- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is a Business Model?
- Digital Economy vs. Traditional Economy: Then vs. Now
- Consumer Behavior Changes:
- Business Operations:
- Marketing Strategies:
- Collaboration and Communication:
- Supply Chain Dynamics:
- Access to Information:
- Disruption and Innovation:
- Regulatory Challenges:
- Globalization:
- Sustainability Considerations:
- Digital Offerings vs. Digital Business Models: Key Differences
- Value Proposition:
- Lifecycle Perspective:
- Integration with Technology:
- Market Dynamics:
- Customer Relationships:
- Revenue Streams:
- Scalability:
- Feedback Loop:
- Innovation and Adaptation:
- Impact of Data:
- Characteristics of Digital Business Models
- Scalability:
- Flexibility:
- Data-Driven Decision Making:
- Customer-Centric Approach:
- Network Effects:
- Global Reach:
- Cost Efficiency:
- Innovative Revenue Streams:
- Sustainability:
- Continuous Improvement:
- Top 10 Emerging Digital Business Models
- 1- Subscription Model
- 2- Freemium Model
- 3- Marketplace Model
- 4- On-Demand Model
- 5- Data Monetization Model
- 6- Crowdsourcing Model
- 7- Affiliate Marketing Model
- 8- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) Model
- 9- Social Commerce Model
- 10- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Model
- How to Implement a Digital Business Model
- 1- Define Your Value Proposition
- 2- Conduct Market Research
- 3- Choose the Right Technology Stack
- 4- Develop a Business Plan
- 5- Build a Strong Online Presence
- 6- Implement Digital Marketing Strategies
- 7- Focus on Customer Experience
- 8- Monitor Performance and Adapt
- 9- Invest in Training and Development
- 10- Scale and Innovate
- Conclusion
Introduction
The landscape of commerce has transformed dramatically over the past few decades, driven by advancements in technology and shifts in consumer behavior. This blog post delves into the concept of digital business models, exploring their definitions, characteristics, and the differences between traditional and digital economies. We will also examine key distinctions between digital offerings and digital business models, highlight emerging trends, and provide insights on implementing these models effectively.
What is a Business Model?
A business model is a strategic framework that outlines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It encompasses the underlying logic of how a business operates, including its target market, value propositions, revenue streams, and operational processes. Essentially, a business model answers critical questions such as:
- Who are the customers?
- What value do we provide?
- How do we deliver that value?
- How do we earn revenue?
Business models are crucial for guiding decision-making and aligning resources to achieve organizational goals. They serve as the blueprint for a company's strategy and are fundamental to its long-term success.
Digital Economy vs. Traditional Economy: Then vs. Now
The emergence of the digital economy has fundamentally altered the way businesses operate and compete. To illustrate the differences between the traditional economy and the digital economy, consider the following comparison:
Aspect | Traditional Economy | Digital Economy |
Nature of Transactions | Primarily face-to-face and physical | Predominantly online and virtual |
Market Reach | Limited to local or regional markets | Global reach, transcending geographical boundaries |
Customer Interaction | Personal and direct engagement | Automated and data-driven interactions |
Information Flow | Slow and often one-way | Instantaneous and multi-directional |
Cost Structure | High overhead costs due to physical presence | Lower costs due to digital operations |
Speed of Innovation | Slower, with longer product development cycles | Rapid, with agile methodologies and iterations |
Data Utilization | Minimal use of data analytics | Extensive use of big data and analytics |
The transition from a traditional economy to a digital economy encompasses more than just the differences highlighted in the table. Here are several key points that further illuminate this transformation:
Consumer Behavior Changes:
- In the traditional economy, consumer behavior was largely influenced by physical interactions, local availability, and word-of-mouth recommendations. Today, consumers are empowered by technology, capable of researching products and services online, comparing prices, and reading reviews before making purchases. This shift has led to a more informed and discerning customer base.
Business Operations:
- Traditional businesses often relied on brick-and-mortar locations, requiring significant investments in physical infrastructure and inventory. In contrast, digital businesses can operate virtually, leveraging cloud technology to reduce overhead costs and streamline operations. This flexibility allows for rapid scaling and adaptation to market demands.
Marketing Strategies:
- Marketing in the traditional economy relied heavily on print media, television, and radio advertisements. The digital economy has revolutionized marketing strategies, enabling businesses to utilize targeted online advertising, social media campaigns, and influencer partnerships. This shift allows for more precise audience targeting and measurable results.
