- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Organisational Change Management?
- What Causes Organisational Change?
- Steps for Organisational Change Management
- Change Management Resources
- The Psychological Side of Change
- The Role of Leadership in Change Management
- The Cultural Transformation: Unleashing Organisational Potential
- Conclusion
Introduction
Change is an inevitable and constant aspect of life, and the same principle applies to organisations. Organisational Change Management (OCM) is the process of strategically planning and implementing alterations within a company to improve its performance, increase its efficiency, and ultimately achieve its goals and objectives. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the concept of Organisational Change Management, exploring its underlying causes, the essential steps for effective implementation, and valuable resources to guide organisations through the process.
What Is Organisational Change Management?
Organisational Change Management (OCM) is much more than a buzzword or a management trend; it is a philosophy that recognises the importance of the human element in the success of organisational transformations. OCM involves a systematic approach that considers the impact of change on individuals, teams, and the overall organisation. By acknowledging that employees are the heart and soul of any company, OCM seeks to minimise resistance, enhance acceptance, and foster a culture of collaboration and adaptability.
The Human Element
Effective OCM requires a deep understanding of the complexities of human behaviour and emotions. It involves empathy, communication, and strong leadership to create an environment where employees feel valued and supported throughout the change process. OCM isn't about imposing change from the top down; it's about engaging employees, building trust, and empowering them to embrace and drive change.
What Causes Organisational Change?
Organisational change is not a random occurrence but rather a response to a multitude of internal and external factors. Understanding these drivers is crucial for organisations to proactively prepare for and effectively manage change. Here, we delve deeper into the various causes of organisational change:
External Market Forces
The dynamic nature of markets is one of the most potent catalysts for change. Markets are in a constant state of flux, influenced by factors like economic conditions, consumer behaviour, technological advancements, and competitive pressures. To remain relevant and competitive, organisations must adapt swiftly. For example, the rise of e-commerce dramatically shifted consumer buying habits, compelling traditional retailers to reevaluate their strategies and embrace online sales channels. Failure to adapt can result in declining market share and a loss of competitive advantage.
Leadership and Strategy
Changes in leadership often bring about changes in strategic direction. New leaders may introduce fresh visions, goals, and priorities, necessitating corresponding shifts within the organisation. For instance, a newly appointed CEO might prioritise innovation and digital transformation, requiring the organisation to realign its resources and focus. These strategic shifts can trigger a cascade of changes throughout the organisation, impacting everything from culture to processes.
Merger and Acquisition
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) represent a significant driver of organisational change. When organisations merge or undergo acquisition, they often bring together different cultures, structures, and processes. Effectively managing this integration is essential for ensuring a smooth transition and realising the anticipated benefits of the deal. This may involve consolidating redundant functions, harmonising corporate cultures, and redefining roles and responsibilities. Failure to manage M&A-related changes effectively can result in employee disengagement and operational disruptions.
Technological Advancements
The relentless pace of technological advancements is another force behind organisational change. Embracing new technologies or undergoing digital transformations can significantly impact workflows, job roles, and communication channels. Organisations must adapt to remain competitive and meet evolving customer expectations. For example, the advent of artificial intelligence and automation has led to changes in how customer service is delivered, with chatbots and virtual assistants becoming common tools for enhancing customer interactions. Adapting to these technologies requires training, process adjustments, and often, changes in employee roles and skill sets.
Regulatory Compliance
Changes in laws, regulations, or industry standards can necessitate organisational adjustments. Ensuring compliance is not only essential for avoiding legal issues but also for maintaining the trust of customers, partners, and stakeholders. For instance, new data protection regulations like the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) forced many organisations worldwide to overhaul their data handling practices, implement stricter security measures, and update their privacy policies. Failure to adapt to regulatory changes can result in legal penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
Internal Performance Issues
Sometimes, organisational change is driven by internal factors, such as declining productivity, inefficiencies, or operational bottlenecks. Recognising these issues and addressing them through change management is essential for improving an organisation's overall performance. Process optimisation, organisational restructuring, and the adoption of new technologies are common strategies to overcome these internal challenges. For example, a manufacturing company experiencing production bottlenecks may implement lean manufacturing principles and invest in automation to streamline its operations.
