- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Are Digital Twins?
- The Foundation of Digital Twins
- The Evolution of Digital Twins
- Types of Digital Twins
- Real-World Applications of Digital Twins
- How Do Digital Twins Impact Decision-Making?
- 1. Enhanced Visualization
- 2. Predictive Maintenance
- 3. Scenario Simulation
- 4. Improved Product Development
- 5. Data-Driven Insights
- 6. Enhanced Collaboration and Cross-Functional Decision-Making
- 7. Strategic Planning and Forecasting
- Challenges of Digital Twins and How to Overcome Them
- 1. Data Integration
- 2. High Initial Costs
- 3. Skills Gap
- 4. Data Security and Privacy
- 5. Change Management
- Conclusion
- How Can Businesses Implement Digital Twins?
- 1. Define Objectives
- 2. Assess Current Infrastructure
- 3. Choose the Right Technology
- 4. Develop a Data Strategy
- 5. Start Small and Scale Up
- 6. Foster Collaboration
- 7. Monitor and Optimize
- The Future of Digital Twins
- 1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- 2. Expansion into New Industries
- 3. Enhanced Interoperability
- 4. Focus on Sustainability
- 5. Increased Use of Augmented and Virtual Reality
- Conclusion
Introduction
Digital twins represent one of the most transformative concepts in the realm of technology and data management. This blog post delves into the intricacies of digital twins, exploring their definition, impact on decision-making, challenges faced during implementation, and the future they hold for businesses across various sectors. By the end of this discussion, readers will gain a thorough understanding of digital twins and how they can leverage this technology for enhanced operational efficiency and strategic growth.
What Are Digital Twins?
Digital twins are sophisticated virtual models that replicate physical entities, systems, or processes in real time. This concept is rooted in the integration of physical and digital worlds, allowing organizations to monitor, analyze, and optimize their operations more effectively. While the term "digital twin" may sound futuristic, it is grounded in established technologies that have evolved over the years.
The Foundation of Digital Twins
At their core, digital twins consist of three primary components:
Physical Entity:
This is the actual object or system being represented. It could be anything from a simple piece of machinery, like a pump, to complex infrastructures, such as entire manufacturing plants or smart cities. The physical entity is equipped with sensors and IoT devices that collect data about its performance, condition, and environment.
Virtual Model:
The virtual model is a digital representation of the physical entity. It captures the physical characteristics, behaviors, and dynamics of the object or system. This model is not static; it evolves over time as new data is integrated. Advanced modeling techniques, including 3D modeling and simulation, are often employed to create accurate and detailed representations.
Data Connection:
A crucial aspect of digital twins is the continuous flow of data between the physical and digital realms. This data connection allows for real-time updates, ensuring that the virtual model reflects the current state of the physical entity. Data is typically gathered through sensors, IoT devices, and other monitoring systems, providing insights into performance metrics, environmental conditions, and operational parameters.
The Evolution of Digital Twins
The concept of digital twins has its roots in the field of product lifecycle management (PLM) and has evolved significantly since its inception. Originally, digital twins were primarily used in manufacturing to improve product design and operational efficiency. However, advancements in technology, such as the proliferation of IoT devices, cloud computing, and big data analytics, have expanded the applicability of digital twins across various industries.
Today, digital twins are utilized in sectors such as healthcare, where they can simulate patient outcomes and treatment plans; agriculture, where they optimize crop yields and resource management; and urban planning, where they model traffic patterns and infrastructure development. This versatility underscores the potential of digital twins to drive innovation and improve decision-making in diverse contexts.
Types of Digital Twins
Digital twins can be categorized into several types, each serving different purposes:
- Component Twins: These represent individual components or assets, such as a valve or a motor. They focus on monitoring the performance and health of specific parts.
- Asset Twins: Asset twins encompass a collection of components that work together, such as a machine or a production line. They provide insights into the overall performance and efficiency of the asset.
- System Twins: These represent entire systems, such as a manufacturing facility or a transportation network. System twins analyze interactions between various assets and components, allowing for comprehensive optimization.
- Process Twins: Process twins model entire processes, such as supply chain operations or manufacturing workflows. They help organizations understand and enhance the efficiency of complex processes.
