisations can anticipate potential fraud risks. Early identification enables organisations to implement targeted preventive measures, such as additional scrutiny of specific vendors or transactions, thereby thwarting fraudsters before they strike.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms excel at detecting patterns in vast datasets. In the fight against procurement fraud, AI and ML algorithms can learn from historical data, adapting to evolving fraud tactics. These algorithms continuously refine their understanding of fraud indicators, allowing organisations to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated fraud schemes. By leveraging AI and ML, organisations can automate the detection of fraud patterns, intervening early to prevent financial losses.
Enhanced Due Diligence
Technology enables organisations to conduct enhanced due diligence on vendors and suppliers. Digital tools can cross-reference vendor information against various databases, ensuring the legitimacy of entities involved in procurement. Suspicious entities, such as shell companies or entities with dubious backgrounds, can be swiftly identified and flagged for further investigation. Enhanced due diligence technologies provide organisations with a robust first line of defence against fraudulent vendors.
Blockchain Technology for Transparency
Blockchain technology offers an immutable, decentralised ledger that records all transactions transparently and securely. By implementing blockchain in procurement processes, organisations can ensure the integrity and transparency of transactions. Any attempts to manipulate procurement data or engage in fraudulent activities are instantly detectable, making it exceptionally difficult for fraudsters to compromise the system. Blockchain technology provides an incorruptible foundation for procurement, deterring fraudsters and instilling confidence in stakeholders.
By harnessing these technological advancements, organisations can establish a proactive and resilient defence against procurement fraud. Early detection, prevention, and transparency become attainable goals, ensuring that businesses not only protect their financial resources but also foster a culture of integrity and trust. The synergy between human expertise and cutting-edge technology creates a formidable barrier against fraud, empowering organisations to safeguard their assets and uphold the principles of ethical procurement practices.
8 Strategies to Mitigate Procurement Fraud
Procurement fraud demands a comprehensive and proactive approach. Mitigating the risks associated with fraudulent activities in procurement processes requires a strategic combination of robust policies, advanced technologies, and a vigilant organisational culture. Here are eight strategies organisations can employ to build resilience, enhance detection, and mitigate the impact of procurement fraud:
1. Implement Robust Internal Controls
Establishing stringent internal controls is the foundation of fraud prevention. Clear segregation of duties, authorisation protocols, and a well-defined procurement approval hierarchy are crucial. Regularly reviewing and updating these controls ensures that they align with the organisation's evolving needs and complexities, creating a formidable barrier against fraudulent activities.
2. Conduct Regular Audits and Forensic Reviews
Regular audits of procurement processes, coupled with forensic reviews, are instrumental in detecting irregularities. Internal and external audits should be conducted periodically, focusing on procurement transactions, vendor relationships, and contract management. Forensic reviews delve deeper, employing specialised techniques to uncover hidden fraud schemes and provide actionable insights for prevention.
3. Foster a Culture of Ethics and Integrity
Organisational culture plays a pivotal role in fraud prevention. By fostering a culture of ethics, transparency, and integrity, organisations create an environment where fraudulent activities are less likely to take root. Comprehensive ethics training, whistleblower programmes, and clear communication of zero-tolerance policies send a strong message, dissuading employees and stakeholders from engaging in fraudulent behaviour.
4. Promote Transparency and Vendor Due Diligence
Transparency in procurement processes acts as a powerful deterrent against fraud. Clearly defined procurement policies and procedures, accessible to all stakeholders, enhance transparency. Rigorous vendor due diligence, including background checks, financial evaluations, and reputation assessments, ensures that organisations engage with legitimate and trustworthy suppliers, reducing the risk of fraudulent vendor relationships.
