- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Business Transformation?
- Types of Business Transformation
- 1- Operational Transformation
- 2- Strategic Transformation
- 3- Technological Transformation
- 4- Cultural Transformation
- What Factors Lead to Business Transformation?
- Market Dynamics
- Technological Advancements
- Regulatory Changes
- Internal Challenges
- Why Is Business Transformation Important?
- Competitive Edge
- Innovation and Agility
- Operational Efficiency
- Customer-Centricity
- Strategic Adaptation
- Step-by-step Process of Business Transformation
- 1- Assessment and Visioning
- 2- Strategic Planning
- 3- Cultural Alignment
- 4- Technology Integration
- 5- Process Optimisation
- 6- Talent Development
- 7- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
- 8- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
- Why Does Business Transformation Fail?
- Lack of Leadership Commitment
- Resistance to Change
- Inadequate Communication
- Insufficient Resources
- Overlooking Cultural Shifts
- Unrealistic Expectations
- Lack of Flexibility and Adaptability
- Poorly Defined Goals and Metrics
- How to Measure Your Business Transformation Strategy’s Success
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Employee Satisfaction and Engagement
- Customer Feedback and Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Financial Performance
- Operational Efficiency Metrics
- Speed of Execution
- Adaptability to Market Changes
- Innovation Metrics
- Customer Retention and Acquisition
- Quality Metrics
- Strategic Goal Achievement
- Data Analytics and Predictive Metrics
- Feedback from Stakeholders
- Benchmarking Against Industry Standards
- Business Transformation in Action: Real-world Examples
- Invoice Process Transformation
- Contract Processes Optimisation
- Supply Chain Overhaul
- Customer Experience Enhancement
- Conclusion
Introduction
Business Transformation is a term that has been circulating the corporate world for quite some time now, but what exactly does it entail? In the dynamic landscape of commerce, where adaptability is key, understanding and implementing business transformation can be the key differentiator between stagnation and flourishing success. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of business transformation, exploring its various types, the driving factors, its paramount importance, the step-by-step process, potential pitfalls, and effective strategies to ensure success.
What Is Business Transformation?
Business Transformation is not a singular event but rather a continuous and purposeful evolution of an organisation to achieve long-term objectives. It involves fundamental changes in the way a business operates, strategises, and delivers value to its customers. This multifaceted process goes beyond incremental adjustments, aiming for a holistic reshaping of the entire business model, culture, and operations.
Types of Business Transformation
When delving into the realm of business transformation, it's essential to recognise that organisations are not uniform entities; they are dynamic, multifaceted entities requiring nuanced approaches. Business transformation is not a one-size-fits-all endeavour but rather a spectrum of strategic shifts, each serving a unique purpose. Let's explore the diverse landscape of business transformation types:
1- Operational Transformation
Operational transformation focuses on the beating heart of an organisation—the internal processes and workflows. It's about meticulously fine-tuning the engine room to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and elevate overall operational effectiveness. From supply chain optimisation to workflow automation, this type of transformation aims to streamline the day-to-day workings of the business, paving the way for increased agility and responsiveness.
2- Strategic Transformation
If operational transformation is about fine-tuning, strategic transformation is about redrawing the entire blueprint. This type involves a fundamental reassessment of the overarching strategy, contemplating significant shifts such as entering new markets, diversifying products or services, or repositioning the business competitively within the industry. It's a bold move that requires a keen understanding of market dynamics, customer needs, and future trends.
3- Technological Transformation
In the digital era, technological transformation is not merely an option; it's a necessity for survival. This type revolves around the adoption and integration of cutting-edge technologies to revolutionise the way business operates. From embracing artificial intelligence and machine learning to implementing robust data analytics, technological transformation is about leveraging the power of innovation to gain a competitive edge and meet evolving customer expectations.
4- Cultural Transformation
Often underestimated but profoundly impactful, cultural transformation is about reshaping the organisational DNA. It involves altering mindsets, values, and behaviours to foster a culture of innovation, collaboration, and adaptability. This type acknowledges that successful business transformation goes beyond processes and technologies—it necessitates a workforce that is not just willing but enthusiastic about embracing change.
Understanding that these types are not mutually exclusive is crucial. Successful business transformation often involves a combination of these approaches, tailored to the specific needs and challenges of the organisation. For example, a strategic shift may demand both operational optimisations and a cultural renaissance to truly take root and thrive.