In summary, the causes of organisational change are diverse and dynamic, reflecting the complex interplay between external and internal factors. Recognising these drivers and their implications is vital for organisations seeking to thrive in an ever-evolving business landscape. Successful change management involves not only reacting to these forces but also proactively shaping the organisation's trajectory to meet future challenges and opportunities head-on.
Steps for Organisational Change Management
Navigating organisational change is akin to embarking on a carefully orchestrated journey. It requires a structured approach that considers the unique needs of the organisation, its employees, and the broader context of the business environment. Here, we explore each step in the process of Organisational Change Management in greater detail:
Table: Key Steps for Organisational Change Management
Step | Description |
Assess the Need for Change | Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the organisation to understand its current state and desired future state. |
Create a Vision for Change | Develop a clear and compelling vision for the change initiative, communicating its benefits and expected outcomes. |
Build a Change Management Team | Establish a diverse team of change agents and subject matter experts to lead and support the change initiatives. |
Develop a Comprehensive Plan | Create a detailed change management plan outlining actions, timelines, resource requirements, and mitigation strategies. |
Communicate Effectively | Foster transparent and consistent communication to build understanding and address concerns among stakeholders. |
Empower and Engage Employees | Actively involve employees in the change process, seek their input, and provide opportunities for skill development. |
Monitor Progress and Adapt | Regularly assess progress and be prepared to make adjustments to the change management plan based on feedback. |
Provide Support and Resources | Offer continuous support through coaching, mentoring, and resources to aid in understanding and adopting new practices. |
Step 1: Assess the Need for Change
The journey begins with a comprehensive assessment of the organisation's current state. Engaging stakeholders, including employees, leaders, and customers, is vital to gain a thorough understanding of the existing challenges and opportunities. This phase involves analysing data, conducting surveys, and holding discussions to identify pain points and areas that require improvement. Understanding the need for change is foundational—it sets the stage for the entire change management process.
Step 2: Create a Vision for Change
With a clear understanding of the need for change, the next step is to develop a compelling vision that outlines the reasons for change, the benefits it will bring, and the expected outcomes. This vision serves as a guiding light, aligning the organisation's efforts and motivating stakeholders. Effective communication of this vision is key; it should resonate with employees at all levels and inspire them to commit to the change journey. A well-crafted vision instils a sense of purpose and direction, ensuring that everyone understands why the change is necessary.
Step 3: Build a Change Management Team
Change is a team effort, and assembling a dedicated team of change agents and subject matter experts is essential. This team should represent various departments and levels within the organisation to ensure inclusivity and diversity of perspectives. These change champions will play a pivotal role in guiding and supporting the change initiatives. Their responsibilities may include fostering buy-in among colleagues, providing expertise, and helping to address concerns.
Step 4: Develop a Comprehensive Change Management Plan
A well-structured plan is the roadmap that guides successful change implementation. It outlines specific actions, timelines, and resource requirements for each phase of the change process. The plan should also address potential challenges and risks, along with mitigation strategies. A comprehensive plan serves as a reference point for all stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is aligned and aware of their roles and responsibilities. It also allows for flexibility, enabling the organisation to adapt to unforeseen circumstances or new insights as the change unfolds.
Step 5: Communicate Effectively
Transparent and consistent communication is the backbone of successful change management. Communicating the vision, objectives, and progress of the change initiative must occur regularly and through multiple channels. Effective communication fosters understanding, addresses concerns, builds trust, and keeps employees and stakeholders informed. Open dialogue is encouraged, and leaders should be receptive to feedback, making adjustments as needed. In essence, communication ensures that everyone is on the same page and understands their role in the change journey.
Step 6: Empower and Engage Employees
Actively involving employees in the change process is a cornerstone of successful change management. Seek their input, encourage their participation, and provide opportunities for skill development and training to support them during the transition. Empowered employees are more likely to embrace change and become advocates for it. Empowerment also extends to decision-making, giving employees a sense of ownership in the change process. Engagement activities such as workshops, training sessions, and feedback mechanisms further solidify their commitment to the change.