Collaboration and Communication:
- Traditional businesses often faced challenges in communication and collaboration, particularly across geographically dispersed teams. The digital economy fosters seamless collaboration through tools like video conferencing, project management software, and instant messaging platforms, which enhance productivity and innovation.
Supply Chain Dynamics:
- The traditional supply chain was often linear and rigid, with limited visibility and flexibility. Digital technologies have introduced concepts like just-in-time inventory, real-time tracking, and automation, allowing for more agile and responsive supply chains that can quickly adapt to changes in demand.
Access to Information:
- In the traditional economy, access to information was often limited and controlled by gatekeepers. The digital economy democratizes information access, enabling anyone with an internet connection to find and utilize vast amounts of data. This shift has empowered consumers and businesses alike to make more informed decisions.
Disruption and Innovation:
- The digital economy fosters a culture of innovation and disruption. Startups can quickly enter the market with innovative solutions that challenge established players. This dynamic environment encourages continuous improvement and adaptation, pushing businesses to evolve or risk obsolescence.
Regulatory Challenges:
- The shift to a digital economy also presents unique regulatory challenges. Governments and regulatory bodies are grappling with issues related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and intellectual property rights in a rapidly evolving landscape. Businesses must navigate these complexities while remaining compliant with changing regulations.
Globalization:
- The digital economy has accelerated globalization, allowing businesses to operate across borders with relative ease. This interconnectedness creates opportunities for collaboration and market expansion, but it also introduces competition from international players, requiring businesses to differentiate themselves.
Sustainability Considerations:
- As consumers become more environmentally conscious, digital businesses are increasingly integrating sustainability into their operations. The digital economy allows for innovative solutions that reduce waste and energy consumption, appealing to a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers.
Digital Offerings vs. Digital Business Models: Key Differences
While digital offerings and digital business models are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct concepts. Understanding these differences is essential for businesses navigating the digital landscape.
Aspect | Digital Offerings | Digital Business Models |
Definition | Products or services delivered through digital channels | Framework for how a business operates in the digital space |
Focus | Emphasis on the product or service itself | Emphasis on the overall strategy and value creation |
Examples | E-books, software applications, online courses | Subscription services, freemium models, e-commerce platforms |
Revenue Generation | Often tied to individual sales or downloads | Involves multiple revenue streams and monetization strategies |
Customer Engagement | Limited to product usage and feedback | Encompasses customer relationships and community building |
Value Proposition:
- Digital offerings focus on delivering specific value to customers through products or services. For instance, a software application may offer enhanced productivity features. In contrast, a digital business model encompasses the entire value proposition of the business, including how it attracts customers, retains them, and generates revenue over time.
Lifecycle Perspective:
- Digital offerings often have a defined lifecycle that includes development, launch, and eventual obsolescence or replacement. Digital business models, however, are more dynamic and can evolve over time. A business may adapt its model based on market feedback, competitive pressures, or technological advancements, allowing for ongoing innovation and relevance.
Integration with Technology:
- Digital offerings rely heavily on technology for delivery and user experience. For example, an online course platform must leverage robust technology to facilitate learning. Digital business models, on the other hand, incorporate technology not just for delivery but also for operational efficiency, data analytics, and customer engagement strategies.
Market Dynamics:
- The success of digital offerings often hinges on market demand and competition for specific products or services. Conversely, digital business models must consider broader market dynamics, including consumer behavior trends, regulatory environments, and economic factors. A well-designed business model anticipates these changes and positions the company strategically within the market.
Customer Relationships:
- While digital offerings may focus on immediate customer satisfaction through product features, digital business models emphasize building long-term relationships with customers. This can include loyalty programs, personalized marketing, and community engagement strategies that foster brand loyalty and repeat business.
Revenue Streams:
- Digital offerings typically generate revenue through direct sales or subscriptions. However, digital business models explore diverse revenue streams, such as advertising, partnerships, and affiliate marketing. For instance, a freemium model may offer basic services for free while charging for premium features, creating multiple avenues for income.
Scalability:
- Digital offerings can be scaled, but the scalability often depends on production capacity and market demand. In contrast, digital business models are inherently designed for scalability. For example, a marketplace model can grow rapidly as more users join, with minimal incremental costs associated with each new customer.
