- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Upskilling?
- Why is Lifelong Learning and Upskilling Important in the Workplace?
- Adaptation to Change
- Career Advancement
- Organizational Growth
- Employee Retention
- Meeting Industry Standards
- Fostering a Culture of Innovation
- Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills
- Building Resilience
- Statistics on the Importance of Upskilling
- Upskilling vs. Reskilling: Key Differences
- Why is Every 6 Months the Ideal Time for Upskilling?
- Rapid Technological Advances
- Market Demand Fluctuations
- Enhanced Retention of Knowledge
- Building a Habit of Learning
- Career Agility
- Networking and Collaboration Opportunities
- Keeping Pace with Industry Standards
- Personal Growth and Confidence
- Addressing Skill Gaps Proactively
- Supporting Organizational Goals
- Upskilling Needs in Every Field
- 1. Marketing
- 2. Technology and Data Analysis
- 3. Human Resources (HR)
- 4. Finance and Banking
- 5. Manufacturing and Production (continued)
- 6. Healthcare
- 7. Education
- 8. Retail and Customer Service
- 9. Legal
- Challenges of Upskilling and How to Overcome Them
- Time Constraints
- Lack of Resources
- Motivation and Engagement
- Resistance to Change
- Skill Overload
- How to Upskill Your Career
- 1. Self-Assessment
- 2. Research Industry Trends
- 3. Set Specific Learning Objectives
- 4. Choose Learning Methods
- 5. Engage in Practical Application
- 6. Seek Feedback and Mentorship
- 7. Network and Collaborate
- 8. Track Your Progress
- 9. Stay Committed to Lifelong Learning
- 10. Leverage Your Skills for Career Advancement
- Conclusion
Introduction
The landscape of work is ever-evolving, shaped by technological advancements, market demands, and shifting job roles. As professionals, the ability to adapt and grow is no longer a luxury but a necessity. This blog post delves into the concepts of lifelong learning and upskilling, exploring their significance in the workplace, the differences between upskilling and reskilling, and the specific needs across various fields. We will also address the challenges associated with upskilling and provide actionable strategies for integrating continuous learning into your career.
What is Upskilling?
Upskilling refers to the process of acquiring new skills or enhancing existing ones to meet the demands of a changing job market. This can involve formal education, online courses, workshops, or self-directed learning. The primary goal of upskilling is to ensure that employees remain relevant in their roles, equipped to tackle new challenges and seize emerging opportunities.
