- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is the Project Life Cycle?
- The 5 Phases of the Project Life Cycle
- 1. Initiation
- 2. Planning
- 3. Execution
- 4. Monitoring and Controlling
- 5. Closing
- Why Is the Project Life Cycle Important?
- 1. Enhances Efficiency
- 2. Manages Risks Effectively
- 3. Facilitates Communication
- 4. Improves Decision-Making
- 5. Promotes Continuous Improvement
- The Role of Project Management Software
- 1. Initiation
- 2. Planning
- 3. Execution
- 4. Monitoring and Controlling
- 5. Closing
- Integrating Project Management Software Across Phases
- Customisation for Unique Organisational Needs
- How to Bring Order to Your Project Life Cycle at Your Organisation
- 1. Standardise Processes
- 2. Invest in Training
- 3. Foster Collaboration
- 4. Embrace Agile Methodologies
- 5. Leverage Project Management Software
- 6. Implement Feedback Loops
- 7. Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- 8. Establish a Project Management Office (PMO)
- Conclusion
Introduction
Embarking on a project is akin to setting sail on a vast, unpredictable sea. To navigate these waters successfully, project managers rely on a structured approach known as the Project Life Cycle. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of the Project Life Cycle, exploring its phases, key steps, and the indispensable role it plays in steering projects toward success. Additionally, we'll unravel the ways in which project management software can streamline this process and offer insights on bringing order to the Project Life Cycle within your organisation.
What Is the Project Life Cycle?
At its core, the Project Life Cycle is a systematic series of phases that a project undergoes from initiation to completion. Think of it as a roadmap, guiding project managers and their teams through the myriad tasks and challenges inherent in any project. Each phase serves a distinct purpose, offering a structured approach to managing resources, mitigating risks, and ensuring that the end result aligns with the project's objectives.
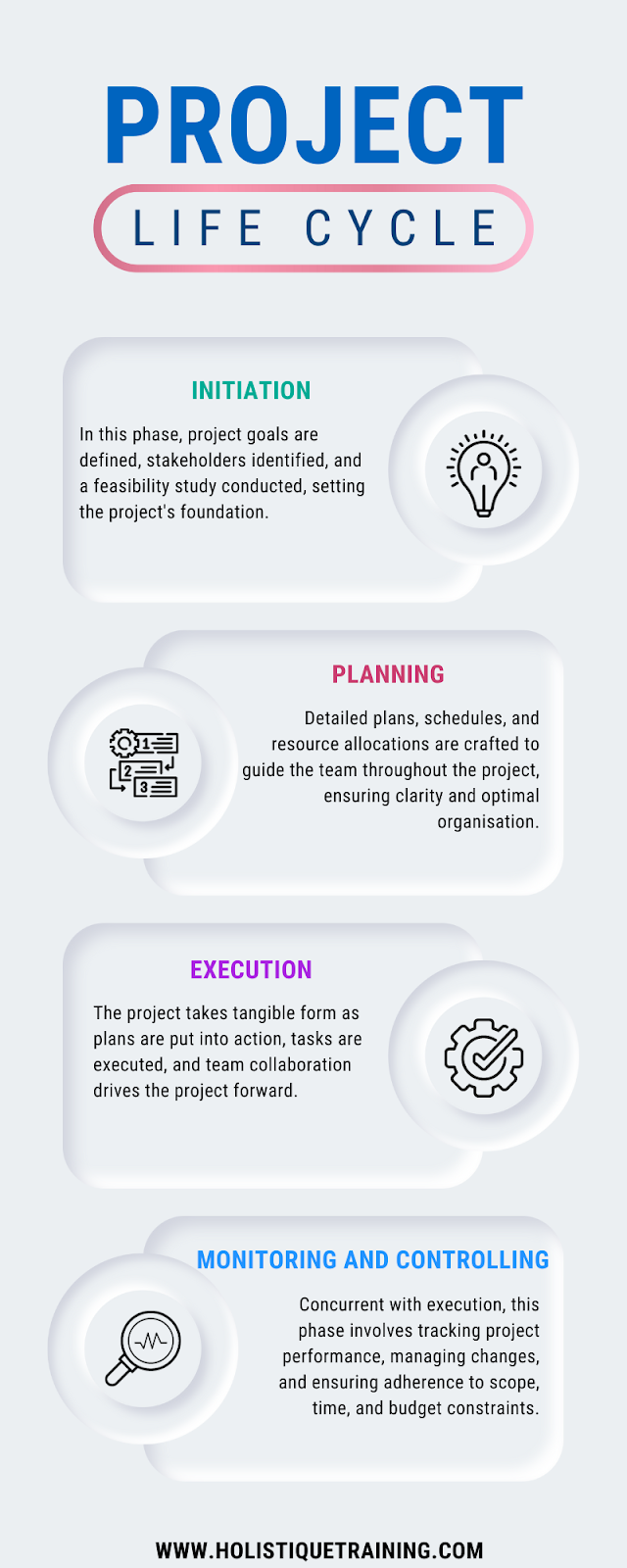
The 5 Phases of the Project Life Cycle
1. Initiation
The initiation phase is the inception point of any project, where ideas take form and possibilities are explored. Key steps in this phase involve meticulous groundwork to ensure the project's viability and alignment with organisational objectives.
