- Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction: A New Era for Contract Management
- 2. Understanding the Contract Management Lifecycle (CMLC)
- a. Contract Creation
- b. Negotiation
- c. Approval and Execution
- d. Performance Monitoring
- e. Renewal or Termination
- 3. What Is Generative AI and How Does It Work?
- 4. Contract Drafting and Review – AI as a Legal Assistant
- 5. Negotiation Support and Scenario Simulation
- 6. Risk Analysis and Compliance Monitoring
- 7. Accelerating Approval Workflows with Automation
- 8. Post-Signature Monitoring and Renewal Alerts
- 9. Security, Ethics, and Trust in AI-driven Contracting
- 10. Conclusion
1. Introduction: A New Era for Contract Management
Contract Management has long been a fundamental aspect of organisational success. It encompasses the creation, negotiation, execution, monitoring, and renewal of agreements that underpin commercial and operational relationships. Traditionally, this process has been manual, time-consuming, and prone to human error. As businesses grow in complexity and volume, managing contracts efficiently becomes increasingly challenging.
In the digital era, automation has played a significant role in streamlining administrative functions. However, a new wave of innovation is reshaping contract management altogether: Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI). Unlike earlier forms of AI that rely on predefined rules, Generative AI uses deep learning and natural language processing to understand context, generate human-like content, and make informed decisions. This evolution allows for smarter, faster, and more reliable contract handling, transforming what was once a burdensome task into a strategic asset.
In this article, we will discuss how Generative AI is revolutionising each phase of the contract management lifecycle. We will explore its applications in drafting, negotiation, compliance, and beyond, while highlighting ethical considerations and future developments. This exploration will offer insight into how organisations can harness AI tools to optimise legal and commercial operations.
2. Understanding the Contract Management Lifecycle (CMLC)
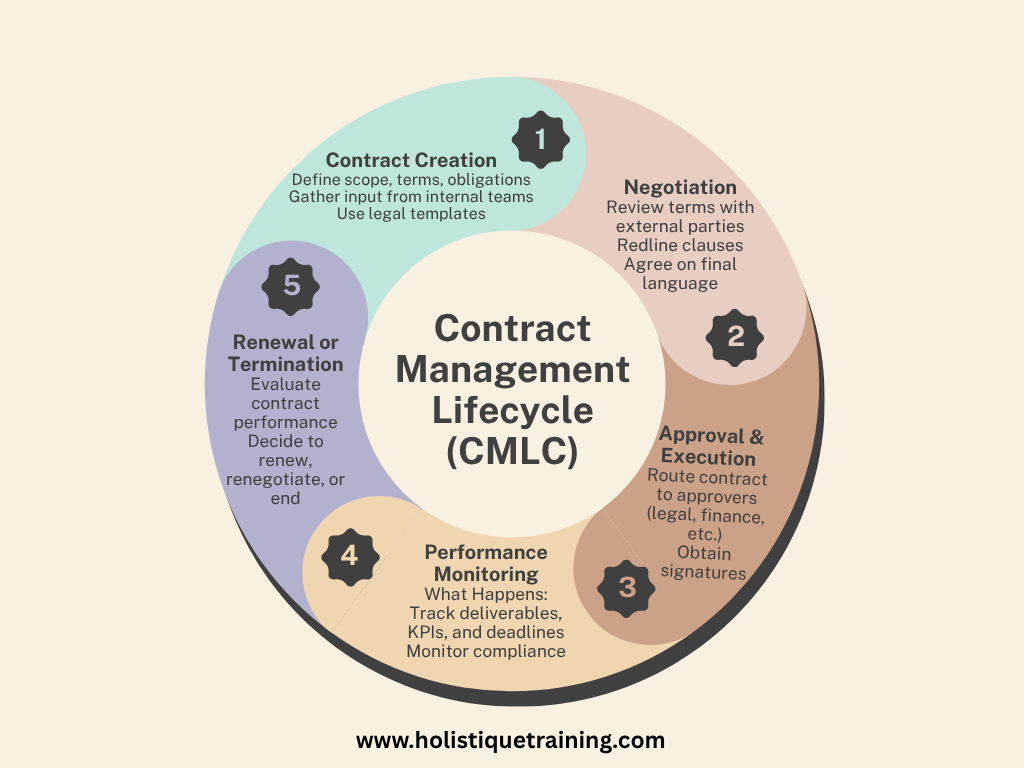
The Contract Management Lifecycle (CMLC) is the comprehensive process that governs how contracts are created, executed, and maintained throughout their duration. It includes multiple structured phases, each with specific objectives, responsibilities, and challenges. Understanding this lifecycle is essential for organisations to pinpoint inefficiencies, reduce risks, and identify areas where technologies like Generative AI can deliver measurable value.