Moreover, the interplay between these types is dynamic. Technological advancements can catalyse strategic shifts, while strategic transformations may necessitate significant cultural adjustments. Recognising these interconnections is key to crafting a comprehensive and effective business transformation strategy.
In essence, business transformation is an orchestra where these types harmonise to create a symphony of change. Operational excellence provides the steady rhythm, strategic innovation sets the melody, technological prowess creates the harmony, and cultural transformation ensures the entire ensemble moves in unison toward a shared vision of success. By embracing the multifaceted nature of business transformation, organisations can navigate the complex landscape of change with agility and purpose.
What Factors Lead to Business Transformation?
Business transformation is often sparked by a combination of internal and external factors. These may include:
Market Dynamics
Change is the only constant, and this holds particularly true in the ever-evolving marketplace. Shifts in consumer preferences, emerging technologies, or alterations in the competitive landscape can trigger the need for business transformation. Organisations must be attuned to the pulse of the market, ready to pivot their strategies to stay relevant and capitalise on emerging opportunities.
Technological Advancements
The relentless march of technology is both a challenge and an opportunity. Organisations embracing technological advancements gain a competitive edge, while those lagging behind risk obsolescence. The rapid evolution of digital tools, artificial intelligence, and automation can render existing processes outdated, compelling businesses to undergo transformation to harness the full potential of these innovations.
Regulatory Changes
The regulatory landscape is dynamic and can undergo significant changes. New laws, compliance requirements, or industry standards can necessitate adjustments to business operations. Adapting to these changes is not just a matter of legal compliance; it's a strategic imperative to ensure the long-term sustainability and ethical standing of the organisation.
Internal Challenges
Sometimes, the impetus for transformation arises from within. Declining performance, outdated business models, or inefficient processes can act as internal catalysts for change. Recognising and addressing these challenges head-on is crucial for organisations committed to not just surviving but thriving in a competitive landscape.
Each of these factors is not isolated; rather, they often intertwine and amplify each other. For instance, a regulatory change might coincide with a technological advancement, creating a potent catalyst for a strategic transformation. Moreover, these factors are not static—a successful organisation continually monitors its environment, identifying potential catalysts and proactively responding to them.
By understanding and proactively responding to these factors, organisations can position themselves not as passive recipients of change but as proactive architects of their destiny. Business transformation becomes not just a reactive measure but a strategic move to shape a future where the organisation is not merely a participant but a leader in its industry. In essence, these factors are the winds of change that, when harnessed strategically, can propel an organisation toward a future of sustained growth and relevance.
Why Is Business Transformation Important?
Business transformation is not merely a buzzword; it's a strategic imperative for sustained success. Here's why:
Competitive Edge
In an era marked by fierce competition, standing still is akin to moving backward. Business transformation is the engine that propels organisations forward, allowing them to gain and sustain a competitive edge. It's not merely about keeping up with competitors; it's about surpassing them by being more agile, innovative, and responsive to market dynamics.
Innovation and Agility
Innovation is the lifeblood of successful organisations. Business transformation cultivates a culture of innovation, encouraging teams to think creatively, experiment with new ideas, and adapt swiftly to changes. An agile organisation is better equipped to navigate uncertainties, seize opportunities, and stay ahead of industry trends.
Operational Efficiency
At the core of business transformation lies the pursuit of operational excellence. By optimising internal processes and workflows, organisations enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall operational effectiveness. This streamlining not only boosts the bottom line but also frees up resources for strategic initiatives and innovation.
Customer-Centricity
The customer is the focal point of any successful business. Business transformation ensures that organisations remain attuned to evolving customer expectations. By adopting a customer-centric approach, businesses can tailor their products, services, and experiences to meet the changing needs of their target audience, fostering loyalty and long-term relationships.
Strategic Adaptation
The business landscape is dynamic, characterised by shifts in technology, market trends, and consumer behaviours. Business transformation equips organisations to strategically adapt to these changes. Whether it's entering new markets, diversifying offerings, or repositioning within the industry, transformation ensures that the organisation remains not just relevant but influential.
In essence, business transformation is the compass that guides organisations through the complexities of the modern business environment. It's not a luxury but a necessity for survival and growth. The importance of business transformation lies in its ability to future-proof an organisation, preparing it to thrive in an environment where change is constant, and adaptability is paramount.
