- Table of Contents
- What Is the EFQM Model?
- Why Was the EFQM Model Developed?
- What Are the Core Components of the EFQM Model?
- Enablers
- Results
- How Can Organizations Implement the EFQM Model?
- What Are the Challenges and Considerations in Adopting the EFQM Model?
- 1. Organizational Culture and Resistance to Change
- 2. Resource Allocation
- 3. Training and Development
- 4. Measurement and Evaluation
- 5. Integration with Existing Systems
- 6. Continuous Improvement
- 7. External Recognition and Benchmarking
- 8. Keeping Pace with Change
- What Are the Benefits of Using the EFQM Model for Businesses?
- 1. Comprehensive Performance Assessment
- 2. Enhanced Operational Excellence
- 3. Improved Customer Satisfaction
- 4. Employee Engagement and Development
- 5. Strategic Alignment and Execution
- 6. Innovation and Creativity
- 7. Sustainability and Social Responsibility
- 8. Enhanced Reputation and Brand Image
- 9. Benchmarking and Continuous Improvement
- 10. Risk Management and Resilience
Introduction
Exploring the EFQM Model unveils a comprehensive framework designed for organizations seeking excellence and sustainable improvement. This article series delves into the essence, importance, and application of the EFQM Model, addressing pivotal questions such as its core components, the rationale behind its development, implementation strategies, and the challenges organizations might face in adopting it. We also shed light on the significant benefits it offers businesses in today's competitive landscape. Through this exploration, the EFQM Model emerges as a crucial tool for organizations aiming to achieve excellence in all facets of their operations, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
What Is the EFQM Model?
The EFQM (European Foundation for Quality Management) Model is a comprehensive management framework used by organizations to improve performance and achieve excellence. Developed in 1988 by the European Foundation for Quality Management, the model provides a holistic tool for assessing and enhancing various aspects of organizational operations, from leadership and strategy to processes, products, and services. Central to the EFQM Model is the idea of self-assessment, encouraging organizations to critically evaluate their own practices against a set of criteria designed to foster continuous improvement and innovation.
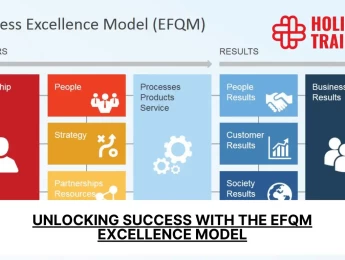
The model is structured around nine criteria, divided into two main groups: Enablers and Results. Enablers cover what an organization does and how it operates, including Leadership, People, Strategy, Partnerships & Resources, and Processes, Products & Services. Results focus on what an organization achieves in terms of People Results, Customer Results, Society Results, and Business Results. This framework supports organizations in understanding their strengths and areas for improvement, enabling them to develop action plans to achieve sustainable excellence and success.
Why Was the EFQM Model Developed?
The EFQM Model was developed to provide organizations with a framework for assessing and improving their performance across various dimensions critical to achieving excellence. Introduced in 1988 by the European Foundation for Quality Management, the model emerged in response to the need for a comprehensive tool that European businesses could use to evaluate their operations and management practices against the best in the world.
The development of the EFQM Model was motivated by several key objectives:
- Promoting Excellence: To encourage organizations to strive for and achieve excellence in all aspects of their operations, from leadership and strategy to processes and results.
- Enabling Benchmarking:To offer a structured approach for organizations to benchmark themselves against best practices and identify areas for improvement.
- Facilitating Continuous Improvement:To foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing a framework that organizations can use to systematically assess and enhance their performance.
- Enhancing Competitiveness: To help European businesses enhance their competitiveness in the global market by adopting principles of excellence in their management practices.
- Encouraging Organizational Learning:To promote learning and innovation by encouraging organizations to understand the cause-and-effect relationships between what they do (enablers) and the results they achieve.
- Supporting Sustainability:To integrate principles of sustainability and corporate social responsibility into the core operations of organizations, ensuring that they contribute positively to society.
What Are the Core Components of the EFQM Model?
The EFQM Model is structured around several core components that serve as the foundation for achieving organizational excellence. These components are categorized into two main groups: Enablers and Results. Here’s a detailed look at the core components of the EFQM Model:
Enablers
- Leadership: Focuses on how leaders develop and facilitate the achievement of the vision and mission, engage with customers, partners, and representatives of external organizations, and create and sustain values and ethics, ensuring long-term success.
- Strategy: Examines how the organization implements its strategy through effectively developing, monitoring, reviewing, and updating its strategic plans and objectives that are linked to the needs and expectations of stakeholders.
- People: Addresses how the organization manages, develops, and unleashes the full potential of its workforce to enhance its capability and capacity.
- Partnerships and Resources: Looks at how the organization plans and manages external partnerships, suppliers, and internal resources to support strategy implementation and the effective operation of processes.
- Processes, Products, and Services: Focuses on how the organization designs, manages, and improves processes to generate increasing value for customers and other stakeholders.