i) Identifying Stakeholders
The first crucial step is identifying and engaging stakeholders. These are individuals or groups who have a vested interest in the project's outcome. By understanding their perspectives, expectations, and requirements, project managers can lay the groundwork for successful collaboration.
ii) Outlining Project Goals
During initiation, clarity in defining project goals is paramount. What does success look like? What are the specific objectives the project aims to achieve? These questions guide the project's trajectory and provide a compass for decision-making throughout its lifecycle.
iii) Conducting a Feasibility Study
The feasibility study is the reality check that ensures the project is not only desirable but also achievable. It involves assessing technical, financial, and operational aspects to determine if the project is feasible within the given constraints.
2. Planning
With the initiation phase setting the project's direction, the planning phase is where the roadmap is meticulously crafted. This phase involves creating a comprehensive plan that outlines the project's scope, timeline, resource allocation, and risk management strategies.
i) Defining Scope
Clearly defining the project's scope sets the boundaries for what is included and excluded. This step helps manage expectations, prevents scope creep, and ensures that the team focuses on delivering the agreed-upon features or deliverables.
ii) Creating Schedules and Timelines
In the planning phase, project managers work closely with team members to create detailed schedules and timelines. Utilising project management tools, they can develop Gantt charts and other visual aids that provide a clear overview of the project's timeline, milestones, and dependencies.
iii) Allocating Resources
Resource allocation involves identifying and assigning the necessary human, financial, and material resources for each phase of the project. This step ensures that the team has the support it needs to meet deadlines and deliver high-quality results.
iv) Risk Management
Anticipating and managing risks is a key aspect of the planning phase. Project managers conduct risk assessments to identify potential challenges and develop strategies to mitigate or respond to them. This proactive approach helps prevent issues from derailing the project later on.
3. Execution
As the project moves into the execution phase, plans transition into action. This is the hands-on stage where the project team collaborates to bring the project to life, and key steps involve team mobilisation, task execution, and continuous monitoring.
i) Team Mobilisation
Team mobilisation involves bringing together the right individuals with the necessary skills to execute the project successfully. This phase includes assigning roles and responsibilities, fostering clear communication channels, and establishing a collaborative team culture.
ii) Task Execution
With plans in place and the team mobilised, task execution begins. Project managers oversee the implementation of the project plan, ensuring that tasks are completed according to specifications, and addressing any challenges or roadblocks that may arise.
iii) Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is a dynamic aspect of the execution phase. Project managers use real-time tracking tools and regular check-ins to monitor progress against the project plan. This allows for early identification of issues, making it possible to implement corrective actions promptly.
4. Monitoring and Controlling
Simultaneous to the execution phase, the monitoring and controlling stage involves keeping a watchful eye on project performance, managing changes, and ensuring that the project remains on track in terms of scope, time, and budget.
i) Tracking Project Performance
Project managers utilise a range of performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. Real-time dashboards provide a bird's-eye view of the project, offering insights into whether the team is meeting milestones and adhering to the project plan.
ii) Managing Changes
Change is inevitable in any project. The monitoring and controlling phase involves a systematic approach to managing changes, ensuring that alterations to the project plan are documented, assessed for impact, and communicated effectively to stakeholders.
iii) Ensuring Compliance
Compliance with established processes and standards is crucial. Project managers use this phase to conduct audits, ensuring that the project aligns with organisational policies and industry regulations. This step reduces the risk of issues arising during the project's lifecycle.
