- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Agile Work?
- Why is Agile the Future of Work?
- Rapid Technological Change
- Dynamic Market Conditions
- Employee Expectations
- Focus on Customer Experience
- Collaboration and Communication
- Enhanced Innovation
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity
- Principles of an Agile Workplace
- 1. Customer Collaboration
- 2. Embracing Change
- 3. Cross-Functional Teams
- 4. Iterative Development
- 5. Empowerment and Autonomy
- 6. Continuous Improvement
- 7. Transparency and Open Communication
- Agile vs. Traditional Work: Key Differences
- Agile Tools and Technologies
- 1. Project Management Tools
- 2. Communication Platforms
- 3. Collaboration Tools
- 4. Version Control Systems
- 5. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
- 6. Feedback and Survey Tools
- 7. Analytics and Reporting Tools
- How to Create an Agile Culture in Your Workplace
- 1. Leadership Commitment
- 2. Empower Teams
- 3. Promote Collaboration
- 4. Embrace Continuous Learning
- 5. Foster a Customer-Centric Mindset
- 6. Implement Agile Practices
- 7. Measure and Celebrate Success
- 8. Encourage Open Communication
- Skills Required in the Agile Future
- Adaptability:
- Collaboration:
- Critical Thinking:
- Technical Proficiency:
- Customer-Centric Mindset:
- Continuous Learning:
- Conclusion
Introduction
The landscape of work is evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven by technological advancements, shifting workforce dynamics, and the need for greater flexibility and responsiveness. This blog post delves into the concept of agile work, exploring its significance in modern workplaces and outlining the principles, tools, and culture that define this approach. As organizations strive to adapt to changing market conditions and employee expectations, understanding the future of agile work becomes essential for leaders and teams alike.
What is Agile Work?
Agile work refers to a flexible, iterative approach to project management and organizational processes that emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and customer-centricity. Originating from software development methodologies, particularly the Agile Manifesto created in 2001, the principles of agile work have since transcended their initial domain, influencing various industries and sectors.
At its core, agile work prioritizes delivering value to customers quickly and efficiently. This is achieved through cross-functional teams that work in short cycles, known as sprints, allowing for continuous feedback and improvement. Agile work fosters an environment where teams can respond swiftly to changes, experiment with new ideas, and collaborate effectively, leading to innovative solutions and enhanced productivity.
Why is Agile the Future of Work?
The shift towards agile work is not merely a trend; it is a response to the rapidly changing landscape of business and society. Several compelling factors illustrate why agile methodologies are increasingly becoming the preferred approach for organizations across various industries:
Rapid Technological Change
The pace of technological advancement is accelerating, leading to constant disruptions in traditional business models. Organizations must adapt quickly to leverage new technologies, whether through automation, artificial intelligence, ordata analytics. Agile methodologies facilitate this adaptability by allowing teams to implement changes incrementally, test new technologies, and pivot based on real-time feedback. This iterative process helps businesses stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge.
Dynamic Market Conditions
Markets are more volatile than ever, influenced by global economic shifts, consumer behavior changes, and unforeseen crises, such as pandemics or geopolitical tensions. Agile work empowers organizations to respond swiftly to these fluctuations. By breaking projects into manageable sprints, teams can adjust their strategies based on market feedback and emerging trends. This responsiveness not only mitigates risks but also enhances the organization’s ability to capitalize on new opportunities as they arise.
Employee Expectations
Today's workforce, particularly younger generations, prioritizes flexibility, autonomy, and meaningful work. Employees seek environments where they can contribute creatively and see the impact of their efforts. Agile work cultures promote these values by encouraging collaboration, empowering teams to make decisions, and fostering a sense of ownership over projects. Organizations that embrace agile practices often experience higher employee satisfaction and retention rates, as workers feel more engaged and valued.
