- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is a Digital Nomad Visa?
- Why Are Countries Now Introducing Digital Nomad Visas?
- 1. Economic Stimulation
- 2. Talent Attraction and Retention
- 3. Diversification of Tourism Revenue
- 4. Promoting International Recognition and Competitiveness
- 5. Leveraging Technological Infrastructure
- 6. Cultural Exchange and Soft Power
- Popular Destinations for Digital Nomad Visas
- Eligibility Criteria and Application Process
- Digital Nomads by Numbers
- Pros and Cons of Digital Nomad Visas for Countries
- Pros
- Cons
- Why Should Individuals Opt for a Digital Nomad Visa?
- 1. Legal Residency and Peace of Mind
- 2. Enhanced Work-Life Flexibility
- 3. Cultural Immersion and Personal Growth
- 4. Networking and Professional Opportunities
- 5. Lifestyle and Well-Being Benefits
- 6. Potential Financial Advantages
- 7. Career Advancement and Skill Development
- The Future of Work and Travel
- 1. Remote Work as a Norm
- 2. Global Talent Mobility
- 3. Hybrid Work Models and Flexibility
- 4. Technological and Infrastructure Investments
- 5. Cross-Cultural Collaboration and Global Workforces
- 6. Sustainability and Lifestyle Considerations
- 7. Long-Term Implications for Work and Travel
- Conclusion
Introduction
The traditional concept of work has evolved dramatically over the past decade. Advancements in technology, the rise of remote work, and shifting attitudes toward work-life balance have given rise to new opportunities for professionals to work from virtually anywhere. Among these opportunities is the increasing popularity of digital nomad visas—a legal framework designed to enable individuals to live and work in foreign countries while maintaining employment or freelance work elsewhere.
This blog post examines the phenomenon of digital nomad visas in depth. It explains what a digital nomad visa is, why countries are introducing them, popular destinations, eligibility criteria, and application processes. Furthermore, it explores the advantages and challenges for countries offering these visas, why professionals might pursue them, and how this trend reflects broader changes in the future of work and travel. By understanding digital nomad visas, both aspiring nomads and policymakers can navigate this emerging landscape more strategically and effectively.
What is a Digital Nomad Visa?
A digital nomad visa is a legal authorization that allows professionals to reside in a foreign country for an extended period while continuing to work remotely for an employer or clients based outside the host nation. Unlike traditional work visas, which are typically tied to employment within the country of residence, digital nomad visas cater specifically to remote workers whose income comes from international sources.
Digital nomad visas are designed to offer flexibility, legitimacy, and stability for remote workers. They often provide benefits such as longer stays than standard tourist visas, access to local healthcare, and sometimes even opportunities to bring family members. However, they usually do not confer permanent residency rights or a pathway to citizenship, as the primary goal is to attract temporary residents who contribute economically without entering the local labor market directly.
The rise of digital nomad visas reflects a broader acknowledgment that work no longer requires physical presence in an office. Professionals equipped with laptops, high-speed internet, and digital collaboration tools can maintain productivity from anywhere, provided legal frameworks accommodate their status. In essence, a digital nomad visa bridges the gap between mobility and legality, enabling global professionals to explore new cultures, countries, and lifestyles while remaining professionally active.
Why Are Countries Now Introducing Digital Nomad Visas?
The emergence of digital nomad visas is not merely a response to remote work trends—it represents a strategic move by governments to attract global talent, stimulate local economies, and position themselves as forward-thinking, digitally advanced nations. Multiple interrelated factors have prompted countries to introduce these visas, each reflecting broader economic, social, and technological motivations.
1. Economic Stimulation
Digital nomads often contribute significant spending power to local economies without competing for jobs in the domestic labor market. Unlike short-term tourists, nomads typically stay for months, renting apartments, dining regularly, and participating in leisure and cultural activities. This extended engagement generates sustained economic benefits for local businesses, including cafes, coworking spaces, gyms, and transport services.
For instance, Barbados launched its 12-month “Barbados Welcome Stamp” visa partly to offset the decline in traditional tourism revenue during global travel restrictions. By attracting remote professionals, the government created a new economic stream that directly supported local hospitality and service sectors, illustrating how digital nomad visas can act as a stabilizing economic tool.
2. Talent Attraction and Retention
Countries increasingly recognize that attracting skilled, globally mobile professionals can enhance innovation, entrepreneurship, and competitiveness. Digital nomads are often highly educated, technologically proficient, and entrepreneurial, making them valuable contributors to local economies—even if indirectly.