5. Closing
As the project nears completion, the closing phase comes into play, involving formalising project completion, obtaining client approval, and releasing resources. Post-project evaluations are conducted to assess successes, challenges, and areas for improvement.
i) Formalising Project Completion
Formalising project completion includes obtaining client or stakeholder approval and ensuring that all deliverables have been met. This phase often involves conducting a project review meeting to celebrate achievements and discuss lessons learned.
ii) Releasing Resources
Resources tied to the project, whether human or material, are released in the closing phase. This step ensures that resources are reallocated efficiently and that the project doesn't incur unnecessary costs once its objectives are met.
iii) Post-Project Evaluations
Post-project evaluations are a critical component of the closing phase. This involves reflecting on the project's overall performance, identifying what went well, what could be improved, and documenting lessons learned. This valuable feedback loop contributes to continuous improvement for future projects.
In essence, the Project Life Cycle, with its five distinct phases and corresponding key steps, provides a comprehensive framework for navigating the complexities of project management. Each phase is intricately connected, forming a seamless continuum that guides project managers and their teams toward successful project completion.
Why Is the Project Life Cycle Important?
Understanding the significance of the Project Life Cycle is paramount for any organisation striving for project success. A well-structured Project Life Cycle:
1. Enhances Efficiency
At its core, the Project Life Cycle serves as a blueprint for project managers and teams to follow. By breaking down the project into well-defined phases, each with its specific goals and tasks, the Project Life Cycle enhances efficiency. This segmentation allows teams to focus on one aspect at a time, preventing overwhelm and ensuring that resources are allocated optimally. From the initiation of ideas to the closing phase's reflection, the Project Life Cycle provides a structured path that streamlines workflows and boosts overall efficiency.
2. Manages Risks Effectively
Risk management is a critical component of project success, and the Project Life Cycle integrates this process seamlessly. During the planning phase, project managers identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. As the project progresses through execution, monitoring, and controlling, the focus on risk management remains constant. This proactive approach ensures that risks are not only identified early but also addressed promptly, minimising the impact on the project's timeline, budget, and overall success.
3. Facilitates Communication
Clear andeffective communication is the lifeblood of successful project management. The Project Life Cycle provides a structured framework for communication at every stage. From the initial communication with stakeholders during the initiation phase to regular updates and reporting throughout execution, the Project Life Cycle ensures that all relevant parties are informed and aligned. This transparency is crucial for building trust, resolving issues, and maintaining a collaborative environment conducive to project success.
4. Improves Decision-Making
In the dynamic landscape of project management, decisions must be made swiftly and accurately. The Project Life Cycle, with its defined phases and key steps, provides project managers with a comprehensive view of the project at any given time. This visibility is instrumental in making informed decisions. Whether it's adjusting the project plan during the planning phase, addressing issues during execution, or adapting to changes in the monitoring and controlling phase, the Project Life Cycle empowers project managers to make decisions that align with the project's objectives and constraints.
5. Promotes Continuous Improvement
The closing phase of the Project Life Cycle is not just a conclusion; it's a springboard for continuous improvement. Post-project evaluations, conducted during the closing phase, provide valuable insights into what worked well, what could be improved, and lessons learned. This feedback loop is essential for refining processes, enhancing team performance, and ensuring that each subsequent project benefits from the knowledge gained. The Project Life Cycle, therefore, becomes a catalyst for ongoing improvement within the organisation's project management practices.
In summary, the importance of the Project Life Cycle lies in its ability to provide structure, mitigate risks, foster communication, enhance decision-making, and promote continuous improvement. As organisations navigate the complex waters of project management, the Project Life Cycle acts as a guiding compass, steering them toward success by instilling discipline, efficiency, and adaptability into the very fabric of their project management processes.