- Environment Twins: These twins simulate environmental factors that influence operations, such as weather conditions or market dynamics. They are particularly useful for industries like agriculture and logistics, where external variables play a critical role.
Real-World Applications of Digital Twins
The practical applications of digital twins are vast and varied. For instance, in the manufacturing sector, companies use digital twins to optimize production lines by simulating different configurations and identifying bottlenecks. In healthcare, digital twins of patients can be created to personalize treatment plans and predict health outcomes based on individual characteristics and medical history.
In the realm of smart cities, digital twins can model urban environments, allowing city planners to simulate traffic flows, energy consumption, and emergency response scenarios. This capability enables more informed decision-making regarding infrastructure development and resource allocation.
In short, digital twins represent a transformative approach to understanding and managing physical entities and systems. By creating virtual replicas that integrate real-time data, organizations can gain unprecedented insights into their operations, leading to improved efficiency, enhanced decision-making, and innovative solutions. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications and benefits of digital twins will only expand, making them an essential tool for organizations aiming to thrive in a data-driven world.
How Do Digital Twins Impact Decision-Making?
The integration of digital twins into business operations significantly enhances decision-making processes, which in turn boosts revenue. In fact,Gartner projects that by 2027, more than 40% of large companies globally will incorporate Digital Twin technology into their projects to boost revenue. Also, according to a 2025 Hexagonsurvey, 92% of companies that implement digital twins experience returns exceeding 10%, with more than half reporting a return on investment of at least 20%. By providing real-time insights and predictive analytics, digital twins empower organizations to make informed choices that drive efficiency and innovation. Here are several ways digital twins impact decision-making:
1. Enhanced Visualization
Digital twins offer a dynamic visual representation of complex systems and processes. This visualization transforms abstract data into intuitive graphics, making it easier for stakeholders to understand intricate operations.
- Improved Communication: Visual models facilitate bettercommunication among teams, breaking down silos and fostering collaboration. When everyone can see the same representation of a process or system, it enhances discussions and aligns objectives.
- Identifying Patterns: By visualizing data trends and patterns over time, decision-makers can quickly identify anomalies or areas requiring attention. This capability allows for proactive problem-solving rather than reactive measures.
2. Predictive Maintenance
One of the most significant advantages of digital twins is their ability to predict equipment failures and maintenance needs. It’s no surprise that The Global Digital Twin Market is expected to grow to USD 149.81 billion by 2030, according toMarkets and Markets.
- Data-Driven Insights: By analyzing data collected from sensors monitoring machinery, digital twins can forecast when a piece of equipment is likely to fail. This predictive capability enables organizations to schedule maintenance before issues arise, reducing unplanned downtime and associated costs.
- Resource Optimization: Predictive maintenance allows businesses to optimize their maintenance schedules and allocate resources more efficiently. Rather than adhering to a fixed maintenance schedule, organizations can perform maintenance based on actual equipment condition and performance data.
3. Scenario Simulation
Digital twins enable organizations to simulate various scenarios and assess the potential impacts of different decisions.
- What-If Analysis: Decision-makers can use digital twins to conduct what-if analyses, exploring how changes in one part of a system might affect the whole. For example, manufacturers can simulate the impact of altering production schedules or introducing new materials without disrupting actual operations.
- Risk Assessment: By simulating potential risks and their consequences, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate those risks. This proactive approach enhances resilience and prepares businesses for unexpected events.
4. Improved Product Development
In product design and development, digital twins play a crucial role in streamlining the process.
- Rapid Prototyping: Digital twins allow engineers to test and iterate on designs virtually, reducing the need for physical prototypes. This capability accelerates the development cycle, enabling faster time-to-market while minimizing costs associated with material and production.
- User-Centric Design: By using data from digital twins to understand how users interact with a product, organizations can make informed design choices that enhance user experience and satisfaction. This user-centric approach leads to better products that meet market demands.
5. Data-Driven Insights
Digital twins generate vast amounts of data that organizations can leverage for strategic decision-making.
- Trend Analysis: By analyzing historical and real-time data, businesses can identify trends and patterns that inform strategic decisions. For example, retailers can use data from digital twins to optimize inventory levels based on customer purchasing behavior.