By offering a digital nomad visa, nations can create a pipeline of talent that may later invest in startups, collaborate with local businesses, or even establish long-term residence. For example, Estonia’s digital nomad visa complements its e-residency program, enabling remote workers to launch and manage a European-based company digitally. This integration of remote work and entrepreneurial opportunities transforms temporary residents into long-term economic and technological contributors.
3. Diversification of Tourism Revenue
Traditional tourism is highly seasonal and vulnerable to global crises, such as pandemics or economic downturns. Digital nomads, by contrast, represent a form of “extended tourism” that provides more consistent income year-round. Countries with strong tourism sectors have realized that attracting nomads can reduce dependence on seasonal flows, helping hotels, restaurants, and service providers maintain stability during off-peak periods.
Croatia, for example, designed its digital nomad visa to extend stays beyond the usual tourist season, bringing a steady stream of international residents who engage in the economy throughout the year. This not only supports local businesses but also encourages investment in infrastructure and urban development in regions less frequented by traditional tourists.
4. Promoting International Recognition and Competitiveness
Digital nomad visas serve as a branding tool, signaling that a country is modern, innovative, and open to global talent. In an increasingly competitive global landscape, countries seek to differentiate themselves to attract professionals who value flexibility, quality of life, and technological readiness.
Portugal has successfully leveraged this strategy, positioning Lisbon and Porto as attractive hubs for remote work and entrepreneurship. By combining visa incentives with vibrant coworking spaces, affordable living, and rich cultural experiences, Portugal has built a reputation as a welcoming, globally connected destination.
5. Leveraging Technological Infrastructure
Countries with advanced digital infrastructure are uniquely positioned to benefit from the influx of remote workers. Reliable internet connectivity, extensive coworking networks, and digital government services enable nomads to maintain productivity while living abroad. Governments are increasingly aware that promoting these assets can attract a highly skilled, mobile workforce.
Estonia again provides a prime example: its robust digital services, from e-residency to online banking and government portals, create an environment where remote professionals can seamlessly work, manage businesses, and engage with society—all from abroad. This combination of legal, technological, and lifestyle support makes the nation particularly appealing to nomads.
6. Cultural Exchange and Soft Power
Beyond economic gains, digital nomads contribute to cultural diversity and international collaboration. Hosting professionals from different countries fosters exchange of ideas, networking, and cross-cultural understanding. This soft power dimension enhances a country’s global image and may attract additional tourism, investment, and collaborative opportunities over time.
By introducing digital nomad visas, countries are effectively creating a win-win scenario: professionals gain legal access to work and live abroad, while host nations benefit economically, socially, and reputationally. This forward-looking approach acknowledges the evolving nature of work in a digitally connected world and positions countries to compete in the global talent marketplace.
Popular Destinations for Digital Nomad Visas
Statistics show that between 40 and 80 million people in the world right now are digital nomads. Which is why several countries have established themselves as popular destinations for digital nomads due to attractive visa conditions, cost of living, and quality of life. Some of the most notable destinations include:
Each destination offers unique incentives, from tax considerations to cultural experiences. For instance, Estonia’s e-residency program complements its digital nomad visa, allowing professionals to establish and manage a European-based company digitally. Portugal, with its sunny climate and growing tech scene, appeals to those seeking both work productivity and a high quality of life. Meanwhile, Caribbean nations like Barbados combine remote work legality with idyllic surroundings, making them attractive for lifestyle-focused nomads.
The choice of destination often depends on a combination of factors including visa duration, tax implications, lifestyle preferences, and access to reliable technology infrastructure. Some countries even provide family-friendly options, allowing spouses and children to join digital nomads, which broadens the appeal for professionals looking for extended stays abroad. For example,statistics show that Spain has become increasingly attractive to remote workers, with cities like Barcelona, Madrid, and Valencia offering a relatively moderate cost of living and ultra-fast internet averaging 248 Mbps, supporting seamless virtual meetings and productivity.
Eligibility Criteria and Application Process
While each country establishes its own requirements for digital nomad visas, common eligibility criteria typically include:
- Proof of Remote Employment or Freelance Income – Applicants must demonstrate that they have a steady source of income from an employer or clients outside the host country. Some countries set a minimum monthly income threshold.
- Valid Passport – Applicants need a passport with sufficient validity, often six months beyond the intended stay.
- Health Insurance – Comprehensive health coverage valid in the host country is usually mandatory to ensure safety and avoid strain on local healthcare systems.