In contrast to reskilling, which focuses on training individuals for a different job or role, upskilling emphasizes deepening expertise in a specific area. For example, a software developer may upskill by learning a new programming language or mastering advanced data analytics tools, while a marketing professional might enhance their digital marketing skills to keep pace with the latest trends.
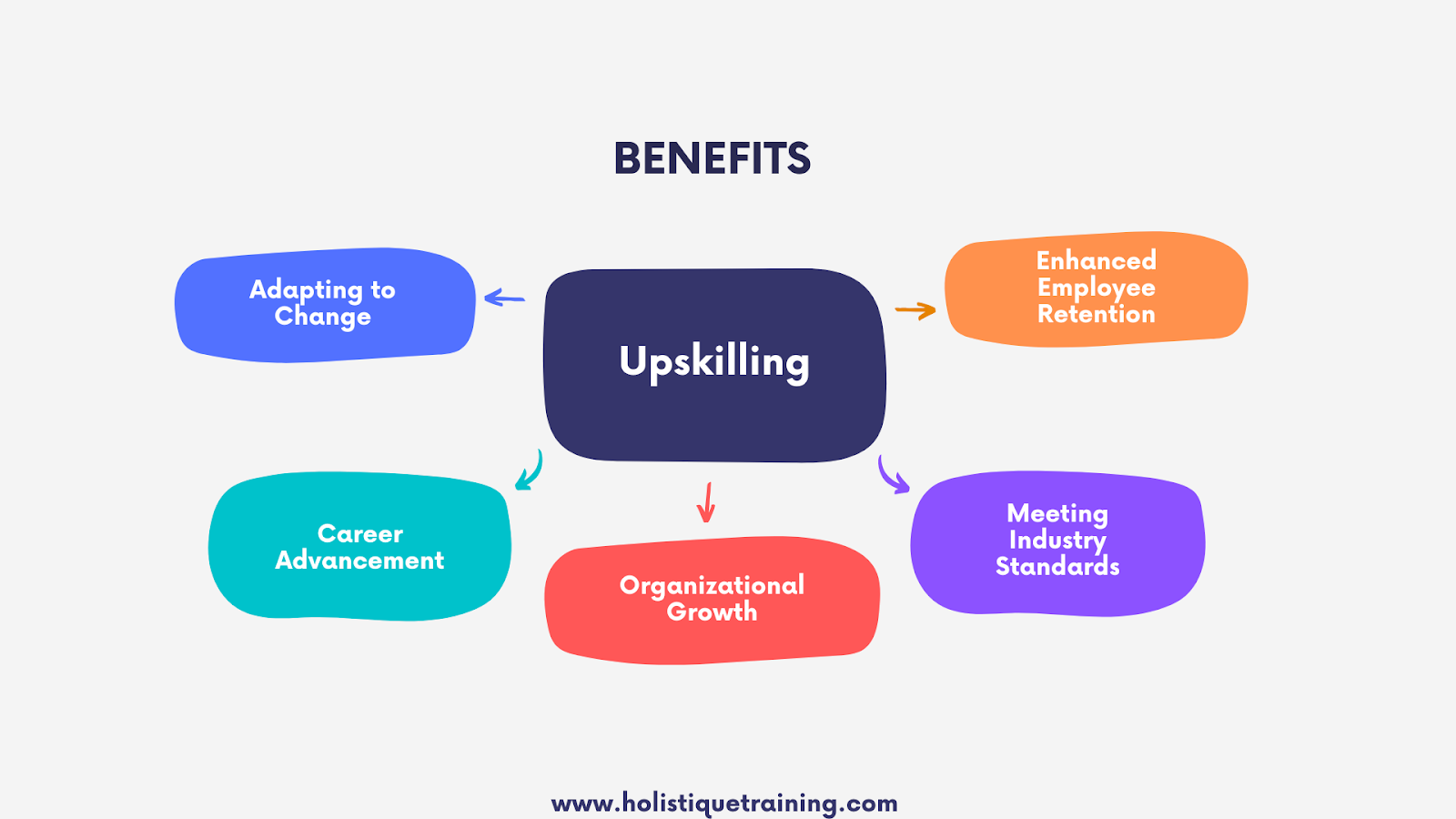
Why is Lifelong Learning and Upskilling Important in the Workplace?
The importance of lifelong learning and upskilling in the workplace cannot be overstated. Here are several key reasons why these concepts are crucial for both employees and employers:
Adaptation to Change
The rapid pace of technological advancement means that the skills required in the workplace are constantly changing. For instance, the rise of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation has transformed how many industries operate. Employees who engage in lifelong learning are better equipped to adapt to these changes, ensuring that they can navigate new technologies and methodologies effectively. This adaptability not only enhances individual performance but also contributes to the overall agility of the organization.
Career Advancement
Continuous learning is a key driver of career progression. Professionals who actively seek to upskill are often more competitive in the job market. Employers value candidates who demonstrate a commitment to personal and professional growth, as this indicates initiative and a willingness to take on new challenges. Upskilling can lead to promotions, salary increases, and opportunities to take on more responsibility within an organization. For example, an employee who learns advanced data analytics may qualify for a leadership role in a data-driven project, significantly enhancing their career trajectory.
Organizational Growth
Companies that foster a culture of lifelong learning and upskilling benefit from a more skilled and knowledgeable workforce. This not only leads to increased productivity but also drives innovation. When employees are encouraged to learn and grow, they bring fresh ideas and perspectives to the table, which can lead to the development of new products, services, or processes. Organizations that prioritize upskilling are better positioned to respond to market demands, adapt to industry trends, and maintain a competitive edge.