Step 7: Monitor Progress and Adapt
Change is not a linear process; it evolves over time. Regularly assessing the progress of the change initiative against predefined key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential. These KPIs should align with the goals set in the vision for change. Staying agile and being prepared to make adjustments to the change management plan based on feedback and evolving circumstances is critical. Continuous monitoring allows organisations to spot potential issues early, celebrate small wins, and ensure the change remains aligned with the initial vision.
Step 8: Provide Support and Resources
Change can be challenging for individuals and teams. Offering continuous support through coaching, mentoring, and resources that aid in understanding and adopting the new practices is crucial. Celebrating small wins along the way helps maintain momentum and enthusiasm. Support also extends to addressing any emotional or psychological challenges that employees may face during the change journey, reinforcing the organisation's commitment to their well-being.
These steps represent a holistic approach to Organisational Change Management. Each step is interdependent, and together, they create a structured framework for successfully navigating the complexities of change. By following these steps diligently, organisations can embrace change as an opportunity for growth, innovation, and improvement, ultimately positioning themselves for long-term success in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Change Management Resources
A successful change management journey relies on leveraging the right resources. Here are some valuable resources that can support organisations through the change process:
Change Management Models
Several change management models offer frameworks that guide organisations through different aspects of the change journey. For instance, Kotter's 8-Step Model emphasises the importance of creating a sense of urgency, forming a powerful coalition, and anchoring the change in the organisation's culture.
Training and Development Programmes
Change management training equips employees, leaders, and change agents with essential skills and tools to manage change effectively. These programmes may focus on communication, emotional intelligence, conflict resolution, and leadership during times of transition.
Change Management Software
Digital tools and platforms can streamline change management processes, facilitate collaboration, and provide real-time insights into project progress. Such software often integrates project management, communication, and reporting features. Some examples of such software tools would be Wrike, SysAid, and Whatfix.
Change Management Consultants
Engaging external change management experts can bring specialised knowledge and experience to complex change projects. Consultants can provide objective assessments, offer fresh perspectives, and guide organisations through potential roadblocks.
The Psychological Side of Change
Change is not just a process; it's also a psychological journey. Understanding the psychological aspects of change can greatly aid in its successful management. Let's explore this in more detail:
The Change Curve
The Change Curve, a concept developed by psychiatrist Elisabeth Kübler-Ross, identifies the emotional stages individuals go through when faced with significant change. These stages include shock, denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance. Recognising where individuals are on this curve can help tailor communication and support strategies accordingly.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common response, and it can be rooted in fear, uncertainty, or a perceived loss of control. Addressing resistance requires empathy, active listening, and providing a clear rationale for the change. It's essential to acknowledge and validate employees' concerns while also emphasising the benefits of the change.
The Role of Leadership in Change Management
Leaders play a pivotal role in guiding organisations through change. Here are some key leadership qualities and actions that can make a difference:
Visionary Leadership
Effective leaders communicate a compelling vision for change that inspires and motivates employees. They articulate the "why" behind the change and help people connect emotionally with the new direction.
Leading by Example
Leaders who lead by example demonstrate their commitment to change. When employees see leaders actively embracing the change, they are more likely to follow suit.
Active Communication
Leaders should maintain open and frequent communication with employees throughout the change process. This includes not only sharing information but also actively seeking feedback and addressing concerns.
Empathy and Support
Empathetic leaders understand the challenges employees may face during change. They provide emotional support, recognise individual efforts, and celebrate achievements.
The Cultural Transformation: Unleashing Organisational Potential
While we've discussed the importance of Organisational Change Management (OCM) as a structured process for managing change, it's equally essential to explore the profound impact that change can have on an organisation's culture. Cultural transformation is an intriguing aspect of OCM that goes beyond processes and strategies, focusing on the very essence of an organisation.
Defining Organisational Culture
Organisational culture encompasses the shared values, beliefs, behaviours, and norms that define how an organisation operates. It's the "personality" of the company, influencing everything from employee interactions to decision-making processes. A strong and positive culture is often linked to increased employee engagement, higher productivity, and improved customer satisfaction.