Feedback Loop:
- Digital offerings benefit from customer feedback to improve product features and usability. Digital business models utilize feedback not only to enhance offerings but also to refine the overall strategy, adjusting marketing approaches and operational processes based on customer insights.
Innovation and Adaptation:
- While digital offerings may undergo updates and enhancements, digital business models require a culture of innovation. Businesses must be willing to explore new models, pivot strategies, and embrace change as market conditions evolve, ensuring ongoing competitiveness.
Impact of Data:
- Digital offerings may collect user data to enhance product features, but digital business models leverage data analytics comprehensively to inform strategic decisions. This includes understanding customer preferences, optimizing pricing strategies, and identifying new market opportunities.
By distinguishing between digital offerings and business models, organizations can better strategize their approach to the digital market, ensuring that they not only deliver valuable products but also create sustainable business frameworks.
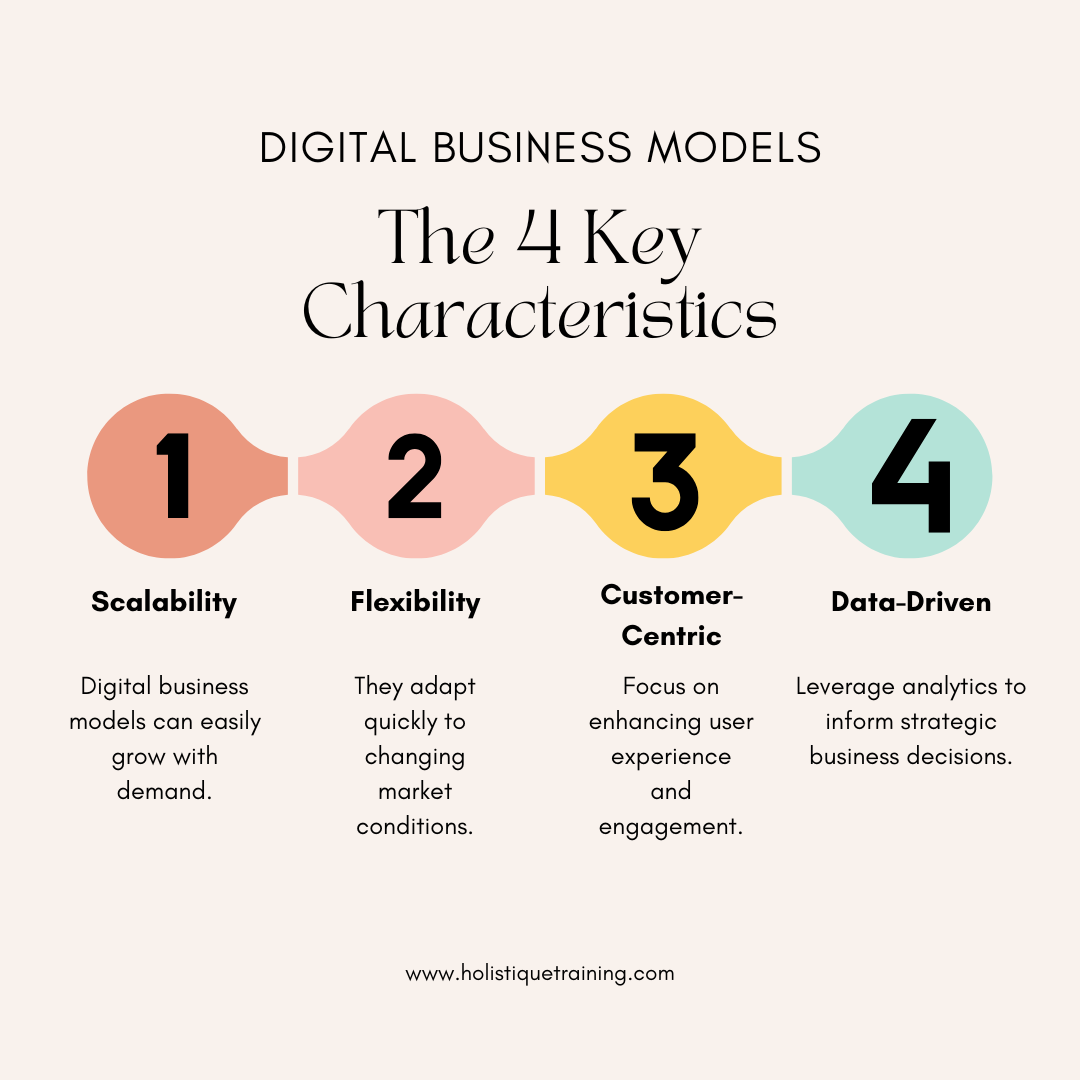
Characteristics of Digital Business Models
Digital business models exhibit several key characteristics that differentiate them from traditional models. These features enable organizations to thrive in the fast-paced digital environment:
Scalability:
Digital business models are designed to scale efficiently. Unlike traditional businesses, which may require significant investments in physical infrastructure to grow, digital models can expand their reach with minimal incremental costs. For example, a SaaS (Software as a Service) company can add thousands of new users without needing to proportionally increase its physical resources or operational costs. This scalability allows businesses to respond quickly to market demand and capitalize on growth opportunities.