a. Contract Creation
This is the foundational stage of the lifecycle, where the contract’s purpose, scope, terms, and conditions are initially drafted. It involves collecting relevant information from internal stakeholders—such as finance, legal, procurement, or sales—and aligning them into a cohesive document. Legal teams often rely on standardised templates, but manual input remains common. Ensuring clause relevance, legal compliance, and consistent terminology can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Missing details or unclear phrasing at this stage can lead to significant issues later in the lifecycle.
b. Negotiation
Once a draft is prepared, it enters the negotiation phase. This involves back-and-forth communication with external parties—clients, vendors, or partners—to reach mutually acceptable terms. This step often includes revisions to pricing, service levels, timelines, confidentiality clauses, and liability terms. Misunderstandings can arise from ambiguous language, cultural or legal differences, or lack of version control. Delays during negotiation are common, particularly when parties struggle to reach alignment or when redlining processes are conducted manually via email.
c. Approval and Execution
After negotiation, the contract needs formal approval from designated stakeholders. This could involve legal, compliance, finance, or executive leadership. In many organisations, approval workflows are not clearly defined, leading to long cycles and lost productivity. Once approved, contracts must be executed—typically through physical signatures or digital signature platforms. Without proper workflow automation, this phase can create bottlenecks and documentation inconsistencies.
d. Performance Monitoring
Following execution, contracts move into an active phase where the agreed-upon terms must be fulfilled. Organisations are responsible for tracking deliverables, performance milestones, deadlines, and payments. This monitoring is often managed through spreadsheets or isolated systems, increasing the risk of oversight. Failure to track obligations may result in non-compliance, financial penalties, or damaged relationships.
e. Renewal or Termination
As contracts near expiration, organisations must assess their effectiveness and determine next steps. Should the contract be renewed under the same terms, renegotiated, or terminated? Without centralised alerts or reporting tools, key deadlines may be missed—leading to automatic renewals or the loss of renegotiation leverage. Evaluating supplier performance and extracting lessons learned are also critical in this stage.
In each of these phases, Generative AI presents opportunities to automate repetitive tasks, ensure consistency, and support decision-making—helping organisations transform contract management from a reactive function into a strategic advantage.
3. What Is Generative AI and How Does It Work?
Generative AI refers to systems capable of creating content—text, images, code, or even audio—based on prompts and learned patterns from vast datasets. In the context of contract management, it enables automation of complex language tasks, such as drafting clauses or analysing legal language.
The core of Generative AI lies in transformer models like OpenAI's GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), trained on billions of documents. These models use deep neural networks to predict the next word in a sequence, generating content that mimics human writing with contextual coherence.
Unlike rule-based automation, Generative AI adapts to nuanced changes in input, learns from feedback, and improves over time. It can read and summarise lengthy contracts, flag risks, or suggest changes in tone and structure.
A study by McKinsey (2023) found that legal departments using AI tools for contract review reduced turnaround time by up to 60%, and increased accuracy in risk detection by 25%.
Feature | Traditional Tools | Generative AI |
Adaptability | Low | High |
Human-like Output | Limited | Natural Language Output |
Legal Context Grasp | Minimal | Advanced Contextualisation |
Drafting Capability | Template-based | Dynamic Clause Generation |
This power makes Generative AI an ideal assistant in managing complex contract workflows.
4. Contract Drafting and Review – AI as a Legal Assistant
Drafting and reviewing contracts demand precision, legal expertise, and attention to detail. Generative AI transforms this process by acting as a virtual legal assistant.
It can generate standard contract templates tailored to industry or jurisdictional norms. By inputting basic details such as the parties involved and contract type, the AI can populate relevant clauses and ensure compliance with local laws.
During review, the system analyses existing documents to identify vague language, missing clauses, or high-risk phrases. It compares new contracts against historical data to ensure consistency and suggest improvements.
This application is especially valuable for high-volume contracting environments, such as procurement, sales, or HR.
Task | Traditional Approach | Generative AI Support |
Clause Generation | Manual drafting | Automated with context awareness |
Risk Flagging | Legal team review | Instant AI-driven alerts |
Language Consistency | Variable by drafter | Standardised across templates |
Legal Benchmarking | Time-consuming research | Integrated comparison models |
By streamlining drafting and review, Generative AI reduces legal costs and shortens contract cycles.