- Clean Criminal Record – Many nations require background checks to maintain safety and security.
- Application Forms and Fees – Submission of formal application forms, supporting documents, and payment of processing fees is standard practice.
The application process often follows these steps:
- Research and Preparation – Identify the country’s requirements, minimum income thresholds, and documentation needs.
- Document Compilation – Gather employment contracts, bank statements, proof of insurance, and other supporting documents.
- Application Submission – Submit the application through the designated government portal or consulate.
- Processing and Approval – Authorities review documentation, verify income, and may request additional information.
- Visa Issuance – Successful applicants receive the visa, typically valid for 6 to 12 months, with possible renewal options.
It is crucial for applicants to thoroughly understand tax implications, residency obligations, and any reporting requirements in both their home country and the host country to avoid legal complications. Additionally, the application process may differ for self-employed freelancers versus full-time employees, requiring tailored documentation and proof of financial stability.
Digital Nomads by Numbers
By 2025, the global digital nomad population has surpassed50 million, up from 35 million in 2023, driven by remote work growth and visa reforms. Freelancers make up the largest group (41%), followed by remote employees (34%) and entrepreneurs or solopreneurs (25%).
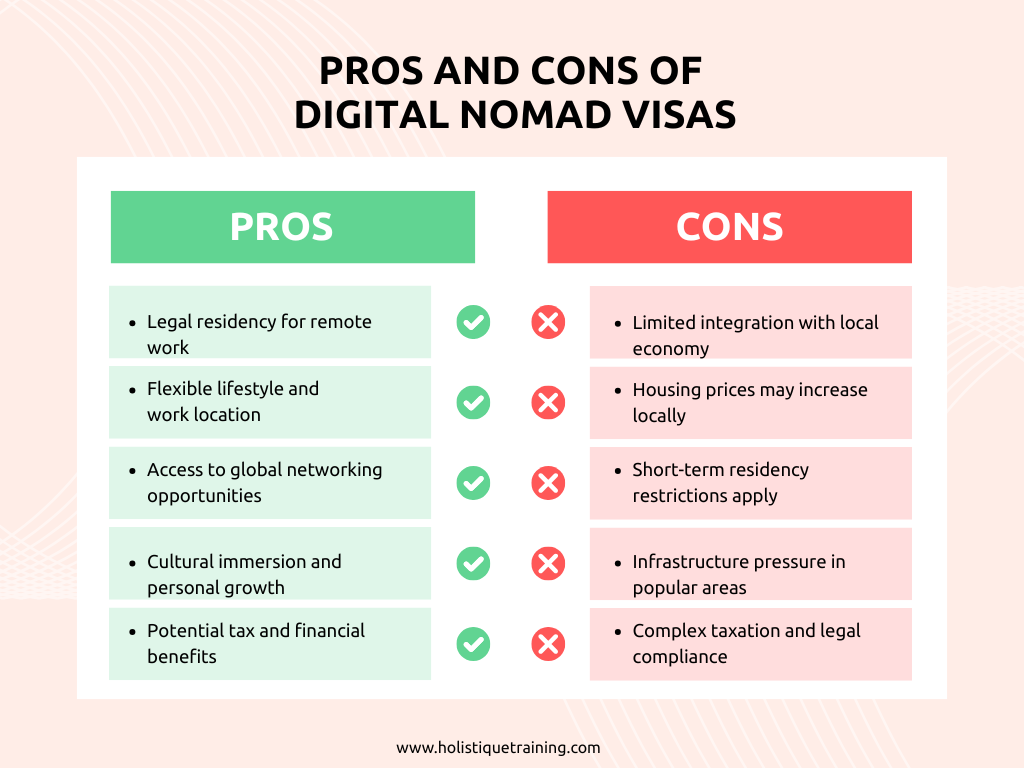
Pros and Cons of Digital Nomad Visas for Countries
Digital nomad visas offer clear benefits but also present challenges for host nations.
Digital nomad visas are increasingly recognized as strategic tools for nations aiming to attract global talent and stimulate economic growth. However, like any policy, they carry both advantages and potential drawbacks. Understanding these pros and cons helps policymakers balance the benefits with possible challenges, ensuring that visa programs maximize value for both the country and visiting professionals.
Pros
Economic Growth and Local Spending
Digital nomads typically spend on housing, food, entertainment, transport, and local services. Unlike short-term tourists, they remain in the country for months, contributing a consistent flow of revenue to local economies. For example, Barbados’ Welcome Stamp program brought hundreds of remote workers during the COVID-19 pandemic, providing crucial income to hotels, restaurants, and coworking spaces when traditional tourism was disrupted.