Employee Retention
Investing in employee development is a powerful strategy for enhancing job satisfaction and loyalty. When organizations provide opportunities for upskilling, employees feel valued and supported in their career growth. This commitment to development fosters a sense of belonging and increases employee morale. Highjob satisfaction is directly linked to lower turnover rates, which can save organizations significant costs associated with recruitment and training new employees. A workforce that is engaged and committed is more likely to stay with an organization long-term.
Meeting Industry Standards
Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements and standards that necessitate continuous education and skill enhancement. For instance, in fields such as healthcare, finance, and technology, staying updated on regulations, compliance standards, and best practices is crucial. Lifelong learning ensures that employees remain compliant and knowledgeable about the latest industry developments. This not only protects the organization from potential legal issues but also enhances its reputation as a leader in its field.
Fostering a Culture of Innovation
A commitment to lifelong learning encourages aculture of innovation within organizations. When employees are encouraged to learn new skills and explore new ideas, they are more likely to experiment and take calculated risks. This culture of experimentation can lead to breakthrough innovations and improvements in processes. For example, teams that regularly engage in upskilling may discover more efficient ways to complete projects or develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills
Upskilling often involves learning new approaches toproblem-solving and critical thinking. As employees acquire new skills, they develop a broader perspective on challenges and are better equipped to tackle them creatively. This enhanced problem-solving ability is invaluable in the workplace, where teams frequently face complex issues that require innovative solutions. Employees who embrace lifelong learning are more likely to approach problems with a growth mindset, seeing them as opportunities for learning rather than obstacles.
Building Resilience
In an era of rapid change and uncertainty, resilience is a critical trait for both individuals and organizations. Lifelong learning fosters resilience by equipping employees with the skills and knowledge needed to navigate challenges effectively. When employees are prepared to adapt and learn, they are less likely to feel overwhelmed by change. This resilience not only benefits individual employees but also contributes to a more robust organizational culture that can withstand external pressures.
By prioritizing lifelong learning and upskilling, both employees and organizations can thrive in an increasingly complex and dynamic work environment. The commitment to continuous growth not only enhances individual careers but also drives organizational success, making it a vital strategy for the future of work.
Statistics on the Importance of Upskilling
Upskilling is crucial, with60% of workers requiring training by 2027. A substantial 77% of employees are eager to learn new skills, and 74% feel it's their personal responsibility. For companies, 93% of CEOs implementing upskilling report productivity improvements, while 51% address skills gaps through this approach, which also boosts employee engagement and retention.
Upskilling vs. Reskilling: Key Differences
Understanding the distinction between upskilling and reskilling is essential for effective workforce development. The following table highlights the key differences between the two concepts:
By recognizing these differences, organizations can tailor their training programs to meet the specific needs of their workforce, ensuring that employees receive the appropriate support for their career development.
Why is Every 6 Months the Ideal Time for Upskilling?
The recommendation to upskill every six months stems from the dynamic nature of the job market and technological advancements. Here are several reasons why this timeframe is considered ideal:
Rapid Technological Advances
The technological landscape is constantly evolving, with new tools, software, and methodologies emerging at an unprecedented rate. For instance, advancements in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and automation can significantly alter job responsibilities and required skill sets. Engaging in upskilling every six months allows professionals to stay abreast of these changes, ensuring they acquire the latest skills and knowledge that are relevant to their roles. This proactive approach helps individuals remain competitive and capable of leveraging new technologies effectively.
Market Demand Fluctuations
The job market is influenced by various factors, including economic conditions, consumer behavior, and industry trends. These factors can lead to shifts in demand for specific skills and roles. By committing to a six-month upskilling cycle, professionals can quickly adapt to these fluctuations. For example, if a new trend emerges in digital marketing, such as the rise of a particular social media platform, marketers who have recently upskilled will be better prepared to capitalize on that trend, ensuring they meet current market demands.
Enhanced Retention of Knowledge
Research suggests that shorter, more frequent learning intervals can enhance knowledge retention. When individuals engage with new material regularly, they reinforce their understanding and improve their ability to apply what they have learned. By upskilling every six months, professionals can revisit and build upon their existing knowledge, making it easier to integrate new skills into their daily work. This continuous reinforcement helps solidify learning and reduces the likelihood of skills becoming obsolete.