Focus on Customer Experience
In an age where customer experience can make or break a business, agile work places a strong emphasis on understanding and meeting customer needs. Agile methodologies involve customers throughout the development process, encouraging regular feedback and collaboration. This customer-centric approach ensures that products and services are tailored to the target audience, enhancing satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately driving revenue. Companies that prioritize customer experience through agile practices are better positioned to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
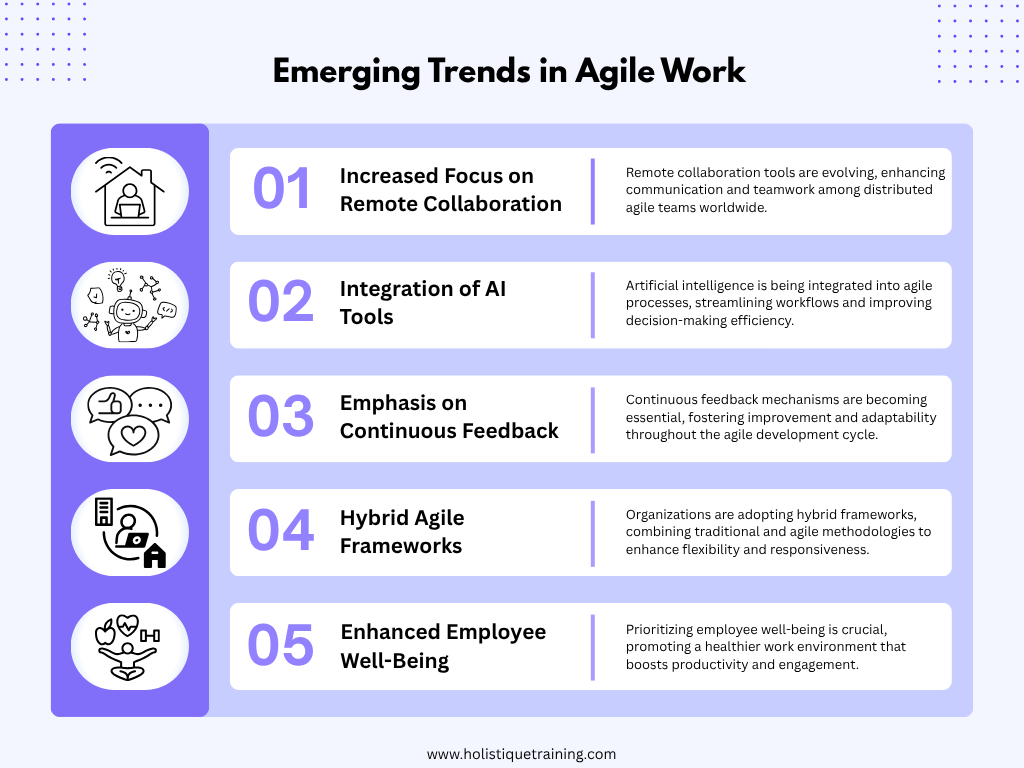
Collaboration and Communication
Agile work fosters a culture of collaboration and open communication, breaking down silos that often exist in traditional hierarchical structures. By promotingcross-functional teams, agile methodologies encourage diverse perspectives and collective problem-solving. This collaborative environment leads to more innovative solutions and faster decision-making, as teams are empowered to share ideas and insights freely. Enhanced communication also helps to build trust among team members, further strengthening the organization's culture.
Enhanced Innovation
Innovation is critical for long-term success, and agile work inherently encourages experimentation and creativity. The iterative nature of agile methodologies allows teams to test new ideas quickly, learn from failures, and iterate on their solutions. This approach reduces the fear of failure, as teams are encouraged to experiment without the pressure of delivering a perfect final product. Organizations that embrace this mindset often find themselves at the forefront of industry innovation, continuously evolving their offerings to meet changing demands.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Agile work is designed to enhance efficiency by streamlining processes and eliminating unnecessary bureaucracy. By focusing on delivering small, incremental improvements, teams can achieve quick wins that contribute to larger goals. This focus on continuous improvement not only boosts productivity but also helps organizations allocate resources more effectively. Agile practices encourage teams to prioritize tasks based on value, ensuring that efforts are aligned with strategic objectives.
The future of work is undeniably agile, driven by the need for organizations to adapt to rapid changes in technology, market conditions, and employee expectations. By embracing agile methodologies, businesses can foster a culture of collaboration, innovation, and responsiveness that positions them for success in an increasingly complex environment. As agile practices continue to gain traction, organizations that prioritize agility will be better equipped to navigate challenges and seize opportunities in the years to come.
Principles of an Agile Workplace
Creating an agile workplace involves adopting a set of foundational principles that guide teams and organizations in their operations. These principles not only enhance collaboration and efficiency but also foster a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability. Here are some key principles that define an agile workplace:
1. Customer Collaboration
At the heart of agile work is a strong emphasis on customer collaboration. Agile teams prioritize engaging with customers throughout the development process, rather than waiting until the end to gather feedback. This ongoing interaction ensures that the products or services being developed align closely with customer needs and expectations. By involving customers early and often, teams can make informed decisions that enhance user satisfaction and loyalty. This principle shifts the focus from merely delivering a product to delivering value that resonates with the target audience.