The Role of Project Management Software
In today's tech-driven landscape, project management software serves as a valuable ally in navigating the complexities of the Project Life Cycle. According to the2020 Project Management Software Market Analysis by Mordor Intelligence, the project management software market was valued at $5.37 billion. Projections indicate a substantial growth, with an estimated value reaching $9.81 billion by 2026. And for good reason. Here's how PMO can enhance each phase of the life cycle:
1. Initiation
During the initiation phase, project management software serves as a collaborative platform, fostering seamless communication and information sharing among stakeholders. Centralised repositories for project documents, discussion forums, and real-time messaging features enable stakeholders to contribute ideas, provide feedback, and collectively shape the project's direction. Additionally, workflow automation can expedite approval processes, ensuring that the initiation phase progresses efficiently.
2. Planning
In the planning phase, project management software becomes the architect's toolkit, assisting project managers in creating detailed plans and schedules.Gantt charts, resource allocation tools, and collaboration features enable teams to collaboratively develop comprehensive project plans. This software allows for real-time adjustments to the plan, accommodating changes and ensuring that everyone is working from the most up-to-date information. The result is a well-structured, dynamic plan that can adapt to the evolving needs of the project.
3. Execution
As the project moves into the execution phase, project management software transitions into the nerve centre for task management, progress tracking, and team collaboration. Task boards,Kanban boards, and collaborative document editing features facilitate real-time collaboration, enabling team members to stay aligned on tasks and deadlines. Notifications and alerts keep everyone informed about updates and changes, promoting a cohesive and productive execution phase.
4. Monitoring and Controlling
The monitoring and controlling phase benefits immensely from the reporting and analytics capabilities of project management software. Real-time dashboards provide project managers with a bird's-eye view of key performance metrics, allowing them to track progress, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. Automated reporting features streamline the process of compiling and sharing project status updates with stakeholders. This level of transparency enhances the monitoring and controlling phase, ensuring that project managers can address issues promptly and keep the project on track.
5. Closing
In the closing phase, project management software contributes to efficiency by facilitating the documentation of lessons learned and automating the creation of post-project reports. Collaboration tools ensure that all team members can contribute to the project review process, sharing their insights and perspectives. This streamlined approach expedites the closing phase, allowing teams to wrap up the project smoothly while capturing valuable information for future improvement.
Integrating Project Management Software Across Phases
Beyond the specific contributions to each phase, the seamless integration of project management software across the entire Project Life Cycle is a game-changer. A unified platform ensures consistency, reduces the risk of information silos, and enhances overall collaboration. For example, a change made during the execution phase is immediately reflected in the planning and monitoring stages, preventing discrepancies and fostering a holistic approach to project management.
Moreover, cloud-based project management solutions enable remote teams to collaborate effectively, breaking down geographical barriers and ensuring that everyone involved in the project has access to real-time information.
Customisation for Unique Organisational Needs
Project management software is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The best platforms offer customisation options, allowing organisations to tailor the software to their unique needs and workflows. Custom fields, templates, and integrations with other tools ensure that the software aligns seamlessly with the organisation's processes, enhancing its effectiveness across all phases of the Project Life Cycle.
In essence, project management software is the digital backbone that supports and enhances the Project Life Cycle. Its capabilities go beyond mere task tracking; it transforms the way teams collaborate, plan, execute, and learn from their projects. As organisations embrace the power of technology in project management, they find themselves not only navigating the Project Life Cycle more efficiently but also unlocking new possibilities for innovation and success.
How to Bring Order to Your Project Life Cycle at Your Organisation
Implementing a structured Project Life Cycle within your organisation requires a concerted effort and a commitment to best practices. Here are key strategies to bring order to your Project Life Cycle:
1. Standardise Processes
Establishing standardised processes for each phase of the Project Life Cycle is foundational to bringing order to your projects. This involves creating documented procedures, templates, and guidelines that serve as a reference for project managers and team members. Standardisation ensures consistency across projects, facilitates training for new team members, and enables the organisation to learn from past experiences. By having a set framework, the organisation can reduce variability, mitigate risks, and enhance overall efficiency.
2. Invest in Training
Equipping your team with the necessary skills and knowledge to navigate the Project Life Cycle is essential. Invest in comprehensivetraining programs that cover project management methodologies, the use of project management software, and interpersonal skills. Training ensures that team members are familiar with the standardised processes, understand their roles within the Project Life Cycle, and can contribute effectively to each phase. Ongoing training and professional development opportunities further enhance the competency and adaptability of your project teams.