Attracting Skilled Talent
Countries offering digital nomad visas can attract highly skilled, internationally mobile professionals. These individuals often bring expertise in tech, marketing, design, and entrepreneurship, enhancing local knowledge networks. Over time, some nomads may establish startups or collaborate with local businesses, indirectly contributing to innovation and job creation. Estonia’s e-residency program, paired with its digital nomad visa, exemplifies how skilled nomads can integrate into entrepreneurial ecosystems.
Promoting Cultural Exchange and Soft Power
Hosting international remote workers fosters cultural exchange, networking, and the creation of globally minded communities. This soft power advantage enhances the country’s international reputation, attracting future tourists, investors, and business partnerships. For instance, Portugal’s coworking hubs and digital nomad communities in Lisbon and Porto have positioned the country as a progressive, globally connected destination.
Year-Round Tourism Stability
Unlike traditional tourism, which fluctuates seasonally, digital nomads often stay for months at a time. This extended residency provides stable economic input throughout the year, benefiting sectors like hospitality, transportation, and entertainment. Countries with off-peak tourism challenges, such as Croatia, use digital nomad visas to ensure steady activity in coastal and urban areas beyond the summer months.
Enhanced Global Competitiveness
Offering digital nomad visas signals that a country is modern, flexible, and technologically advanced. This enhances global competitiveness in the “race for talent,” attracting not only temporary residents but also investors, entrepreneurs, and companies seeking favorable business environments.
Cons
Housing Pressure and Affordability Issues
An influx of remote workers can increase demand for rental properties, driving up prices and potentially displacing local residents. In popular destinations such as Lisbon, rising rents have been partially attributed to growing numbers of digital nomads, creating concerns over housing affordability for locals.
Limited Local Economic Integration
Many digital nomads spend primarily within expatriate or nomad-oriented networks, which can limit their contribution to the broader local economy. While they pay for accommodation, cafes, and coworking spaces, engagement with traditional local businesses may be minimal, reducing potential economic spillover.
Infrastructure Strain
An increased population of remote workers may put pressure on internet bandwidth, public utilities, transportation, and coworking facilities. Countries need to invest in infrastructure to accommodate this influx without compromising services for permanent residents.
Complex Taxation and Regulatory Challenges
Ensuring compliance with tax laws for non-resident workers can be challenging. Countries must carefully design regulations to avoid loopholes or unintentional burdens, balancing income reporting, social security contributions, and residency obligations.
Short-Term Residency Limitations
Digital nomads typically stay for limited periods, meaning long-term benefits such as deep community integration or permanent economic contributions may be limited. Policymakers must manage expectations about the duration and impact of nomad residency to ensure sustainable benefits.
In summary, digital nomad visas present a promising opportunity for countries to stimulate economic activity, attract talent, and enhance global visibility. However, careful planning, regulatory clarity, and infrastructure investment are crucial to mitigate potential downsides such as housing pressure, limited integration, and tax complexities. Countries that strike this balance can harness digital nomad programs as a sustainable, mutually beneficial strategy in the modern era of work and mobility.
Why Should Individuals Opt for a Digital Nomad Visa?
For many professionals, the concept of working remotely from anywhere in the world is highly appealing, but it also comes with legal, logistical, and practical challenges. Digital nomad visas provide a formalized pathway that enables individuals to work abroad while ensuring compliance with immigration and labor laws. Choosing a digital nomad visa can be transformative, offering numerous personal, professional, and lifestyle benefits.
1. Legal Residency and Peace of Mind
One of the primary reasons to pursue a digital nomad visa is the legal certainty it provides. Unlike attempting to work abroad on a tourist visa—which is often illegal—digital nomad visas allow individuals to reside in a foreign country for extended periods without risking fines, deportation, or legal complications. This peace of mind enables professionals to focus on productivity and lifestyle rather than worrying about overstaying or violating local regulations.
For example, a freelancer from the United States can live and work legally in Estonia for up to 12 months under the country’s digital nomad visa, paying local taxes only as required and benefiting from clear residency rules. This legal clarity is essential for long-term planning and ensures that work abroad is sustainable and stress-free.
2. Enhanced Work-Life Flexibility
Digital nomad visas offer an unprecedented level of flexibility in combining professional obligations with personal exploration. Professionals can design schedules around local time zones, cultural experiences, and lifestyle preferences, making it easier to achieve a balance between productivity and leisure.