Moreover, it's not a one-time event but an ongoing process. The ability to continually transform, innovate, and stay ahead of the curve is what sets apart organisations that merely survive from those that truly thrive. Business transformation is not just about changing for the sake of change; it's about evolving with purpose, shaping a future where the organisation is not just a participant but a trailblazer in its industry.
Step-by-step Process of Business Transformation
Business transformation is a journey, not a destination. To navigate this intricate process successfully, organisations need a well-defined roadmap that guides them through each phase of change. Let's delve into the step-by-step process of business transformation, providing insights into how organisations can strategically chart their course toward a more resilient and innovative future:
1- Assessment and Visioning
The journey begins with a comprehensive assessment of the current state of the organisation. This involves scrutinising existing processes, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and gauging the internal and external factors influencing the business. Simultaneously, leadership collaborates to define a clear and compelling vision for the future. This vision serves as the guiding star, aligning the entire organisation toward a common objective.
2- Strategic Planning
With a clear vision in place, the next step is strategic planning. Organisations articulate specific goals, timelines, and success metrics. This involves delineating the strategies and initiatives required to achieve the envisioned transformation. The strategic plan acts as a roadmap, providing a structured framework for implementation and ensuring that every step aligns with the overarching vision.
3- Cultural Alignment
Business transformation is not just about changing processes; it's about fostering a culture that embraces change and innovation. Cultural alignment involves communicating the vision, values, and goals of the transformation, engaging employees at all levels, and cultivating a mindset that sees challenges as opportunities for growth. It's about creating a shared sense of purpose that propels the entire organisation forward.
In a recent analysis by McKinsey, data from 60 organisations, each at least two years into their transformations, revealed a notable correlation. Transformations wherein a minimum of 7 percent of employees take ownership of the process are twice as likely to yield superior total shareholder returns. Despite the seemingly modest percentage, even within a medium-sized organisation, this translates to the involvement of hundreds of employees.
4- Technology Integration
In the digital age, technology is a catalyst for transformation. This step involves identifying and integrating cutting-edge technologies that support the strategic goals. Whether it's adopting new software, upgrading systems, or implementing innovative solutions, technology integration is pivotal for enhancing efficiency, improving customer experiences, and staying ahead of the competition.
5- Process Optimisation
A critical aspect of business transformation is the optimisation of internal processes. This involves a thorough review of existing workflows, identifying bottlenecks, and streamlining operations to improve efficiency. The goal is to create a more agile and responsive organisational structure that can adapt swiftly to changing market conditions.
6- Talent Development
Transformation is not just about technology; it's about people. Organisations need to invest in developing the skills and capabilities of their workforce to ensure they are equipped for the challenges of the transformed organisation. Training programs, mentorship initiatives, and a focus on continuous learning are integral to this step.
7- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Effective communication is the glue that holds the transformation process together. Organisations must communicate transparently about the changes, the reasons behind them, and the expected outcomes. Engaging with and involving all stakeholders—employees, customers, and partners—creates a sense of ownership and support for the transformation journey.
8- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
The journey doesn't end with the implementation of changes. Continuous monitoring is crucial to assess progress against set goals. Regular feedback loops, performance metrics, and a commitment to adapt strategies based on evolving circumstances ensure that the organisation remains agile and responsive throughout the transformation process.
This step-by-step process is not linear; rather, it forms a dynamic and iterative cycle. Successful business transformation requires an ongoing commitment to improvement, a readiness to adapt, and a culture that embraces change. By following this comprehensive process, organisations can navigate the complexities of transformation with clarity and purpose, ensuring that each step contributes to the realisation of a more resilient and innovative future.