Building a Habit of Learning
Establishing a routine for upskilling fosters a culture of continuous learning. By committing to a six-month schedule, professionals create a structured approach to their development, making learning a regular part of their lives. This habit not only encourages individuals to seek out new knowledge but also helps them stay motivated and engaged in their careers. When learning becomes a routine practice, it leads to a mindset that embraces growth and adaptability.
Career Agility
In today’s fast-paced work environment, the ability to pivot and adapt is crucial. Regular upskilling every six months equips professionals with the agility needed to respond to new challenges and opportunities. For example, an employee who has recently learned about emerging technologies or industry best practices is more likely to seize new responsibilities or projects that align with those skills. This agility not only enhances individual career prospects but also benefits organizations that rely on a versatile workforce.
Networking and Collaboration Opportunities
Engaging in upskilling every six months often involves participating in workshops, seminars, or online courses, which provide valuable networking opportunities. These interactions facilitate connections with industry peers, experts, and mentors, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing. By regularly participating in learning opportunities, professionals can expand their professional networks, which can lead to new job prospects, partnerships, and collaborative projects.
Keeping Pace with Industry Standards
Many industries have specific standards and regulations that require ongoing education and skill enhancement. For instance, in fields like finance, healthcare, and technology, staying compliant with industry standards is essential. A six-month upskilling schedule ensures that professionals remain informed about the latest regulations, best practices, and technological advancements, reducing the risk of non-compliance and enhancing overall professional credibility.
Personal Growth and Confidence
Regular upskilling contributes to personal growth and boosts confidence. As individuals acquire new skills and knowledge, they become more competent in their roles, leading to increased job satisfaction and self-efficacy. This confidence can translate into a willingness to take on new challenges, pursue leadership opportunities, or engage in innovative projects. By committing to a six-month upskilling cycle, professionals can continuously build their self-assurance and position themselves as valuable contributors within their organizations.
Addressing Skill Gaps Proactively
The job market is increasingly competitive, and skill gaps can hinder career advancement. By upskilling every six months, professionals can proactively address these gaps before they become significant barriers to success. This proactive approach allows individuals to identify and fill skills shortages in their knowledge base, making them more attractive candidates for promotions or new job opportunities.
Supporting Organizational Goals
Organizations benefit from a workforce that is consistently upskilling. By encouraging employees to engage in learning every six months, companies can ensure that their teams are aligned with organizational goals and industry trends. This alignment enhances overall productivity and innovation, as employees are equipped with the skills needed to contribute effectively to the organization’s objectives.
In summary, committing to upskilling every six months is a strategic approach that empowers professionals to stay relevant, competitive, and agile in their careers. This proactive mindset fosters a culture of continuous learning, enabling individuals and organizations to thrive in an ever-evolving work environment. By recognizing the importance of regular upskilling, professionals can take charge of their career development and position themselves for long-term success.
Upskilling Needs in Every Field
The need for upskilling varies across different fields, reflecting the unique demands and challenges of each industry. Below are some specific upskilling needs in key sectors:
1. Marketing
The marketing landscape is rapidly changing, driven by digital transformation and consumer behavior shifts. Key upskilling areas include:
- Digital Marketing: Proficiency in search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), social media marketing, and content marketing is critical. Marketers must understand how to leverage digital platforms to reach and engage target audiences effectively.
- Data Analytics: With the increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making, marketers need to develop skills in data analysis and interpretation. This includes understanding customer behavior, campaign performance metrics, and market trends to optimize marketing strategies.
- Marketing Automation: Familiarity with marketing automation tools, such as HubSpot or Marketo, is essential for streamlining marketing efforts. Learning how to set up automated campaigns, segment audiences, and analyze results can significantly enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
2. Technology and Data Analysis
The technology sector is characterized by rapid innovation and constant evolution. Professionals in this field should focus on:
- Programming Languages: Mastering languages such as Python, Java, or JavaScript is crucial for software development and data analysis. These languages are foundational for building applications, conducting data analysis, and automating processes.