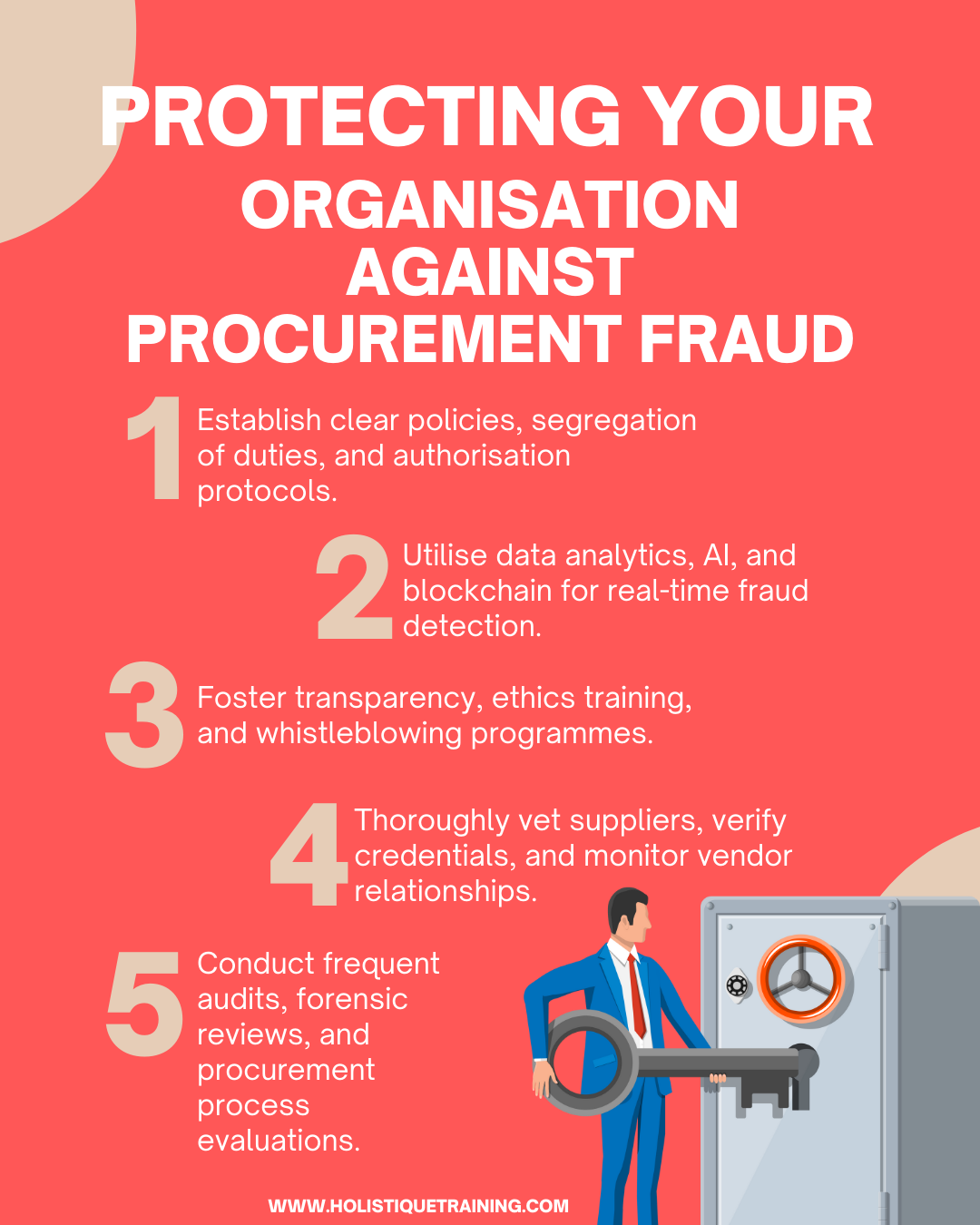
5. Leverage Advanced Data Analytics and AI
Advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) empower organisations to proactively detect fraud patterns. Implementing AI-driven algorithms that analyse vast datasets can identify anomalies, irregularities, and suspicious patterns in real-time. Machine learning algorithms adapt and evolve, staying ahead of fraudsters' tactics, making it possible to detect and prevent fraud early.
6. Strengthen Collaboration Between Departments
Collaboration between departments, particularly procurement, finance, legal, and IT, strengthens the organisation's ability to combat fraud. Shared insights and coordinated efforts allow for a holistic view of procurement activities. Regular communication channels and joint training programmes ensure that employees are vigilant and well-informed about the latest fraud schemes.
7. Implement Blockchain Technology for Transparency
Blockchain technology provides an immutable, transparent ledger that enhances the integrity of procurement processes. By recording transactions in a tamper-proof manner, organisations create a transparent audit trail. Any attempts to manipulate procurement data are instantly detectable, discouraging fraudulent activities. Blockchain technology provides a robust layer of security, bolstering the organisation's defence against fraud.