For instance, a remote worker in Portugal can take advantage of the country’s sunny climate, vibrant cities, and coastal towns to structure a day that blends work, outdoor activities, and cultural immersion. The ability to live and work in new environments encourages creativity, reduces burnout, and fosters a sense of freedom that traditional office-bound work cannot match.
3. Cultural Immersion and Personal Growth
Living abroad provides a unique opportunity for cultural enrichment. Digital nomads experience local customs, cuisine, language, and community life firsthand, which can broaden perspectives and improve cross-cultural communication skills. Exposure to diverse cultures often promotes empathy, adaptability, and resilience—qualities that are increasingly valuable in globalized professional settings.
For example, a nomad living in Croatia may participate in local festivals, learn basic Croatian, and interact with both locals and international professionals, creating a multi-dimensional experience that enriches both personal and professional life.
4. Networking and Professional Opportunities
Digital nomad visas enable individuals to connect with global communities, including fellow remote workers, entrepreneurs, and local business leaders. These connections can lead to collaboration opportunities, mentorship, and access to international markets. Cities like Lisbon and Tallinn have thriving coworking ecosystems where nomads regularly meet, exchange ideas, and form partnerships.
Such networking often extends beyond professional growth. Engaging with like-minded individuals in a dynamic, international environment can inspire innovation, spark entrepreneurial ventures, and open doors to projects that would be difficult to access from a home-based setting.
5. Lifestyle and Well-Being Benefits
For many professionals, lifestyle considerations are a major factor in choosing a digital nomad visa. Extended stays in desirable locations can improve mental health, reduce stress, and encourage a more balanced daily routine. Nomads can design their workspaces, choose outdoor activities, and explore surroundings that contribute to a healthier, more fulfilling life.
For example, a nomad in Barbados can combine work with beach walks, water sports, or cultural excursions, integrating relaxation and recreation into daily life. This lifestyle flexibility often results in increased motivation, creativity, and overall job satisfaction.
6. Potential Financial Advantages
In some cases, digital nomad visas offer favorable tax treatment or exemptions that can enhance financial efficiency. Countries may classify remote workers as non-resident for tax purposes, meaning income earned abroad is not subject to local income tax. While regulations vary, this can provide significant savings, making extended international living more feasible.
It is important for applicants to research local tax laws and consult with financial professionals to ensure compliance while optimizing benefits. Knowledge of these financial advantages allows individuals to make informed decisions about where and how to live as a digital nomad.
7. Career Advancement and Skill Development
Living abroad challenges individuals to adapt, solve problems independently, and manage remote work in diverse contexts. These experiences develop soft skills such as communication, resilience, time management, and cross-cultural competency—traits that enhance career prospects in an increasingly globalized workforce.
By combining professional work with international exposure, nomads can expand their skill set while building a portfolio of experiences that differentiates them in competitive job markets. Employers often value candidates who demonstrate adaptability, initiative, and global awareness—qualities naturally cultivated through digital nomad experiences.
In summary, a digital nomad visa is more than a legal document—it is a gateway to freedom, growth, and opportunity. It empowers individuals to work safely and legally abroad, explore new cultures, develop global networks, enhance well-being, and expand professional capabilities. For anyone seeking to blend work and travel in a sustainable, structured manner, digital nomad visas provide an ideal solution that balances legal certainty, lifestyle enrichment, and career advancement.
The Future of Work and Travel
The rise of digital nomad visas is just one manifestation of a broader transformation in how people approach work, mobility, and lifestyle. The traditional model of commuting to a fixed office location is increasingly being replaced by flexible, outcome-focused arrangements that prioritize productivity, well-being, and global engagement. This shift is driven by technological advancements, changing employee expectations, and a growing desire for meaningful work-life integration.
1. Remote Work as a Norm
Remote work is no longer a temporary adjustment but a permanent feature in many industries. Companies across technology, marketing, consulting, and creative sectors have adopted hybrid and fully remote models, recognizing that employees can maintain—or even increase—productivity outside the office. As businesses continue to embrace flexible arrangements, digital nomad visas will likely expand in relevance, offering formalized pathways for professionals to live and work internationally while remaining connected to their employers.
For example, multinational corporations are increasingly supporting employees who wish to temporarily relocate to other countries, allowing them to gain new perspectives and experiences while maintaining their current roles. This flexibility also helps organizations attract and retain top talent in competitive job markets.