2. Embracing Change
Agile workplaces thrive on the ability to embrace change rather than resist it. In a rapidly evolving business landscape, flexibility is crucial. According to Deloitte’s 2024 Global Human Capital Trends Report,87% of executives believe that navigating constant change is essential for their organization’s success; however, only 45% feel prepared to lead through such uncertainty. Agile teams view changes—whether they stem from market shifts, customer feedback, or new technologies—as opportunities for growth and improvement. This mindset encourages teams to be proactive in adapting their strategies and processes, fostering resilience and innovation. By cultivating an environment where change is welcomed, organizations can respond more effectively to challenges and seize new opportunities.
3. Cross-Functional Teams
Agile work emphasizes the importance of cross-functional teams, which bring together individuals with diverse skill sets and expertise. These teams are empowered to collaborate on projects, leveraging their varied perspectives to solve complex problems. By breaking down silos and encouraging collaboration across departments, agile workplaces foster a culture of knowledge sharing and creativity. This diversity not only enhances problem-solving capabilities but also leads to more innovative solutions, as team members challenge each other's assumptions and contribute unique insights.
4. Iterative Development
The principle of iterative development is fundamental to agile methodologies. Instead of attempting to deliver a complete product in one go, agile teams work in short cycles, known as sprints. Each sprint focuses on delivering a small, functional increment of the product, allowing teams to gather feedback and make adjustments quickly. This iterative approach minimizes risk, as teams can identify and address issues early in the process. It also enables organizations to respond to changing requirements and market conditions, ensuring that the final product is aligned with customer needs.
5. Empowerment and Autonomy
Agile workplaces empower employees by granting them the autonomy to make decisions related to their work. This principle fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, as team members are encouraged to take initiative and contribute their ideas. When employees feel trusted to make decisions, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated, leading to higher levels of productivity and creativity. Empowerment also encourages individuals to take risks and experiment with new approaches, driving innovation within the organization.
6. Continuous Improvement
A commitment to continuous improvement is a hallmark of agile workplaces. Agile teams regularly reflect on their processes, outcomes, and performance, seeking ways to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. This practice, often referred to as retrospectives, allows teams to identify areas for improvement and implement changes based on collective insights. By fostering a culture of learning and adaptation, organizations can ensure that they are always evolving and optimizing their operations. This principle not only drives individual and team growth but also contributes to the overall success of the organization.
7. Transparency and Open Communication
Transparency and open communication are essential components of an agile workplace. Agile teams thrive in environments where information is freely shared, enabling team members to make informed decisions and collaborate effectively. Regular check-ins, stand-up meetings, and progress updates foster a culture of accountability and trust. When team members are aware of each other's work and challenges, they can support one another and address issues collaboratively. This openness enhances team cohesion and ensures that everyone is aligned toward common goals.
The principles of an agile workplace serve as a foundation for fostering a culture of collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement. By prioritizing customer collaboration, embracing change, and empowering teams, organizations can navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape with confidence. These principles not only enhance productivity and innovation but also create an environment where employees feel valued and engaged. As businesses continue to evolve, embracing these agile principles will be essential for achieving long-term success and resilience.
Agile vs. Traditional Work: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between agile and traditional work models is crucial for organizations considering a shift to agile practices. Here are some of the key distinctions:
Aspect | Traditional Work | Agile Work |
Structure | Hierarchical and rigid | Flat and flexible |
Planning | Long-term planning with fixed timelines | Short-term planning with adaptability |
Decision-Making | Centralized decision-making | Decentralized and collaborative |
Feedback | Infrequent and often retrospective | Frequent and ongoing |
Customer Involvement | Limited to end of the project | Continuous involvement throughout |
Team Dynamics | Siloed departments | Cross-functional collaboration |
Risk Management | Risk-averse and cautious | Embraces risk as part of the process |
These differences highlight how agile work fosters a more dynamic and responsive organizational culture, enabling teams to thrive in a fast-paced environment.
Agile Tools and Technologies
To effectively implement agile practices, organizations can leverage a variety of tools and technologies designed to enhance collaboration, communication, and project management. Some popular agile tools include:
1. Project Management Tools
Project management tools play a crucial role in agile environments by providing teams with a structured framework to plan, track, and manage their work. These tools enable teams to break down projects into manageable tasks, assign responsibilities, and set deadlines. By visualizing workflows, teams can easily monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and adjust priorities as needed. The ability to create and manage backlogs, sprints, and iterations helps teams stay organized and focused on delivering incremental value. Overall, project management tools enhance transparency and accountability within teams, ensuring everyone is aligned and aware of project statuses.