5. Negotiation Support and Scenario Simulation
Negotiating contract terms is a critical phase that often determines the success of a deal. Generative AI enhances this process by simulating potential negotiation outcomes and offering optimal wording suggestions.
AI tools can analyse counterparties' preferences based on previous agreements, industry standards, or real-time data. They simulate best- and worst-case scenarios, helping users prepare better offers or counteroffers.
For example, when negotiating service level agreements (SLAs), the AI can suggest acceptable thresholds, highlight compromise zones, and evaluate historical concessions.
Additionally, generative AI ensures that tone and phrasing remain professional and consistent across iterations, which is essential for international negotiations.
This predictive support equips negotiators with data-driven insights, improving confidence and reducing time-to-agreement.
6. Risk Analysis and Compliance Monitoring
Managing legal and operational risks in contracts requires vigilance. Generative AI helps identify potential pitfalls and ensures compliance across evolving regulations.
AI models can scan contracts for indemnity clauses, non-compete terms, or governing law selections that may pose liabilities. It flags inconsistencies, outdated legal references, or conflicting terms.
Furthermore, Gen AI can cross-reference internal policies and external legal requirements to verify alignment. This is particularly beneficial in regulated sectors like healthcare, finance, or international trade.
The system also adapts as regulations change, updating compliance benchmarks and alerting legal teams proactively.
By automating these checks, businesses gain greater control over risk exposure and maintain regulatory readiness.
7. Accelerating Approval Workflows with Automation
In many organisations, contract approvals require multiple sign-offs—legal, finance, compliance, or operations. Delays often arise due to lack of clarity on who needs to approve what and when.
Generative AI can analyse the contract content to identify responsible approvers and automatically route documents to the appropriate stakeholders. It generates summaries for quick decision-making and tracks progress in real time.
A report by Deloitte (2022) noted that AI-powered contract lifecycle platforms reduced approval delays by up to 40%, freeing staff to focus on strategic priorities.
AI also enables integrations with e-signature tools and ERP systems, ensuring a seamless flow from approval to execution.
This automation significantly reduces bottlenecks, improves accountability, and enhances collaboration across departments.
8. Post-Signature Monitoring and Renewal Alerts
Once a contract is signed, ongoing performance monitoring is crucial to ensure deliverables, milestones, and obligations are met. Generative AI plays a key role in tracking and flagging these elements.
It parses the contract to identify deadlines, payment terms, audit rights, and renewal dates. AI tools then set up alerts and dashboards that notify stakeholders well in advance.
Moreover, AI can link performance data with contract terms to assess vendor or partner compliance. This helps in enforcing terms or renegotiating from a position of data-backed insight.
The automation of reminders and performance tracking leads to better lifecycle management, preventing value leakage or missed opportunities.
9. Security, Ethics, and Trust in AI-driven Contracting
While Generative AI offers transformative benefits, its implementation raises ethical and security concerns. Sensitive legal data must be protected, and transparency in AI decision-making is critical.
One concern is bias in language generation—AI may inherit biases from training data, leading to skewed contract terms. Similarly, hallucinations (fabricated facts) can result in incorrect clauses.
Organisations must ensure data encryption, access control, and adherence to data protection laws like GDPR.
Concern | Risk Example | Mitigation Strategy |
Data Privacy | Exposure of client-sensitive data | Encryption, on-premise deployment |
AI Hallucination | Inserting non-existent obligations | Human review and validation layers |
Algorithmic Bias | Unfair clauses influenced by datasets | Bias audits and diverse training data |
Lack of Transparency | Decisions without explainability | XAI (Explainable AI) tools |
Balancing innovation with accountability is vital to building trust in AI-driven legal processes.
10. Conclusion
Looking ahead, Generative AI will lead to self-evolving contract ecosystems—platforms that not only manage contracts but learn from each transaction to improve future workflows.
AI will increasingly integrate with blockchain for secure and transparent contract records, and with IoT for real-time performance data. Smart contracts that automatically execute based on external triggers will become more prevalent.
As AI systems become more sophisticated, they will support multilingual negotiations, cross-border compliance, and instant regulatory updates.
To stay competitive, organisations must invest in upskilling legal teams and adopting AI-driven tools. Platforms like Holistique Training offer specialised courses in AI-powered legal operations and contract lifecycle management.
Enrolling in such courses empowers professionals to harness AI's full potential while navigating its complexities ethically and strategically.