2. Global Talent Mobility
The future of work is inherently global. With digital infrastructure enabling seamless communication and collaboration across borders, professionals can engage with teams, clients, and projects worldwide. Digital nomad visas are a practical response to this trend, creating legal and logistical frameworks that support cross-border work without the complications of traditional work permits.
Countries offering these visas are effectively building global talent hubs, attracting skilled professionals who may contribute to local economies, innovation ecosystems, and cultural exchange. Estonia, Portugal, and Barbados are early examples of nations that have successfully positioned themselves as attractive destinations for international remote workers, leveraging visa programs to enhance competitiveness.
3. Hybrid Work Models and Flexibility
The hybrid work model—combining remote and in-office work—will continue to grow. Digital nomad visas complement this approach by offering employees the option to live abroad for extended periods while maintaining access to office resources, mentorship, and team collaboration virtually.
This flexibility benefits both employers and employees. Organizations can reduce overhead costs associated with office space, while employees gain the autonomy to design their living and working environment. Cities and countries that provide supportive infrastructure, coworking spaces, and networking opportunities will become increasingly attractive for this mobile workforce.
4. Technological and Infrastructure Investments
As remote work and nomadic lifestyles expand, countries will continue investing in technological infrastructure, such as high-speed internet, digital services, and coworking facilities. Reliable connectivity and seamless online services are no longer optional—they are critical for attracting and retaining digital nomads.
For instance, Estonia’s e-government platform allows residents and nomads alike to access digital services efficiently, from business registration to tax filing. Similarly, coworking networks in Lisbon, Bali, and Medellín provide reliable spaces, networking opportunities, and community support, reflecting how infrastructure and technology shape the future of work and travel.
5. Cross-Cultural Collaboration and Global Workforces
The growing presence of remote professionals from different countries fosters a more interconnected, cross-cultural workforce. Teams will increasingly comprise individuals from diverse backgrounds, collaborating virtually across time zones and geographies. This global perspective enhances creativity, problem-solving, and innovation, providing organizations with competitive advantages in an interconnected economy.
Moreover, digital nomads themselves benefit from this exchange. Exposure to diverse work styles, business practices, and cultural perspectives cultivates adaptability, emotional intelligence, and international awareness—skills that are invaluable in a rapidly changing global market.
6. Sustainability and Lifestyle Considerations
The future of work and travel will also be influenced by sustainability concerns. Remote work and digital nomadism can reduce commuting-related emissions, promote environmentally conscious travel choices, and encourage decentralized living. However, the environmental impact of increased global mobility will require careful planning, such as responsible tourism practices, energy-efficient infrastructure, and policies that balance economic growth with ecological stewardship.
Simultaneously, lifestyle priorities will continue to shape where and how people choose to work. Professionals increasingly value experiences, wellness, and personal development alongside career advancement. Digital nomad visas align with these priorities, enabling individuals to explore new cultures, develop soft skills, and create fulfilling work-life integration.
7. Long-Term Implications for Work and Travel
Looking ahead, digital nomadism and flexible work arrangements are likely to become more mainstream. Governments, businesses, and professionals will adapt to a world where mobility, connectivity, and lifestyle are integral to career success. Visa programs, international labor laws, taxation rules, and infrastructure investments will evolve to accommodate this new paradigm.
Ultimately, the convergence of remote work, global mobility, and digital nomad visas signals a future where work is defined less by location and more by outcomes, engagement, and personal fulfillment. Countries that embrace this evolution, invest in supportive infrastructure, and provide clear legal pathways for remote professionals will be better positioned to thrive in a highly interconnected, mobile global economy.
Conclusion
Digital nomad visas epitomize the transformation of work in the 21st century. By enabling professionals to reside and work legally in foreign countries, these visas support economic growth, cultural exchange, and personal fulfillment. Countries offering these visas benefit from tourism revenue, international talent, and enhanced global reputation, while individuals gain flexibility, legal certainty, and the chance to explore diverse cultures.
While challenges exist—including regulatory complexities, infrastructure demands, and integration limitations—the benefits of digital nomad visas for both host nations and professionals are significant. As remote work continues to expand, these visas are likely to become an integral component of global mobility strategies, reflecting a future where work and travel coexist seamlessly.
For aspiring nomads and policymakers alike, understanding the opportunities and challenges of digital nomad visas is essential. With careful planning, digital nomad visas can transform the way people live, work, and experience the world—turning professional mobility into a gateway for cultural enrichment, economic growth, and personal exploration.