2. Communication Platforms
Effective communication is fundamental to the success of agile teams, particularly in environments where team members may be working remotely or across different locations. Communication platforms facilitate real-time interactions, allowing team members to share ideas, provide updates, and resolve issues quickly. These tools support both synchronous (live) and asynchronous (delayed) communication, enabling teams to collaborate effectively regardless of time zones. By fostering open lines of communication, these platforms enhance team cohesion and ensure that everyone is informed about project developments and changes.
3. Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools are essential for promoting teamwork and facilitating joint efforts among team members. These tools enable individuals to work together seamlessly, whether they are brainstorming ideas, sharing documents, or conducting discussions. Features such as file sharing, co-editing, and commenting allow for dynamic collaboration, ensuring that all team members can contribute their insights and expertise. By breaking down geographical barriers and encouraging collaborative problem-solving, these tools help teams leverage diverse perspectives and drive innovation.
4. Version Control Systems
For teams involved in software development, version control systems are vital for managing changes to codebases. These systems allow multiple developers to work on the same project simultaneously without conflicts, enabling efficient collaboration. By tracking changes and maintaining a history of revisions, version control systems provide a safety net, allowing teams to revert to previous versions if necessary. This capability is particularly important in agile environments, where iterative development and frequent updates are common. Version control systems enhance code quality and facilitate smoother integration of new features.
5. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
CI/CD tools automate the processes of integrating code changes and deploying them to production environments. These tools are crucial for agile teams, as they enable frequent and reliable releases of software. By automating testing and deployment, CI/CD tools reduce the risk of errors and ensure that new features are delivered quickly and efficiently. This automation supports the agile principle of iterative development, allowing teams to gather feedback and make improvements rapidly. The ability to deploy changes frequently also enhances responsiveness to customer needs and market demands.
6. Feedback and Survey Tools
Gathering feedback is a cornerstone of the agile process, and feedback tools help organizations capture insights from customers, stakeholders, and team members. These tools enable teams to conduct surveys, polls, and interviews to gather valuable input on products and services. By integrating feedback into the development process, teams can make informed decisions and prioritize features that align with customer needs. This focus on continuous feedback ensures that the final product is not only functional but also resonates with users, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
7. Analytics and Reporting Tools
Analytics and reporting tools provide teams with the ability to measure performance, track progress, and analyze data related to their projects. These tools help teams assess key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and evaluate the effectiveness of their processes. By leveraging data-driven insights, teams can make informed decisions, optimize workflows, and continuously improve their practices. Analytics tools also support transparency, allowing stakeholders to gain visibility into project statuses and outcomes.
The diverse array of agile tools and technologies plays a pivotal role in enabling organizations to implement agile methodologies effectively. By enhancing project management, communication, collaboration, and feedback processes, these tools empower teams to work more efficiently and respond to changes with agility. As organizations continue to embrace agile practices, investing in the right tools and technologies will be essential for fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Ultimately, these tools not only streamline processes but also contribute to the overall success and resilience of agile teams in a dynamic business environment.
How to Create an Agile Culture in Your Workplace
Establishing an agile culture within an organization is essential for fostering flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. An agile culture encourages teams to embrace change, prioritize customer needs, and work collaboratively towards common goals. Here are some key strategies to create and nurture an agile culture in your workplace:
1. Leadership Commitment
Creating an agile culture starts at the top. Leadership must demonstrate a commitment to agile principles and practices by modeling the behaviors they wish to see throughout the organization. Leaders should actively promote agility by being open to feedback, embracing change, and encouraging experimentation. By championing agile values, leaders can inspire teams to adopt similar mindsets, fostering a culture of trust and empowerment.
2. Empower Teams
Empowering teams is a fundamental aspect of an agile culture. Organizations should encourage autonomy by giving teams the authority to make decisions related to their work. This empowerment fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, motivating team members to take initiative and contribute their ideas. When employees feel trusted to make decisions, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to achieving team goals. Encouraging self-organizing teams allows for greater flexibility and responsiveness to changing circumstances.
3. Promote Collaboration
Collaboration is at the heart of agile methodologies. Organizations should create an environment that encourages teamwork and open communication. This can be achieved through regular team meetings, collaborative workspaces, and the use of digital collaboration tools. Encouraging cross-functional teams can also enhance collaboration by bringing together diverse perspectives and expertise. By fostering a culture of collaboration, organizations can leverage the collective intelligence of their workforce, leading to more innovative solutions and improved problem-solving.