- Data Science: Skills in machine learning, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics are increasingly important. Professionals should learn how to use tools like R, TensorFlow, or Apache Spark to analyze large datasets and derive actionable insights.
- Cybersecurity: With the rise in cyber threats, knowledge of cybersecurity protocols, risk management, and ethical hacking is vital. Upskilling in this area involves understanding how to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with security regulations.
3. Human Resources (HR)
The HR landscape is evolving with a focus on employee engagement and strategic workforce planning. Key skills to develop include:
- Employee Engagement: Techniques for fostering a positive workplace culture and enhancing employee satisfaction are essential. HR professionals should learn about motivation strategies, performance management, and employee feedback mechanisms.
- HR Technology: Familiarity with human resource information systems (HRIS) and digital recruitment tools is increasingly important. Learning how to utilize these technologies can streamline HR processes and improve data management.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Training on best practices for creating inclusive workplaces is critical. HR professionals should focus on understanding unconscious bias, implementing diversity initiatives, and promoting an inclusive culture.
4. Finance and Banking
The finance sector is highly regulated and influenced by technological advancements. Key upskilling areas include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Staying updated on financial regulations and compliance standards is essential. Professionals should engage in continuous education to understand the implications of regulations such as Dodd-Frank or GDPR.
- Financial Technology (FinTech): Understanding emerging technologies such as blockchain, cryptocurrency, and digital payment systems is crucial. Upskilling in this area involves learning how these technologies impact traditional financial services.
- Risk Management: Skills in assessing and mitigating financial risks are vital for professionals in finance. Learning about risk assessment frameworks and financial modeling can enhance decision-making capabilities.
5. Manufacturing and Production (continued)
- Automation Technologies: Knowledge of robotics, Internet of Things (IoT), and smart manufacturing processes is essential. Professionals should learn how to integrate automated systems into production lines, optimize workflows, and maintain advanced machinery. Understanding how to use data from IoT devices to improve operational efficiency is also crucial.
- Lean Manufacturing: Skills in lean manufacturing principles focus on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity. Professionals should be trained in methodologies like Six Sigma, Kaizen, and value stream mapping to enhance efficiency and quality in production processes.
- Quality Control: Proficiency in quality assurance techniques is vital for maintaining product standards. Upskilling in statistical process control, inspection methods, andquality management systems (QMS) ensures that products meet regulatory and customer expectations.
6. Healthcare
The healthcare industry is rapidly evolving due to technological advancements, regulatory changes, and a growing emphasis on patient-centered care. Key upskilling areas include:
- Telehealth Technologies: With the rise of telemedicine, healthcare professionals must become proficient in using telehealth platforms and understanding best practices for remote patient care. This includes skills in virtual communication, electronic health records (EHR), and data privacy.
- Data Management and Analytics: The ability to analyze patient data and derive insights is increasingly important. Healthcare professionals should learn about data analytics tools and methodologies to improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Knowledge: Staying informed about healthcare regulations, such asHIPAAand the Affordable Care Act, is crucial. Continuous education in compliance and ethical considerations ensures that professionals adhere to legal standards while providing care.
7. Education
The education sector is also experiencing significant changes, driven by technology and evolving teaching methodologies. Key areas for upskilling include:
- Digital Learning Tools: Educators should be familiar with various digital platforms and tools that enhance learning experiences, such as Learning Management Systems (LMS), virtual classrooms, and interactive content creation tools.
- Inclusive Education Practices: Understanding how to create inclusive learning environments for diverse student populations is essential. Educators should learn about differentiated instruction, Universal Design for Learning (UDL), and culturally responsive teaching.
- Data-Driven Instruction: Skills in data analysis can help educators assess student performance and tailor instruction accordingly. Learning how to interpret assessment data and implement evidence-based practices can improve educational outcomes.
8. Retail and Customer Service
The retail and customer service sectors are rapidly changing, influenced by e-commerce growth and evolving consumer expectations. Key upskilling needs include:
- E-commerce Platforms: Familiarity with online retail platforms and digital sales strategies is essential. Retail professionals should learn how to manage online inventories, optimize product listings, and utilize digital marketing techniques to drive sales.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Proficiency in using CRM software to track customer interactions and preferences is crucial. Upskilling in this area helps professionals provide personalized service and build long-term customer relationships.