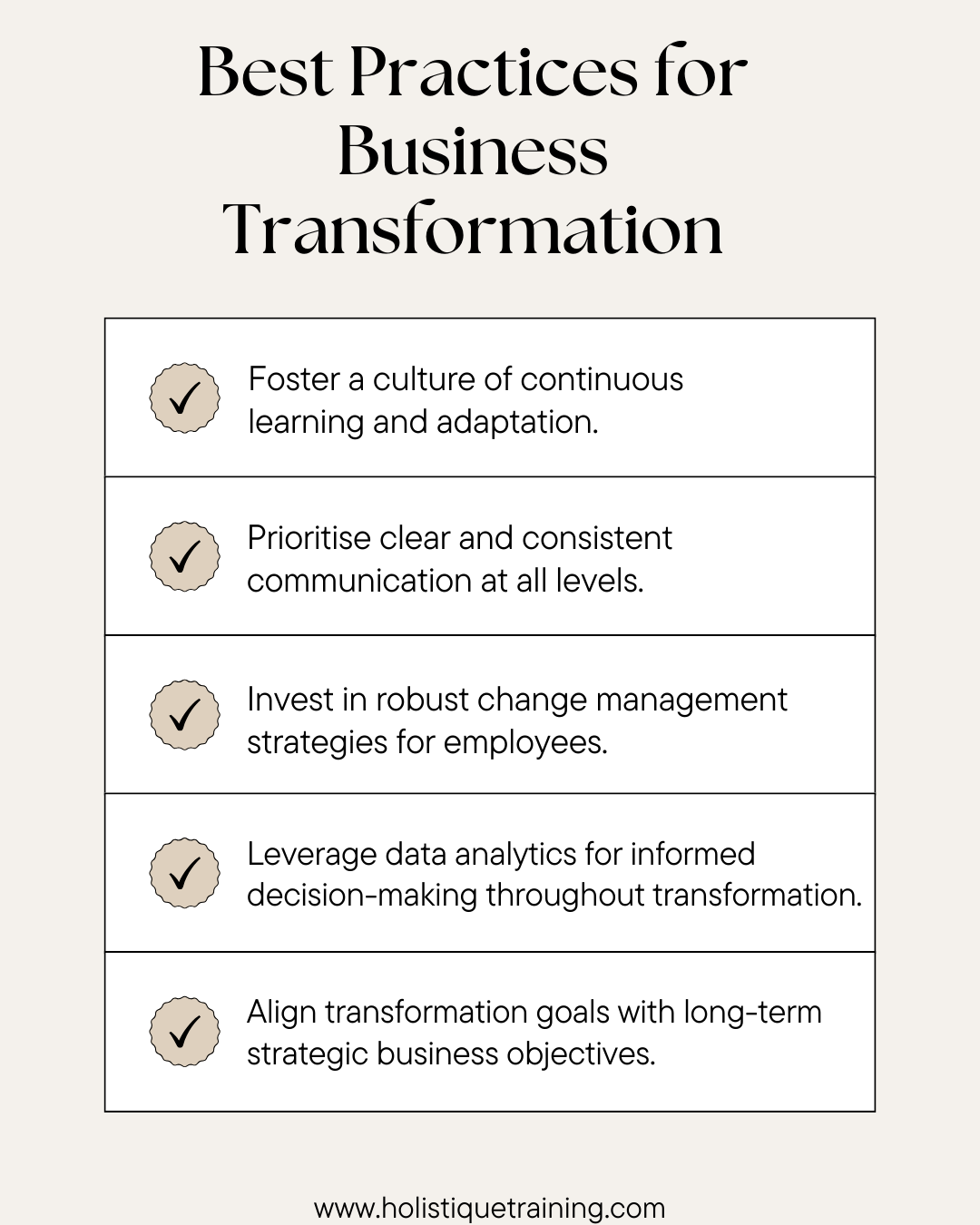
Why Does Business Transformation Fail?
While the promise of business transformation is alluring, the reality is that not all journeys reach the desired destination. Understanding the potential pitfalls and challenges that put business transformation at risk is crucial for organisations aiming to navigate this complex process successfully. Here are some key reasons why business transformation initiatives may falter:
Lack of Leadership Commitment
Unwavering commitment from leadership is at the forefront of successful transformations. The entire initiative is at risk when leaders are not fully invested in the process, whether due to competing priorities, scepticism, or insufficient understanding. Without strong and consistent leadership, the organisation may lack the necessary direction, resources, and motivation to see the transformation through.
Resistance to Change
Change is inherently unsettling, and organisations are composed of individuals with diverse attitudes toward it. Employee resistance, often rooted in fear of the unknown, job insecurities, or simply discomfort with change, can sabotage even the most well-designed transformation plans. Ignoring or underestimating this resistance is a recipe for failure.
Inadequate Communication
Communication is the lifeblood of successful transformation. When communication is insufficient, unclear, or inconsistent, it creates confusion and uncertainty. Employees and stakeholders need a clear understanding of the transformation vision, goals, and their role. Failing to establish effective communication channels puts the entire initiative at risk.