4. Embrace Continuous Learning
An agile culture thrives on continuous learning and improvement. Organizations should encourage employees to seek out opportunities for professional development, whether through training programs, workshops, or knowledge-sharing sessions. Creating a safe space for experimentation allows teams to learn from failures without fear of repercussions. Regular retrospectives should be held to reflect on successes and challenges, enabling teams to identify areas for improvement and implement changes based on collective insights. This commitment to learning helps organizations adapt to new challenges and stay ahead of industry trends.
5. Foster a Customer-Centric Mindset
A customer-centric approach is essential for an agile culture. Organizations should prioritize understanding and meeting customer needs at every stage of the development process. Encouraging teams to gather customer feedback regularly and involve customers in product development can help ensure that offerings align with market demands. By fostering a culture that values customer insights, organizations can enhance satisfaction, build loyalty, and drive business success.
6. Implement Agile Practices
To create an agile culture, organizations should adopt agile practices and frameworks that align with their goals. This may include implementing Scrum, Kanban, or other agile methodologies that promote iterative development, regular feedback, and continuous improvement. Training employees on these methodologies and providing the necessary tools and resources can help facilitate the transition to an agile way of working. By embedding agile practices into daily operations, organizations can reinforce agile values and behaviors.
7. Measure and Celebrate Success
Tracking progress and celebrating successes is vital for reinforcing an agile culture. Organizations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with agile principles, such as customer satisfaction, team velocity, and quality of deliverables. Regularly reviewing these metrics allows teams to assess their performance and identify areas for improvement. Furthermore, research fromWorkhuman indicates that employees who receive meaningful recognition are 20 times more likely to be engaged compared to those who receive little acknowledgment. This highlights the importance of human-first leadership in motivating teams. Recognizing and celebrating achievements—whether big or small—helps to reinforce the value of agility. Celebrations can take the form of team shout-outs, awards, or informal gatherings, fostering a sense of community and shared purpose.
Metric | Description |
Customer Satisfaction | Measures how well the product meets customer needs and expectations. |
Team Velocity | Tracks the amount of work completed in a given iteration, often measured in story points. |
Quality of Deliverables | Assesses the defect rate and overall quality of the products delivered to customers. |
Cycle Time | Measures the time taken from the start of work on a feature to its completion. |
Employee Engagement | Evaluates the level of team members' commitment and involvement in their work. |
8. Encourage Open Communication
Open communication is critical for fostering an agile culture. Organizations should create channels for transparent communication where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas, concerns, and feedback. Regular check-ins, stand-up meetings, and feedback sessions can help facilitate open dialogue and ensure that everyone is aligned on goals and expectations. Encouraging a culture of psychological safety, where employees feel safe to express their thoughts without fear of judgment, is essential for promoting honest communication and collaboration.
Creating an agile culture in the workplace requires a deliberate and sustained effort across all levels of the organization. By committing to agile principles, empowering teams, promoting collaboration, and fostering continuous learning, organizations can cultivate an environment that embraces change and innovation. As teams become more agile, they will be better equipped to respond to challenges, meet customer needs, and drive business success in a dynamic and competitive landscape. Ultimately, an agile culture not only enhances organizational performance but also contributes to a more engaged and motivated workforce.
Skills Required in the Agile Future
As the workplace continues to evolve, certain skills will become increasingly important for success in an agile environment. Key skills include:
Adaptability:
The ability to adjust to changing circumstances and embrace new challenges is crucial in an agile workplace.
Collaboration:
Strong interpersonal skills and the ability to work effectively in diverse teams are essential for fostering collaboration.
Critical Thinking:
Agile teams must analyze problems, evaluate options, and make informed decisions quickly.
Technical Proficiency:
Familiarity with agile tools and technologies is important for effective project management and collaboration.
[Agile Project Portfolio Management Post-COVID course]
Customer-Centric Mindset:
Understanding customer needs and incorporating feedback into the development process is vital for delivering value.
Continuous Learning:
A commitment to ongoing learning and professional development is essential for staying relevant in an agile landscape.
By cultivating these skills, individuals can position themselves for success in the agile future of work.
Conclusion
The future of work is undeniably agile, reflecting a fundamental shift in how organizations operate and respond to challenges. Embracing agile principles, tools, and practices not only enhances productivity but also fosters a culture of collaboration, innovation, and customer-centricity. As businesses navigate the complexities of the modern workplace, understanding and implementing agile work can provide a competitive advantage, ensuring that organizations remain responsive and resilient in an ever-changing environment. By investing in agile culture and skills, leaders can prepare their teams for the future, unlocking new opportunities for growth and success.