Results
- Customer Results:Concerns the results achieved by the organization in relation to its external customers, measuring satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement.
- People Results: Relates to what the organization has achieved in satisfying the needs of its workforce, covering aspects such as satisfaction, engagement, and well-being.
- Society Results:Focuses on what the organization has accomplished in contributing to local, national, and global communities, including environmental sustainability and social responsibility.
- Business Results:Evaluates the organization's achievements in crucial areas such as financial health, market presence, and efficiency.
These core components are interconnected, with the Enablers driving the Results. The EFQM Model emphasizes the importance of understanding and managing these elements as part of an integrated system to achieve sustainable excellence. It encourages organizations to assess their performance in these areas, identify areas for improvement, and implement strategies that lead to enhanced outcomes for all stakeholders.
How Can Organizations Implement the EFQM Model?
Organizations can implement the EFQM Model through a systematic approach that aligns their strategic objectives with the principles of excellence. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing the EFQM Model:
- Understand the EFQM Model: Begin with educating the leadership and employees about the EFQM Model, its core components, criteria, and the benefits of implementing it. Understanding the model is crucial for successful implementation.
- Conduct a Self-Assessment: Use the EFQM’s self-assessment tools to evaluate the current performance of the organization against the EFQM criteria. This helps identify strengths and areas for development.
- Develop an Action Plan: Based on the self-assessment results, develop an action plan that addresses identified gaps and leverages strengths. The plan should outline specific initiatives, responsible parties, timelines, and resources needed for implementation.
- Engage Employees: Embrace employees at all levels in the implementation process. Their engagement is critical for fostering a culture of excellence and ensuring the success of the EFQM model implementation.
- Train and Develop Skills:Provide training for employees on the principles of the EFQM Model, quality management, continuous improvement, and specific skills needed to achieve the goals outlined in the action plan.
- Implement Initiatives: Execute the initiatives outlined in the action plan. This could involve process improvements, leadership development programs, customer engagement strategies, or any other actions identified during the self-assessment.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly monitor the progress of the initiatives against the action plan. Use performance indicators and benchmarks to measure success and make adjustments as necessary.
- Foster Continuous Improvement: The EFQM Model is based on the principle of continuous improvement. Encourage a culture that seeks out opportunities for improvement, learns from experiences, and adapts to changing circumstances.
- Seek Recognition: Organizations can apply for recognition through the EFQM recognition schemes, such as the EFQM Global Excellence Award. While not a necessary step, seeking recognition can provide external validation of the organization's achievements and commitment to excellence.
- Review and Refine: Regularly review the entire process, including the outcomes of the initiatives and the overall impact on the organization. Refine strategies and actions based on feedback and the evolving needs of the organization and its stakeholders.
Implementing the EFQM Model is a strategic decision that requires commitment, leadership, and a willingness to engage in continuous learning and development. By following these steps, organizations can enhance their performance, achieve sustainable excellence, and deliver value to all stakeholders.
What Are the Challenges and Considerations in Adopting the EFQM Model?
Adopting the EFQM Model presents several challenges and considerations for organizations aiming to enhance their performance and operational excellence. Here are some key challenges & considerations to keep in mind:
1. Organizational Culture and Resistance to Change
- Challenge: Implementing the EFQM Model often requires significant cultural shifts and a commitment to continuous improvement, which may encounter resistance from employees accustomed to existing practices.
- Consideration: Organizations must focus on change management strategies, communicate the benefits clearly, and involve employees in the process to foster a culture of excellence and innovation.
2. Resource Allocation
- Challenge: The assessment, planning, and implementation of the EFQM Model demand substantial resources, including time, personnel, and financial investment.
- Consideration: Organizations need to ensure they have allocated adequate resources for the implementation and sustainment of the model, balancing short-term costs with long-term benefits.
3. Training and Development
- Challenge: There may be a lack of understanding or expertise in applying the EFQM Model, necessitating extensive training and development efforts.
- Consideration: Organizations should invest in comprehensive training programs for employees at all levels to ensure they understand the model's principles, criteria, and the importance of their role in its implementation.
4. Measurement and Evaluation
- Challenge: Effectively measuring and evaluating performance against the EFQM criteria can be complex, requiring robust data collection and analysis systems.
- Consideration: Developing clear metrics, utilizing technology fordata management, and conducting regular reviews can help organizations accurately assess their performance and identify areas for improvement.
5. Integration with Existing Systems
- Challenge: Integrating the EFQM Model with existing management systems and processes can be challenging, requiring adjustments to ensure alignment and coherence.
- Consideration: Organizations should carefully map out how the EFQM Model will complement and enhance current systems, making necessary adjustments to ensure seamless integration.
6. Continuous Improvement
- Challenge: The principle of continuous improvement demands ongoing effort and commitment, which can be challenging to maintain over time.
- Consideration: Embedding continuous improvement into the organizational culture and establishing mechanisms for regular feedback and adaptation can help sustain momentum.