- Performance Benchmarking: Digital twins enable organizations to benchmark their performance against industry standards or competitors. This insight can drive continuous improvement efforts and help organizations maintain a competitive edge.
Table: Metrics to measure the effectiveness of digital twins
6. Enhanced Collaboration and Cross-Functional Decision-Making
Digital twins foster collaboration across departments by providing a shared platform for data and insights.
- Cross-Departmental Insights: When different teams—such as engineering, operations, and marketing—access the same digital twin, they can collaborate more effectively. This cross-functional approach ensures that all perspectives are considered in decision-making.
- Real-Time Updates: As digital twins provide real-time data, teams can make timely decisions based on the most current information. This agility is crucial in fast-paced environments where conditions can change rapidly.
7. Strategic Planning and Forecasting
Digital twins aid in long-term strategic planning by providing insights into future trends and scenarios.
- Market Forecasting: By analyzing data from digital twins, organizations can forecast market trends and customer demands. This foresight enables businesses to align their strategies with anticipated changes, ensuring they remain competitive.
- Resource Allocation: Digital twins help organizations optimize resource allocation by simulating different operational scenarios. Decision-makers can evaluate how best to utilize resources to achieve desired outcomes, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
The impact of digital twins on decision-making is profound and multifaceted. By enhancing visualization, enabling predictive maintenance, facilitating scenario simulations, and providing data-driven insights, digital twins empower organizations to make informed, strategic choices. As businesses continue to embrace this technology, the ability to leverage real-time data and predictive analytics will become increasingly essential for thriving in today’s dynamic and competitive landscape. Digital twins not only enhance operational efficiency but also foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, positioning organizations for long-term success.
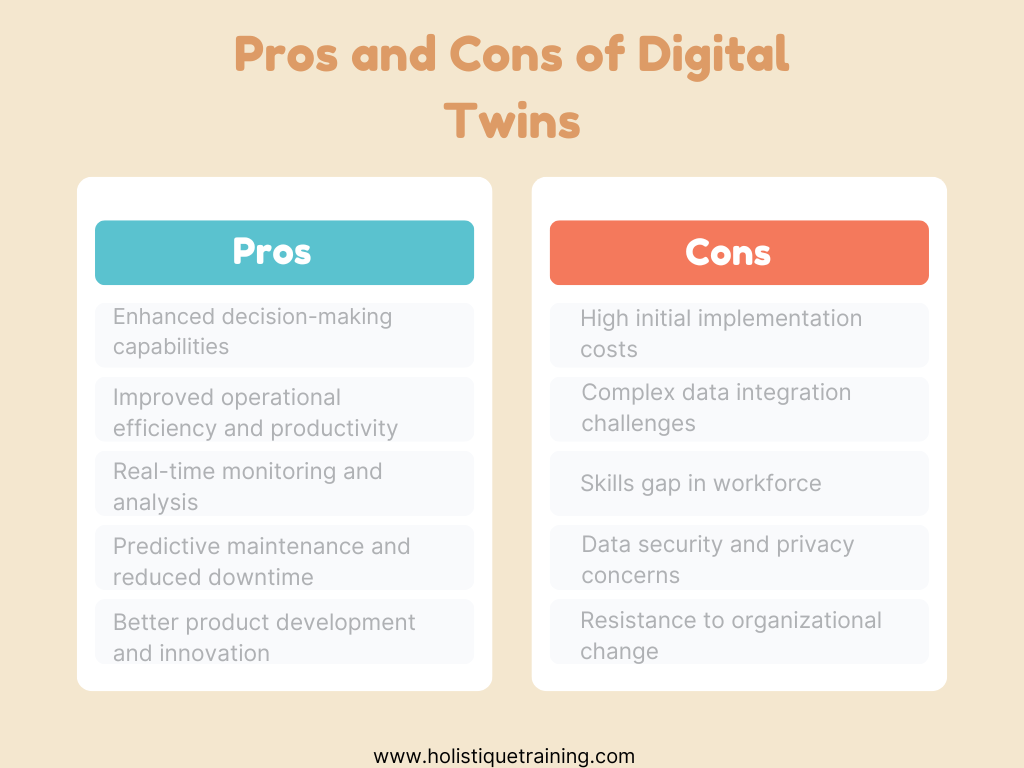
Challenges of Digital Twins and How to Overcome Them
While the benefits of digital twins are substantial, implementing this technology is not without challenges. Organizations may encounter several obstacles that can hinder the successful adoption of digital twins. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
1. Data Integration
Challenge: Digital twins rely on vast amounts of data from diverse sources, including sensors, IoT devices, legacy systems, and external databases. Integrating this data into a cohesive and accurate digital twin can be complex and time-consuming.