Culture and Change: A Symbiotic Relationship
When an organisation embarks on a change journey, it has a unique opportunity to shape and refine its culture. Change can act as a catalyst for cultural transformation, and here's how it works:
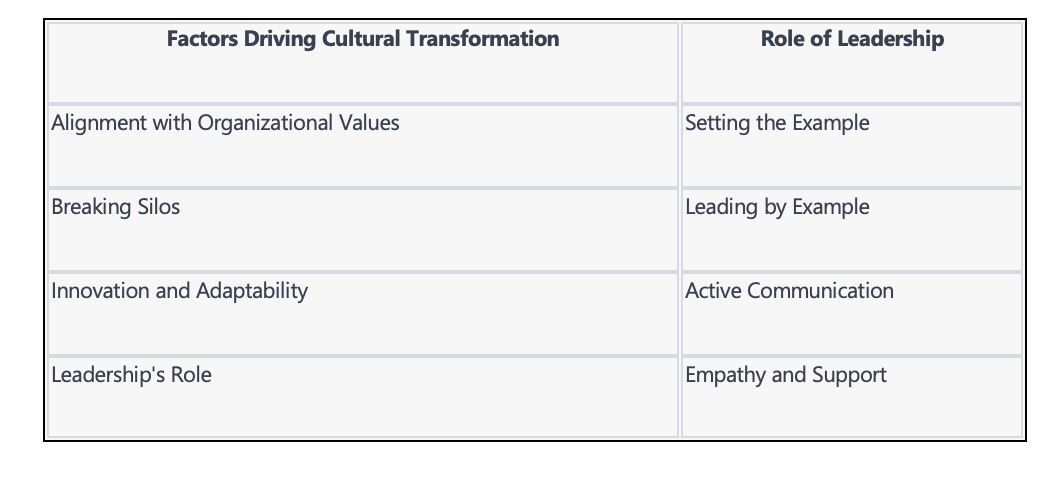
Alignment with Values
Change initiatives that align with an organisation's core values reinforce those values among employees. When employees see that change is consistent with what the organisation stands for, they are more likely to embrace it.
Breaking Silos
Change often requires cross-functional collaboration. As teams from different departments come together to implement change, it can break down silos and foster a culture of collaboration and teamwork.
Innovation and Adaptability
Change encourages organisations to innovate and become more adaptable. Cultures that embrace change are more likely to encourage innovation, experimentation, and learning.
Leadership's Role
Leaders play a crucial role in modelling the desired culture during change. Their actions, decisions, and behaviours send a powerful message about the organisation's culture.
Employee Involvement
Engaging employees in the change process empowers them and reinforces a culture of participation and shared responsibility.
Cultural Transformation Challenges
While cultural transformation through change can be immensely beneficial, it's not without challenges. Here are some common hurdles organisations may encounter:
Resistance to Cultural Change
Just as there can be resistance to change in general, employees may resist shifts in culture if they perceive it as too drastic or incompatible with their existing beliefs.
Cultural Clash in Mergers
In mergers and acquisitions, merging two different organisational cultures can be complex and may require careful navigation to create a harmonious, unified culture.
Sustainability
Sustaining cultural transformation over the long term can be challenging. It requires ongoing commitment, reinforcement, and a clear vision of the desired culture.
The Role of Leadership in Cultural Transformation
Leadership is pivotal in shaping and nurturing the desired culture during change. They must:
Set the Example
Leaders should model the values and behaviours they want to see in the organisation.
Communicate Culture
Clearly communicate the desired culture and its importance to employees.
Empower Cultural Champions
Identify and empower cultural champions within the organisation to drive cultural change at all levels.
Measure Progress
Establish metrics to track cultural transformation progress, and be willing to adjust strategies as needed.
Conclusion
Organisational Change Management is a fundamental discipline that enables businesses to adapt, innovate, and thrive in an ever-changing landscape. By recognising the significance of the human element, embracing transparency, and leveraging valuable resources, organisations can navigate the seas of transformation successfully. A culture that embraces change as an opportunity for growth and improvement fosters resilience and positions the organisation for long-term success. Empowered employees, clear communication, and effective planning are the winds that steer organisations toward a brighter future. With Organisational Change Management as their compass, organisations can confidently navigate change and emerge stronger, more agile, and ready to embrace the challenges and opportunities of tomorrow.
Don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter! Fresh insights, tips, and updates delivered every week.