Flexibility:
The ability to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions is crucial in the digital landscape. Digital business models can quickly adjust their offerings, pricing strategies, and operational processes based on consumer feedback and market trends. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many businesses shifted from in-person services to online platforms, demonstrating the flexibility inherent in digital models. This adaptability helps businesses stay relevant and competitive in a rapidly evolving environment.
Data-Driven Decision Making:
Leveraging data analytics is fundamental to digital business models. Companies can collect and analyze vast amounts of data regarding customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making, allowing businesses to optimize their strategies, improve customer experiences, and identify new revenue opportunities. For example, e-commerce platforms use data analytics to personalize shopping experiences, recommend products, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Customer-Centric Approach:
Digital business models prioritize customer experience, utilizing technology to enhance interactions and build long-term relationships. This customer-centric mindset involves understanding customer needs, preferences, and pain points. Businesses can engage with customers through various digital channels, gather feedback, and tailor their offerings accordingly. Companies like Amazon excel in this area by providing personalized recommendations and seamless customer service, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
Network Effects:
Many digital business models benefit from network effects, where the value of the service increases as more users join. For example, social media platforms become more valuable as their user base grows, attracting even more users in a self-reinforcing cycle. This characteristic creates a competitive advantage for businesses that can successfully build and maintain large user communities, making it challenging for new entrants to compete.
Global Reach:
Digital businesses can operate across borders, accessing international markets and diversifying their customer base. The internet allows companies to reach customers anywhere in the world, breaking down geographical barriers that traditionally limited market access. This global reach opens up new revenue streams and opportunities for growth, enabling businesses to tap into emerging markets and diverse consumer segments.
Cost Efficiency:
By eliminating the need for physical infrastructure and utilizing cloud-based services, digital models can operate with lower overhead costs. This cost efficiency allows businesses to offer competitive pricing, invest in innovation, and increase profitability. For instance, many startups leverage cloud computing to avoid the high costs associated with maintaining physical servers, enabling them to allocate resources toward product development and marketing.
Innovative Revenue Streams:
Digital business models often explore diverse monetization strategies beyond traditional sales. Companies can generate revenue through subscriptions, advertising, affiliate marketing, and partnerships. For instance, platforms like YouTube and Spotify utilize ad-supported models alongside premium subscription options, creating multiple revenue streams that enhance financial sustainability.
Sustainability:
Many digital models integrate sustainable practices, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Digital businesses can reduce their carbon footprint by minimizing physical resources and optimizing supply chains through technology. Additionally, they can promote sustainable products and practices, resonating with a growing segment of eco-aware customers.
Continuous Improvement:
Digital businesses embrace a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. They regularly iterate on their products and services based on user feedback and technological advancements. This commitment to improvement enables organizations to stay ahead of competitors and meet evolving customer expectations. Companies like Apple exemplify this characteristic by consistently releasing updated versions of their products, incorporating user feedback and emerging technologies.
These characteristics collectively define the landscape of digital business models, enabling organizations to navigate the complexities of the digital economy. By leveraging these traits, businesses can create sustainable competitive advantages and foster long-term success in an increasingly digital world.
Top 10 Emerging Digital Business Models
As technology evolves, new digital business models continue to emerge. Here are ten noteworthy models that are shaping the future of commerce:
1- Subscription Model
- Overview: This model charges customers a recurring fee to access a product or service. It can be applied to various industries, including software, media, and consumer goods.
- Examples: Netflix offers streaming services for a monthly fee, while software companies like Adobe provide access to their creative tools through subscription plans.