Insufficient Resources
Business transformation demands resources—financial, human, and technological. Inadequate funding, manpower, or technology can hinder the implementation of transformation initiatives, leading to suboptimal results. Organisations must realistically assess and allocate the resources required for successful execution.
Overlooking Cultural Shifts
Business transformation is not only about changing structures and processes; it's also about cultural shifts. Neglecting the cultural aspect, which includes values, behaviours, and attitudes, can result in a misalignment that hampers the transformation's success. A culture resistant to change or incompatible with the transformation vision poses a significant risk.
Unrealistic Expectations
Setting unrealistic expectations, whether in terms of timelines, outcomes, or the level of disruption involved, can set the transformation up for failure. Transformation is a gradual process that requires patience and persistence. Overestimating the speed of results or underestimating the challenges can lead to disappointment and a loss of momentum.
Lack of Flexibility and Adaptability
The business landscape is dynamic, and transformation plans must be flexible and adaptable. Failing to recognise the need for adjustments based on feedback, changing market conditions, or unforeseen challenges can lead to a rigid approach that is ill-suited to the environment's realities.
Poorly Defined Goals and Metrics
Clear and measurable goals are the foundation of successful transformation. When goals are vague, undefined, or lack clear metrics for success, it becomes challenging to gauge progress and adjust strategies accordingly. A lack of clarity in the transformation objectives can result in a sense of aimlessness and a loss of organisational focus.
Understanding these risks is the first step towards mitigating them. Successful business transformation requires a holistic approach that addresses structural and process changes and the human and cultural dimensions. By proactively managing these challenges, organisations can enhance their resilience and increase the likelihood of a successful transformation journey.
How to Measure Your Business Transformation Strategy’s Success
A critical aspect of business process transformation is the ability to measure success accurately. Establishing clear metrics provides organisations with valuable insights into the effectiveness of their strategies, identifies areas for improvement, and ensures that the transformation aligns with overarching business goals. Here are key metrics and strategies for measuring the success of your business process transformation:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establishing KPIs is fundamental to tracking the success of your transformation strategy. These should be specific, measurable, and directly tied to the goals outlined in your transformation roadmap. Examples include financial metrics (revenue growth, cost reduction), operational efficiency indicators, and customer satisfaction scores.
KPI | Description |
Financial Impact | Measure revenue growth, cost savings, and ROI. |
Operational Efficiency | Evaluate cycle time, process lead time, efficiency gains. |
Customer Satisfaction | Assess customer feedback, NPS, and retention rates. |
Employee Engagement | Monitor employee satisfaction, involvement, and adaptation. |
Innovation Metrics | Track new ideas, successful innovations, and technology integration. |
Table 1: KPIs of a Business Transformation Strategy
Employee Satisfaction and Engagement
Engaged and satisfied employees are often more productive and adaptable to change. Regularly surveying employees and analysing their feedback can provide valuable insights into their satisfaction levels, their perception of the transformation process, and any potential areas of concern. High employee engagement is often indicative of successful transformation.
Customer Feedback and Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The ultimate success of any transformation lies in its impact on customers. Regularly solicit and analyse customer feedback to gauge satisfaction levels. The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a particularly useful metric, indicating the likelihood of customers recommending your products or services. A rising NPS can be a strong indicator of a successful transformation strategy.
Financial Performance
Transformation initiatives should ultimately contribute to the organisation's financial health. Evaluate financial metrics such as revenue growth, cost savings, and return on investment (ROI). Ensure that the financial impact aligns with the goals outlined in the strategic planning phase of your transformation.
Operational Efficiency Metrics
One of the primary objectives of business process transformation is to enhance operational efficiency. Metrics such as cycle time, process lead time, and resource utilisation can provide insights into the efficiency gains achieved through the transformation. A reduction in these metrics signifies improved operational effectiveness.
Speed of Execution
Assess the speed and agility with which the organisation can implement and adapt to changes. This includes evaluating the time taken to implement new processes, launch products, or respond to market shifts. A faster execution of initiatives can indicate the successful integration of transformation into the organisation's DNA.
Adaptability to Market Changes
The ability to adapt to evolving market conditions is a critical success factor. Regularly monitor the organisation's responsiveness to market changes, including shifts in customer preferences, industry trends, and competitive dynamics. Successful transformation enables the organisation to navigate these changes effectively.