- Soft Skills: Strong communication, empathy, and problem-solving skills are vital in customer service roles. Training in emotional intelligence and conflict resolution can enhance customer interactions and improve satisfaction.
9. Legal
The legal field is undergoing transformations due to technology and changing regulations. Key upskilling areas include:
- Legal Technology: Familiarity with legal research tools, document management systems, and e-discovery platforms is increasingly important. Legal professionals should learn how to leverage technology to improve efficiency and accuracy in their work.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding evolving regulations, such as data protection laws and compliance standards, is crucial for legal practitioners. Continuous education in these areas ensures that lawyers and paralegals remain knowledgeable about their responsibilities.
- Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR): Skills in mediation and arbitration are becoming more valuable as organizations seek to resolve disputes outside of traditional litigation. Training in ADR techniques can enhance a legal professional's ability to serve clients effectively.
In short, upskilling needs vary significantly across different fields, reflecting the unique challenges and opportunities within each industry. By identifying and addressing these specific requirements, professionals can enhance their skills, remain competitive, and contribute effectively to their organizations. Continuous learning is not just an individual responsibility but a shared commitment among organizations to foster a culture of growth and adaptability. As industries continue to evolve, embracing upskilling will be essential for both personal career advancement and organizational success.
Challenges of Upskilling and How to Overcome Them
While the benefits of upskilling are clear, there are several challenges that individuals and organizations may face. Here are some common obstacles and strategies to overcome them:
Time Constraints
- Challenge: Busy schedules can make it difficult to find time for learning.
- Solution: Integrate learning into daily routines, such as setting aside a specific time each week for online courses or workshops.
Lack of Resources
- Challenge: Limited access to training programs or financial constraints can hinder upskilling efforts.
- Solution: Explore free or low-cost online resources, such as MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) and webinars, or seek employer-sponsored training opportunities.
Motivation and Engagement
- Challenge: Staying motivated to learn can be challenging, especially when juggling multiple responsibilities.
- Solution: Set clear, achievable goals and track progress. Joining study groups or finding an accountability partner can also enhance motivation.
Resistance to Change
- Challenge: Some individuals may resist learning new skills due to fear of failure or discomfort with change.
- Solution: Cultivate a growth mindset by reframing challenges as opportunities for growth. Encourage a supportive learning environment that celebrates progress and learning.
Skill Overload
- Challenge: With an overwhelming number of skills to learn, individuals may struggle to prioritize.
- Solution: Focus on skills that align with career goals and market demands. Create a personalized learning path that prioritizes the most relevant skills first.
By addressing these challenges head-on, individuals can create a more conducive environment for upskilling, leading to greater career success and personal fulfillment.
How to Upskill Your Career
Upskilling your career is a strategic process that involves acquiring new skills and knowledge to enhance your professional capabilities and advance your career. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to effectively upskill your career, including practical steps, resources, and strategies to make the most of your learning journey.
1. Self-Assessment
Understand Your Current Skills and Gaps:
- Conduct a Skills Inventory: Start by evaluating your current skills and competencies. Create a list of your strengths, weaknesses, and areas where you excel. This self-assessment can help you identify specific skills that need improvement or enhancement.
- Identify Career Goals: Define your short-term and long-term career objectives. Consider what roles you aspire to, the skills required for those positions, and the industries you want to target. Setting clear goals will guide your upskilling efforts.
2. Research Industry Trends
Stay Informed About Market Demands:
- Analyze Job Descriptions: Review job postings in your desired field to identify commonly required skills and qualifications. This will provide insight into the competencies that are currently in demand.
- Follow Industry News: Subscribe to industry publications, blogs, and newsletters to stay updated on emerging trends, technologies, and best practices. Understanding the direction of your industry will help you prioritize your upskilling efforts.
3. Set Specific Learning Objectives
Create a Structured Learning Plan:
- Define Clear Goals: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) learning objectives. For example, instead of saying, "I want to learn data analysis," specify, "I will complete an online data analysis course within three months."