- Benefits: Provides predictable revenue streams, fosters customer loyalty, and allows for continuous engagement with users.
2- Freemium Model
- Overview: In this model, basic services are offered for free, while premium features or content are available for a fee. This strategy attracts a large user base, some of whom may convert to paying customers. In fact, according to Business Insider, approximately60% of Spotify's monthly active users access the platform for free.
- Examples: LinkedIn offers free access to its professional networking platform, with premium features like advanced search and InMail available through paid subscriptions.
- Benefits: Lowers the barrier to entry for users, encourages widespread adoption, and creates opportunities for upselling.
3- Marketplace Model
- Overview: This model connects buyers and sellers on a single platform, facilitating transactions without holding inventory. Marketplaces earn revenue through commissions or listing fees.
- Examples: Amazon and eBay serve as platforms where various sellers can list their products, while the marketplace handles transactions and logistics.
- Benefits: Reduces operational costs, provides a wide variety of products to consumers, and leverages network effects to grow user bases. Also, digital marketplaces have seen substantial growth, with over50% of Amazon's sales generated by external sellers.
4- On-Demand Model
- Overview: This model provides immediate access to services or products, often through mobile applications. It caters to consumers' desire for convenience and instant gratification.
- Examples: Uber and Lyft offer ride-hailing services, while food delivery apps like DoorDash and Grubhub connect customers with local restaurants.
- Benefits: Enhances customer satisfaction by meeting immediate needs, utilizes flexible labor, and can adapt quickly to market demands.
5- Data Monetization Model
- Overview: Companies collect and analyze user data to create insights that can be sold to third parties or used to enhance their own offerings. This model capitalizes on the value of big data.
- Examples: Google and Facebook leverage user data to provide targeted advertising services, generating substantial revenue from advertisers seeking specific demographics.
- Benefits: Unlocks new revenue streams, enhances product development through insights, and improves marketing effectiveness.
6- Crowdsourcing Model
- Overview: This model relies on contributions from a large group of people, often through online platforms, to gather ideas, funding, or labor for projects. It democratizes innovation and resource allocation.
- Examples: Kickstarter allows creators to raise funds for projects by receiving small contributions from many backers, while platforms like Wikipedia rely on volunteers to contribute content.
- Benefits: Reduces costs associated with research and development, fosters community engagement, and accelerates project timelines.
7- Affiliate Marketing Model
- Overview: Businesses earn commissions by promoting other companies' products or services through affiliate links. This model leverages the influence of bloggers, social media personalities, and content creators.
- Examples: Amazon Associates allows website owners to earn commissions by linking to Amazon products, while influencers on platforms like Instagram promote brands in exchange for a fee or commission.
- Benefits: Lowers marketing costs, expands reach through partnerships, and provides performance-based compensation for affiliates. No wonder a whopping81% of brands utilize affiliate marketing programs.
8- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) Model
- Overview: This model provides a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without the complexity of maintaining the underlying infrastructure. It streamlines development processes.
- Examples: Google Cloud Platform and Microsoft Azure offer PaaS solutions that enable developers to focus on coding while the platform handles hosting and scalability.
- Benefits: Accelerates development cycles, reduces costs associated with infrastructure management, and fosters innovation by providing access to advanced tools.
9- Social Commerce Model
- Overview: This model integrates social media and e-commerce, allowing users to discover and purchase products directly through social platforms. It capitalizes on social interactions and user-generated content.
- Examples: Instagram and Facebook enable businesses to set up shops where users can browse and buy products seamlessly within the app.
- Benefits: Enhances customer engagement through social interactions, leverages influencer marketing, and creates a seamless shopping experience.
10- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Model
- Overview: This model utilizes blockchain technology to provide financial services without traditional intermediaries such as banks. DeFi platforms offer lending, borrowing, and trading services in a decentralized manner.
- Examples: Platforms like Uniswap and Aave allow users to trade cryptocurrencies and earn interest on their assets without relying on centralized institutions.
- Benefits: Increases accessibility to financial services, reduces transaction costs, and promotes transparency and security through blockchain technology.
These emerging digital business models reflect the ongoing transformation of the business landscape driven by technology and changing consumer preferences. By understanding and adopting these models, businesses can enhance their competitiveness, create new revenue streams, and better meet the needs of their customers in an increasingly digital world. Each model offers unique advantages and challenges, requiring organizations to carefully consider their strategies and operational frameworks to maximize success.