Innovation Metrics
Measure the organisation's commitment to innovation. This includes tracking the number of new ideas generated, successful implementations of innovative solutions, and integrating emerging technologies. Innovation metrics provide a qualitative assessment of the organisation's ability to embrace change and stay ahead of the curve.
Customer Retention and Acquisition
Assess the impact of transformation on customer retention and acquisition. A successful transformation should increase customer retention rates and attract new customers. Track customer acquisition costs, customer churn rates, and customer lifetime value to gauge the effectiveness of your transformation efforts.
Quality Metrics
Evaluate the quality of products or services delivered due to the transformation. This could include metrics related to defect rates, customer complaints, and adherence to quality standards. Improved quality is often a tangible outcome of successful business process transformation.
Strategic Goal Achievement
Regularly revisit the strategic goals outlined in the transformation roadmap. Evaluate the progress made toward achieving these goals and assess whether the organisation is on track. Adjust goals if necessary, ensuring they remain aligned with the evolving needs of the business and the market.
Data Analytics and Predictive Metrics
Leverage advanced data analytics to gain predictive insights into future trends and potential challenges. Predictive metrics can help the organisation anticipate and proactively address issues before they impact the success of the transformation strategy.
Feedback from Stakeholders
Gather feedback from key stakeholders, including customers, employees, and partners. Their perceptions and experiences provide qualitative insights into the transformation's success. Address any concerns or suggestions to enhance the overall impact.
Benchmarking Against Industry Standards
Compare your organisation's performance and transformation outcomes against industry benchmarks. Understanding how your organisation stacks up against industry standards can highlight areas for improvement and help set realistic performance expectations.
Remember that measuring the success of business process transformation is an ongoing process. Regularly revisit and adjust your metrics to ensure they remain relevant as the organisation evolves. A holistic approach, combining quantitative and qualitative metrics, provides a comprehensive view of the transformation's impact and contributes to sustained success in the long run.
Business Transformation in Action: Real-world Examples
To provide concrete insights into the effectiveness of Business Process Transformation, let's examine four noteworthy examples where organisations successfully navigated change to achieve significant improvements:
Invoice Process Transformation
Many organisations grapple with cumbersome and time-consuming invoice processing. In a survey of businesses that handle at least 350,000 invoices each year, as cited by kissflow, mistakes resulted in up to 32 per cent of late payments from customers and around 36 per cent of calls from suppliers. A good example of how a company could handle this is by leveraging automation tools to streamline its invoice approval workflow. Implementing intelligent systems reduced processing times, minimised errors, and improved cash flow management. This transformation not only increased efficiency but also enhanced supplier relationships.
Contract Processes Optimisation
Legal and contract management processes can be labyrinthine, causing delays and potential risks. A corporation undertook a transformation initiative by implementing a centralised contract management system. This accelerated contract lifecycles, improved compliance, and reduced legal risks. The result was a more agile and legally sound organisation.
Supply Chain Overhaul
A manufacturing company initiated a comprehensive supply chain transformation. They gained real-time visibility into their supply chain by integrating advanced analytics and IoT devices. This allowed for proactive decision-making, reduced lead times, minimised stockouts, and optimised inventory levels. The transformation significantly enhanced the company's overall supply chain resilience.
Customer Experience Enhancement
For businesses heavily reliant on customer interactions, a transformation focused on enhancing the customer experience can be transformative. A retail brand employed data analytics and personalised marketing strategies to better understand customer preferences. By tailoring products and services, they increased customer satisfaction and witnessed a notable boost in customer loyalty and repeat business.
These examples illustrate that Business Process Transformation is not a one-size-fits-all endeavour. Tailoring strategies to address specific pain points, whether in invoicing, contracts, supply chain, or customer experience, can lead to tangible improvements, demonstrating the versatility and impact of strategic transformations in various business domains.
Conclusion
In conclusion, business transformation is a dynamic and essential process that requires strategic vision, leadership commitment, and the active involvement of every stakeholder. By understanding the types, factors, and importance of business transformation, and by following a well-defined step-by-step process while being mindful of potential pitfalls, organisations can navigate the journey towards success. With the right mindset, effective communication, and a commitment to continuous improvement, businesses can survive and thrive in an ever-evolving marketplace.