8. Engage in Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Fraud prevention is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Continuous monitoring of procurement activities, coupled with regular updates to fraud detection systems, ensures that the organisation remains resilient against evolving fraud tactics. By staying informed about the latest fraud schemes and adapting preventive measures accordingly, organisations can maintain their vigilance and protect their assets effectively.
By implementing these strategies, organisations can create a robust defence against procurement fraud. A multi-faceted approach, incorporating internal controls, advanced technologies, ethical culture, and vigilant collaboration, establishes a resilient shield. In the face of ever-changing fraud tactics, organisations equipped with these strategies can confidently navigate the procurement landscape, ensuring the integrity of their processes and the trust of their stakeholders.
Federal Programmes and Procurement Fraud
Procurement fraud doesn't just pose a threat to private enterprises; it also jeopardises the integrity of government contracts and federal programmes. As public funds are at stake, governments worldwide have established stringent regulations and programmes to combat fraudulent activities within procurement processes. In the United States, for instance, federal programmes and laws are in place to safeguard taxpayers' money and maintain the transparency and fairness of government contracts.
1. The False Claims Act (FCA)
The False Claims Act, dating back to the Civil War era, remains a cornerstone in the fight against fraud. Under the FCA, individuals, often referred to as whistleblowers or realtors, can file lawsuits on behalf of the government if they suspect fraudulent activities involving federal funds. Whistleblowers are incentivised by receiving a percentage of recovered funds, encouraging them to come forward and report fraud. This powerful tool allows the government to recover funds lost to fraudulent procurement activities.
2. The Whistleblower Protection Act
The Whistleblower Protection Act provides legal protections to federal employees who report fraud, waste, or abuse within the government. This legislation shields whistleblowers from retaliation, ensuring that employees who expose fraudulent activities are safeguarded against adverse employment actions. By providing legal protections, the act encourages federal employees to report procurement fraud without fear of reprisal.
3. The Procurement Integrity Act (PIA)
The Procurement Integrity Act establishes ethical standards and safeguards the integrity of the federal procurement process. It outlines rules regarding the disclosure of confidential procurement information, ensuring that sensitive data is not misused to gain unfair advantages. Violations of the PIA can result in severe penalties, reinforcing the importance of ethical conduct within government procurement.
4. Inspector General Oversight
Various government agencies have Inspector General (IG) offices tasked with investigating and preventing fraud, waste, and abuse within federal programmes. These offices conduct audits, investigations, and evaluations to ensure compliance with procurement regulations. The findings of these investigations can lead to legal actions against individuals or entities involved in fraudulent activities, acting as a deterrent to potential fraudsters.
5. Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR)
The Federal Acquisition Regulations serve as the primary set of rules governing the procurement process for federal agencies. The FAR outlines guidelines for contracts, ethics, and procurement procedures. Adherence to these regulations is mandatory for government contractors, ensuring that procurement processes are transparent, competitive, and fair. Violations of FAR can result in legal consequences for contractors engaged in fraudulent activities.
6. Government Accountability Office (GAO) Oversight
The Government Accountability Office serves as the auditing body for the U.S. Congress. It investigates federal spending and ensures that funds are allocated and used efficiently. GAO reports shed light on irregularities within federal programmes, prompting corrective actions and, in some cases, legal proceedings against entities involved in fraudulent activities.
By integrating these legal safeguards and oversight mechanisms, federal programmes in the United States can actively combat procurement fraud. The combination of legal consequences, whistleblower protections, ethical standards, and strict regulations serves as a robust defence against fraudulent activities, ensuring that taxpayer money is spent wisely and ethically. These measures not only deter fraudsters but also contribute to maintaining the public's trust in government institutions and their procurement processes.
In Conclusion
In the relentless battle against procurement fraud, knowledge, vigilance, and technological prowess stand as our greatest allies. By implementing the strategies outlined here, businesses can fortify their defences, ensuring the integrity of their procurement processes and safeguarding their financial well-being. Remember, staying one step ahead of fraudsters requires continuous education and adaptation.
Are you ready to equip yourself and your team with the expertise to combat fraud effectively? Elevate your defences by enrolling in our comprehensive ‘Fraud Prevention Training’ course. Gain in-depth knowledge, practical insights, and hands-on skills that empower you to protect your business from the ever-evolving tactics of fraudsters. Don't just defend your organisation; lead the charge against fraud with confidence and competence!