How to Implement a Digital Business Model
Transitioning to a digital business model requires careful planning and execution. Here are key steps to consider when implementing a digital business model:
1- Define Your Value Proposition
Clearly articulate what makes your digital offering unique and valuable to your target audience. This involves understanding customer pain points and identifying how your product or service addresses those needs. Conduct market research to gather insights about customer preferences and behaviors, which will help refine your value proposition. Ensure that your value proposition is communicated effectively across all marketing channels to resonate with potential customers.
2- Conduct Market Research
Engage in comprehensive market research to identify trends, competitors, and customer demographics. Utilize surveys, focus groups, and analytics tools to gather data on consumer behavior and preferences. This research will inform your business decisions and help you identify gaps in the market that your digital business model can fill. Additionally, staying updated on industry trends will allow you to anticipate changes and adapt your strategy accordingly.
3- Choose the Right Technology Stack
Select the appropriate technology infrastructure that supports your digital business model. This includes choosing platforms for website development, e-commerce, customer relationship management (CRM), and data analytics. Consider scalability, security, and user experience when making technology decisions. Collaborate with IT professionals or consultants to ensure that your technology stack aligns with your business goals and can accommodate future growth.
4- Develop a Business Plan
Create a detailed business plan that outlines your objectives, target market, revenue model, and marketing strategy. This plan should include financial projections, operational plans, and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success. A well-structured business plan serves as a roadmap for your digital transformation and helps secure investment or buy-in from stakeholders. Regularly review and update the plan to reflect changes in the market or your business environment.
5- Build a Strong Online Presence
Establish a professional and user-friendly online presence through a well-designed website and active social media profiles. Optimize your website for search engines (SEO) to increase visibility and attract organic traffic. Create engaging content that resonates with your audience and showcases your expertise in the industry. Leverage social media platforms to connect with customers, promote your offerings, and build a community around your brand.
6- Implement Digital Marketing Strategies
Develop and execute digital marketing strategies that align with your business goals. This may include content marketing, email marketing, social media advertising, and search engine marketing (SEM). Utilize data analytics to track the performance of your campaigns and make data-driven adjustments. A targeted marketing approach will help you reach your desired audience more effectively and maximize your return on investment.
7- Focus on Customer Experience
Prioritize delivering an exceptional customer experience at every touchpoint. This includes ensuring that your website is easy to navigate, providing responsive customer support, and personalizing interactions based on customer data. Gather feedback through surveys and reviews to identify areas for improvement. A positive customer experience fosters loyalty and encourages word-of-mouth referrals, which are crucial for growth in a digital landscape.
8- Monitor Performance and Adapt
Continuously monitor key performance metrics to assess the effectiveness of your digital business model. Use analytics tools to track website traffic, conversion rates, customer engagement, and other relevant KPIs. Regularly review this data to identify trends, successes, and areas needing improvement. Be willing to adapt your strategies based on performance insights and changing market conditions to ensure long-term success.
9- Invest in Training and Development
Equip your team with the necessary skills and knowledge to thrive in a digital environment. Provide training on new technologies, digital marketing techniques, and customer engagement strategies. Encourage a culture of continuous learning and innovation within your organization. Investing in your workforce not only enhances productivity but also fosters a proactive approach to adapting to digital changes.
10- Scale and Innovate
Once your digital business model is established, focus on scaling operations and exploring new opportunities for innovation. Assess market feedback and emerging trends to identify potential areas for expansion or diversification. Consider partnerships or collaborations that can enhance your offerings or broaden your reach. Embrace a mindset of agility and flexibility, allowing your business to evolve in response to new challenges and opportunities in the digital landscape.
Implementing a digital business model requires careful planning and execution across multiple dimensions. By following these steps, organizations can successfully transition to a digital-first approach, enhance customer engagement, and drive sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive marketplace. Each step contributes to building a robust foundation for long-term success in the digital economy.
Conclusion
The rise of digital business models represents a profound shift in the way companies operate and engage with customers. By understanding the nuances of digital offerings, the characteristics of successful models, and the emerging trends shaping the landscape, businesses can navigate the complexities of the digital economy. Implementing a digital business model requires strategic planning, a customer-centric approach, and a commitment to continuous improvement. As technology continues to evolve, those who embrace innovation and adaptability will thrive in the ever-changing world of commerce.