Solutions:
- Invest in Robust Data Management Systems: Organizations should prioritize investing in advanced data management solutions that facilitate seamless integration of data from multiple sources. This includes using middleware or data integration platforms that can standardize and consolidate data streams.
- Establish Data Protocols: Developing clear data protocols and standards can streamline the data integration process. Organizations should define data formats, structures, and communication protocols to ensure consistency and compatibility across systems.
- Utilize APIs: Application programming interfaces (APIs) can enable real-time data exchange between different systems, allowing for smoother integration and ensuring that the digital twin remains up-to-date.
2. High Initial Costs
Challenge: Implementing digital twins often requires significant upfront investment in technology, infrastructure, and training. This can be a barrier for organizations, particularly smaller businesses with limited budgets.
Solutions:
- Start with Pilot Projects: Organizations can mitigate high initial costs by launching pilot projects in specific areas rather than attempting a full-scale implementation. This approach allows businesses to demonstrate value, learn from the experience, and gradually secure additional funding for broader initiatives.
- Leverage Cloud Solutions: Cloud-based digital twin solutions can reduce infrastructure costs by minimizing the need for on-premises hardware. Organizations can take advantage of pay-as-you-go pricing models, which allow them to scale resources as needed without incurring large upfront expenses.
- Seek Partnerships: Collaborating with technology providers or industry partners can help organizations share costs and resources associated with digital twin implementation. Partnerships can also provide access to expertise and technologies that may otherwise be unavailable.
3. Skills Gap
Challenge: The successful implementation and management of digital twins require a skilled workforce proficient in data analytics, AI, and IoT technologies. Organizations may struggle to find employees with the necessary expertise.
Solutions:
- Invest in Training and Development: Organizations should prioritize training programs to upskill their existing workforce. This could include workshops, online courses, and certification programs focused on data analytics, machine learning, and digital twin technologies.
- Create a Culture of Continuous Learning: Fostering a culture that encourages continuous learning and professional development can help attract and retain talent. Providing opportunities for employees to enhance their skills will prepare the organization for future technological advancements.
- Collaborate with Educational Institutions: Partnering with universities and technical schools can help organizations tap into emerging talent. Internship programs and collaborative research projects can provide students with hands-on experience while allowing organizations to evaluate potential hires.
4. Data Security and Privacy
Challenge: The extensive data collection involved in digital twins raises concerns about data security and privacy. Organizations must protect sensitive information from cyber threats and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Solutions:
- Implement Robust Cybersecurity Measures: Organizations should invest in comprehensive cybersecurity strategies that include encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments can help identify and mitigate potential risks.
- Establish Data Governance Policies: Developing clear data governance policies can help organizations manage data privacy and security effectively. This includes defining roles and responsibilities for data management, establishing access controls, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
- Educate Employees: Training employees on data security best practices is essential. Staff should be aware of potential threats, such as phishing attacks, and understand the importance of safeguarding sensitive information.
5. Change Management
Challenge: Introducing digital twins often requires a cultural shift within organizations. Employees may resist changes to established processes and workflows, leading to challenges in adoption.
Solutions:
- Engage Stakeholders Early: Involving key stakeholders in the digital twin implementation process from the outset can foster buy-in and support. By soliciting feedback and addressing concerns early, organizations can create a sense of ownership among employees.
- Communicate the Benefits: Clearly communicating the benefits of digital twins—such as improved efficiency, enhanced decision-making, and reduced costs—can help alleviate resistance to change. Providing examples of successful implementations can further illustrate the value of the technology.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Offering continuous training and support during and after the implementation process can help employees adapt to new systems and processes. This support can include access to resources, mentorship, and dedicated help desks.