7. External Recognition and Benchmarking
- Challenge: Pursuing external recognition through EFQM assessments and awards requires meeting high standards of excellence, which can be demanding for organizations.
- Consideration: Organizations should view external recognition as a long-term goal, focusing first on internal improvements and gradually progressing towards meeting the criteria for external awards.
8. Keeping Pace with Change
- Challenge: The business environment and organizational priorities are constantly evolving, necessitating that the EFQM Model implementation remains relevant and adaptable.
- Consideration: Regular reviews of strategic goals, environmental scanning, and flexibility in approach can ensure that the EFQM Model implementation remains aligned with changing organizational and market dynamics.
Adopting the EFQM Model requires thoughtful planning, commitment across the organization, and a willingness to engage in continuous learning and improvement. Addressing these challenges and considerations thoughtfully can enable organizations to maximize the benefits of the EFQM Model, driving excellence and sustainable success.
What Are the Benefits of Using the EFQM Model for Businesses?
Using the EFQM (European Foundation for Quality Management) Model offers numerous benefits for businesses aiming to improve their performance, competitiveness, and sustainability. Here are the key advantages of implementing the EFQM Model:
1. Comprehensive Performance Assessment
- The EFQM Model provides a holistic framework for assessing organizational performance across all areas, including leadership, strategy, people, partnerships, processes, and results. This comprehensive approach helps identify strengths and areas for improvement.
2. Enhanced Operational Excellence
- By focusing on best practices and continuous improvement, the EFQM Model drives operational excellence. It encourages organizations to innovate and optimize their processes, leading to increased efficiency and effectiveness.
3. Improved Customer Satisfaction
- The model emphasizes the importance of understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations. Implementing its principles can lead to higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy, contributing to business growth.
4. Employee Engagement and Development
- The EFQM Model promotes a people-oriented approach, recognizing the crucial role of employees in achieving excellence. It supports employee development, engagement, and well-being, leading to a motivated and skilled workforce.
5. Strategic Alignment and Execution
- It aids in aligning organizational activities withstrategic goals, ensuring that resources are effectively utilized to achieve desired outcomes. The model facilitates strategic planning and execution, enhancing business agility and resilience.
6. Innovation and Creativity
- Encouraging a culture of innovation, the EFQM Model helps businesses to develop new products, services, and processes. This fosters creativity and innovation, keeping the organization competitive in a rapidly changing market.
7. Sustainability and Social Responsibility
- The model integrates principles of sustainability and corporate social responsibility, urging businesses to consider their environmental, social, and economic impact. This leads to sustainable business practices that benefit society and the environment.
8. Enhanced Reputation and Brand Image
- Achieving high standards of excellence through the EFQM Model can enhance an organization's reputation and brand image. Recognition through awards and certifications can attract customers, partners, and talent.
9. Benchmarking and Continuous Improvement
- The EFQM Model provides a basis for benchmarking against best practices and industry standards. It instills a culture of continuous improvement, driving ongoing enhancements in performance.
10. Risk Management and Resilience
- By fostering a comprehensive understanding of the operational environment and stakeholder needs, the EFQM Model enhances risk management capabilities. It helps organizations anticipate and mitigate risks, enhancing long-term resilience.
Implementing the EFQM Model can transform a business, leading to superior performance, market differentiation, and sustainable success. By adopting its principles, businesses not only enhance their internal processes and outcomes but also contribute positively to their stakeholders and society at large.
Table 1:Key Benefits of Implementing the EFQM Model for Businesses
Benefit | Description |
Comprehensive Performance Assessment | Holistic framework assessing all organizational areas, identifying strengths and areas for improvement. |
Enhanced Operational Excellence | Promotes best practices and continuous improvement for increased efficiency and effectiveness. |
Improved Customer Satisfaction | Emphasizes understanding and meeting customer needs, leading to higher satisfaction and growth. |
Employee Engagement and Development | Recognizes the role of employees in excellence, supporting their development and well-being. |
Strategic Alignment and Execution | Aligns activities with strategic goals, enhancing business agility and resilience. |
Innovation and Creativity | Fosters a culture of innovation, keeping the organization competitive. |
Sustainability and Social Responsibility | Integrates sustainable practices that benefit society and the environment. |
Enhanced Reputation and Brand Image | Achieving excellence enhances reputation, attracting stakeholders. |
Benchmarking and Continuous Improvement | Basis for benchmarking against best practices, driving ongoing performance enhancements. |
Risk Management and Resilience | Enhances risk management, anticipating and mitigating risks for resilience. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the EFQM Model stands as a beacon for organizations striving towards excellence, offering a structured and comprehensive framework to evaluate and enhance their operations. By embracing its principles and integrating its core components, businesses can navigate the challenges of implementation, unlocking a plethora of benefits including improved performance, customer satisfaction, and employee engagement. As the business landscape continues to evolve, the EFQM Model provides the tools necessary for organizations to remain adaptable, competitive, and aligned with their strategic objectives, ultimately paving the way for sustainable success and a lasting impact on society.