- Prioritize Skills: Focus on the most critical skills that align with your career goals. Determine which skills will have the greatest impact on your professional development and prioritize them in your learning plan.
4. Choose Learning Methods
Select the Right Learning Resources:
- Online Courses and MOOCs: Platforms likeHolistique Training offer a wide range of courses across various fields. Choose courses that align with your learning objectives and provide recognized certifications.
- Workshops and Seminars: Attend industry workshops, webinars, and conferences to gain hands-on experience and network with professionals in your field. These events often provide valuable insights and practical skills.
- Books and Articles: Read books, articles, and research papers relevant to your field. This can deepen your understanding of concepts and provide theoretical knowledge that complements practical skills.
5. Engage in Practical Application
Apply What You Learn:
- Real-World Projects: Look for opportunities to apply your new skills in real-world scenarios. This could involve taking on new responsibilities at work, volunteering for projects, or participating in internships that allow you to practice what you’ve learned.
- Personal Projects: Consider starting personal projects that align with your interests and career goals. For example, if you’re learning web development, create a personal website or contribute to open-source projects to gain practical experience.
6. Seek Feedback and Mentorship
Enhance Your Learning Experience:
- Find a Mentor: Seek out mentors who can provide guidance, share their experiences, and offer constructive feedback on your progress. A mentor can help you navigate challenges and provide valuable insights into your chosen field.
- Request Feedback: Regularly seek feedback from peers, supervisors, and mentors to identify areas for improvement. Constructive criticism can help you refine your skills and enhance your learning process.
7. Network and Collaborate
Build Professional Relationships:
- Join Professional Associations: Become a member of industry-related organizations or associations. These groups often offer networking opportunities, resources, and access to exclusive training programs.
- Participate in Online Forums: Engage in online communities, forums, and social media groups related to your field. Sharing knowledge and experiences with others can provide additional insights and learning opportunities.
8. Track Your Progress
Monitor Your Development:
- Keep a Learning Journal: Document your learning journey, including courses completed, skills acquired, and projects undertaken. Reflecting on your progress can help you stay motivated and recognize your achievements.
- Evaluate Your Skills: Periodically assess your skills against your initial self-assessment. This will help you determine if you’ve successfully closed any skill gaps and identify new areas for further development.
Table: Metrics to measure the effectiveness of upskilling
9. Stay Committed to Lifelong Learning
Embrace a Growth Mindset:
- Cultivate Curiosity: Foster a mindset of curiosity and a willingness to learn continuously. Stay open to new ideas, technologies, and methodologies that can enhance your skill set.
- Adapt to Change: Be prepared to adapt your learning plan as industry demands evolve. Regularly reassess your skills and goals to ensure they align with your career aspirations and market trends.
10. Leverage Your Skills for Career Advancement
Position Yourself for Opportunities:
- Update Your Resume and LinkedIn Profile: Reflect your newly acquired skills and certifications on your resume and LinkedIn profile. Highlight specific projects and achievements that demonstrate your competence in these areas.
- Seek New Opportunities: Actively pursue promotions, lateral moves, or new job opportunities that align with your enhanced skill set. Use your upskilling efforts as leverage during performance reviews or job interviews.
In summary, upskilling your career is a proactive and ongoing process that requires dedication, planning, and a willingness to embrace new challenges. By following these steps and continuously seeking opportunities for growth, you can enhance your skills, increase your value in the job market, and position yourself for long-term career success. Remember, the journey of lifelong learning not only benefits your professional development but also enriches your personal growth and adaptability in an ever-changing world.
Conclusion
The journey of lifelong learning and upskilling is essential in today’s rapidly changing work environment. By embracing continuous learning, professionals can adapt to new challenges, enhance their skills, and drive their careers forward. Organizations that prioritize upskilling not only foster a culture of growth but also position themselves for long-term success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
As we navigate the complexities of modern work, the commitment to lifelong learning and upskilling will empower individuals and organizations alike to thrive in the face of change. Embrace the opportunity to learn, grow, and shape your future—your career depends on it.