Conclusion
Successfully implementing digital twins requires organizations to navigate a range of challenges, from data integration and high initial costs to skills gaps and change management. By adopting proactive strategies to address these obstacles, businesses can unlock the full potential of digital twins, driving innovation and operational excellence. Embracing digital twins is not merely about technology adoption; it is a holistic approach that involves people, processes, and culture. With the right strategies in place, organizations can position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly digital landscape.
How Can Businesses Implement Digital Twins?
Implementing digital twins requires a strategic approach that encompasses planning, execution, and ongoing management. Here are key steps businesses can take to successfully implement digital twins:
1. Define Objectives
Organizations should begin by clearly defining their objectives for implementing digital twins. Whether the goal is to improve operational efficiency, enhance product development, or optimize maintenance processes, having a clear vision will guide the implementation process.
2. Assess Current Infrastructure
Before deploying digital twins, businesses must assess their existing infrastructure, including data sources, technology stack, and analytical capabilities. Understanding the current state will help identify gaps and areas for improvement.
3. Choose the Right Technology
Selecting the appropriate technology is crucial for the success of digital twins. Organizations should evaluate various platforms and tools that align with their objectives and infrastructure. Factors to consider include scalability, data integration capabilities, and ease of use.
4. Develop a Data Strategy
A robust data strategy is essential for the successful implementation of digital twins. Organizations should establish protocols for data collection, storage, and analysis, ensuring data quality and integrity. Additionally, businesses should consider how to leverage real-time data from IoT devices to enhance the accuracy of digital twins.
5. Start Small and Scale Up
Rather than attempting to implement digital twins across the entire organization at once, businesses should start with pilot projects. By focusing on specific use cases, organizations can demonstrate value, gather insights, and refine their approach before scaling up.
6. Foster Collaboration
Successful implementation of digital twins requires collaboration across departments. Involving stakeholders from various functions, such as IT, operations, and data analytics, will ensure that the digital twin aligns with organizational goals and meets the needs of different teams.
7. Monitor and Optimize
Once digital twins are implemented, organizations should continuously monitor their performance and gather feedback from users. This ongoing evaluation will help identify areas for improvement and optimization, ensuring that digital twins remain relevant and effective.
By following these steps, businesses can effectively implement digital twins and harness their potential to drive innovation and operational excellence.
The Future of Digital Twins
The future of digital twins is promising, with advancements in technology and increasing adoption across industries. Several trends are shaping the evolution of digital twins:
1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
As AI and machine learning technologies continue to advance, digital twins will become even more sophisticated. These technologies will enable digital twins to learn from historical data and improve their predictive capabilities, leading to more accurate simulations and insights.
2. Expansion into New Industries
While digital twins have primarily been adopted in manufacturing and engineering, their application is expanding into new industries, such as healthcare, agriculture, and urban planning. This trend will drive innovation and open new opportunities for businesses to leverage digital twins for enhanced decision-making.
3. Enhanced Interoperability
The future will see improved interoperability among digital twin platforms, allowing for seamless data exchange and collaboration across different systems. This integration will enable organizations to create more comprehensive digital twins that encompass multiple facets of operations.
4. Focus on Sustainability
As businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability, digital twins will play a crucial role in optimizing resource usage and minimizing waste. By simulating various scenarios, organizations can identify sustainable practices and make informed decisions that align with their environmental goals.
5. Increased Use of Augmented and Virtual Reality
The integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies with digital twins will enhance visualization and interaction. This development will enable stakeholders to engage with digital twins in immersive environments, facilitating better understanding and collaboration.
The future of digital twins holds immense potential for innovation and transformation. As organizations continue to explore and adopt this technology, they will unlock new opportunities for growth and efficiency.
Conclusion
Digital twins represent a groundbreaking advancement in technology, offering organizations the ability to create real-time digital replicas of physical entities. By enhancing decision-making, enabling predictive maintenance, and facilitating scenario simulation, digital twins empower businesses to navigate complexities and drive innovation.
While challenges exist in implementing digital twins, proactive strategies can help organizations overcome obstacles and unlock the full potential of this technology. As digital twins continue to evolve and expand across industries, their impact on operational efficiency and strategic growth will only grow stronger.
Embracing digital twins is not just about adopting a new technology; it is about fostering a culture of innovation, data-driven decision-making, and continuous improvement. As businesses look to the future, those who leverage digital twins effectively will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.