3. Foster Collaboration
Collaboration is at the heart of successful project management. Fostering acollaborative culture within your organisation involves creating an environment where team members feel empowered to share ideas, provide feedback, and work together toward common goals. Project management software, with its collaborative features, can be a catalyst for fostering teamwork. Utilise tools that enable real-time communication, document sharing, and collaborative editing. Encourage open communication channels, hold regular team meetings, and celebrate achievements to strengthen the bonds within your project teams.
4. Embrace Agile Methodologies
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, inject flexibility and adaptability into your Project Life Cycle. These methodologies promote iterative development, allowing for incremental progress and continuous feedback. Embracing Agile principles enables your teams to respond quickly to changes in project scope, priorities, or market conditions. This approach fosters a culture of adaptability and responsiveness, enhancing the organisation's ability to deliver value to stakeholders consistently.
5. Leverage Project Management Software
Selecting the right project management software is a pivotal decision in bringing order to your Project Life Cycle. Look for a solution that aligns with your organisation's needs, offers scalability, and provides robust features for planning, execution, monitoring, and reporting. The software should integrate seamlessly with your standardised processes, facilitating a smooth flow of information and tasks across each phase. Regularly assess and update your software to leverage the latest features and ensure compatibility with evolving project requirements.
6. Implement Feedback Loops
Feedback loops are essential for continuous improvement. Establish mechanisms for gathering feedback at each phase of the Project Life Cycle. This can include project retrospectives, stakeholder surveys, and post-project evaluations. Analyse feedback systematically, identify areas for improvement, and incorporate lessons learned into your standardised processes. By institutionalising feedback loops, your organisation creates a culture of learning and refinement, ensuring that each project contributes to the organisation's collective knowledge and expertise.
7. Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) provides valuable insights into the health of your projects. Define relevant KPIs for each phase of the Project Life Cycle, such as project completion rates, adherence to timelines, and client satisfaction. Regularly analyse these metrics to identify trends, potential issues, and areas for optimisation. KPI monitoring serves as an early warning system, allowing project managers and leadership to take proactive measures to address challenges and maintain project success.
Table 1: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Each Phase
Phase | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) |
Initiation | Stakeholder engagement and project feasibility assessment. |
Planning | Project scope definition, resource allocation, and timelines. |
Execution | Task completion rates and team collaboration effectiveness. |
Monitoring & Controlling | Progress tracking, change management effectiveness, and compliance. |
Closing | Client satisfaction, on-time completion, and lessons learned documentation. |
8. Establish a Project Management Office (PMO)
For larger organisations or those handling complex projects, establishing a Project Management Office (PMO) can bring an additional layer of structure and oversight. A PMO acts as a centralised hub for project management resources, best practices, and governance. It ensures consistency in project management methodologies, provides support to project managers, and facilitates knowledge sharing across projects. The PMO serves as a strategic enabler, aligning project management efforts with organisational goals and standards.
According toMonday.com, currently, 89% of organisations boast a dedicated Project Management Office (PMO), with half of them managing multiple PMOs.
In short, bringing order to your Project Life Cycle involves a holistic approach that combines standardised processes, training, collaboration, agility, technology, feedback loops, KPI monitoring, and strategic oversight. By implementing these strategies, your organisation can cultivate a culture of efficiency, adaptability, and continuous improvement, positioning itself for sustained success in the dynamic landscape of project management.
Conclusion
Mastering the Project Life Cycle is an indispensable skill for organisations aiming to deliver successful projects consistently. By understanding each phase, embracing best practices, and leveraging the power of project management software, you can navigate the complexities of project management with confidence. As your organisation refines its approach to project management, the Project Life Cycle becomes not just a roadmap but a compass, guiding you toward the shores of success in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Finally, if you’re looking to elevate your skills further, check out our course, ‘Creating a Roadmap for a Complex Project,’ where we provide in-depth insights, practical strategies, and hands-on experience to empower you in steering your projects to triumph. Enrol now and chart a course for unparalleled project management proficiency!